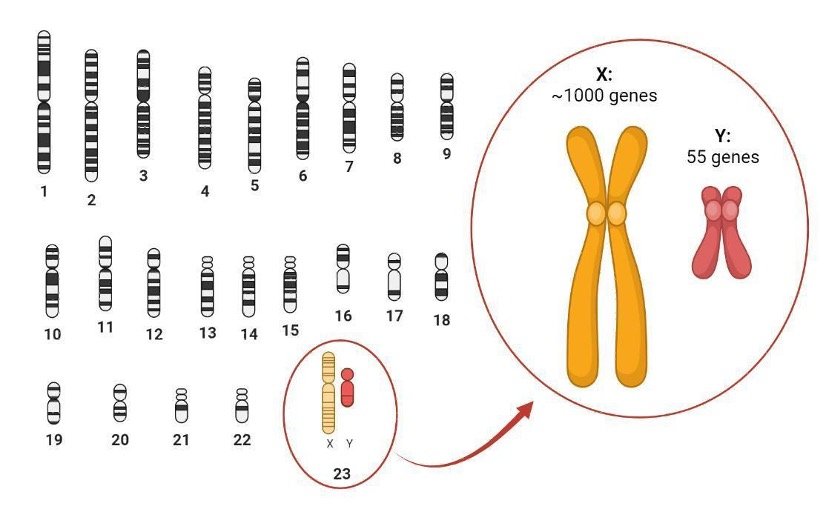
Cat Color X Chromosome
The black gene also has a lighter cinnamon recessive gene. Orange Cats The orange gene controls the orange color and always overrides the black gene. This means that black and orange will not appear together on the same chromosome and creates the possibility of patterned cat coats.

Did you know that most solid orange cats are male? A comprehensive genetic linkage map of the domestic cat X chromosome was generated with the goal of localizing the genomic position of the classic X-linked orange (O) locus. Microsatellite markers with an average spacing of 3 Mb were selected from. The sex-linked red "Orange" locus, O/o, determines whether a cat will produce eumelanin.
Dilute Tortie: Cat Guide & 6 Interesting Facts (With Pictures) - Catster
In cats with orange fur, phaeomelanin (red pigment) completely replaces eumelanin (black or brown pigment). [2] This gene is located on the X chromosome. The orange allele is O, and non.
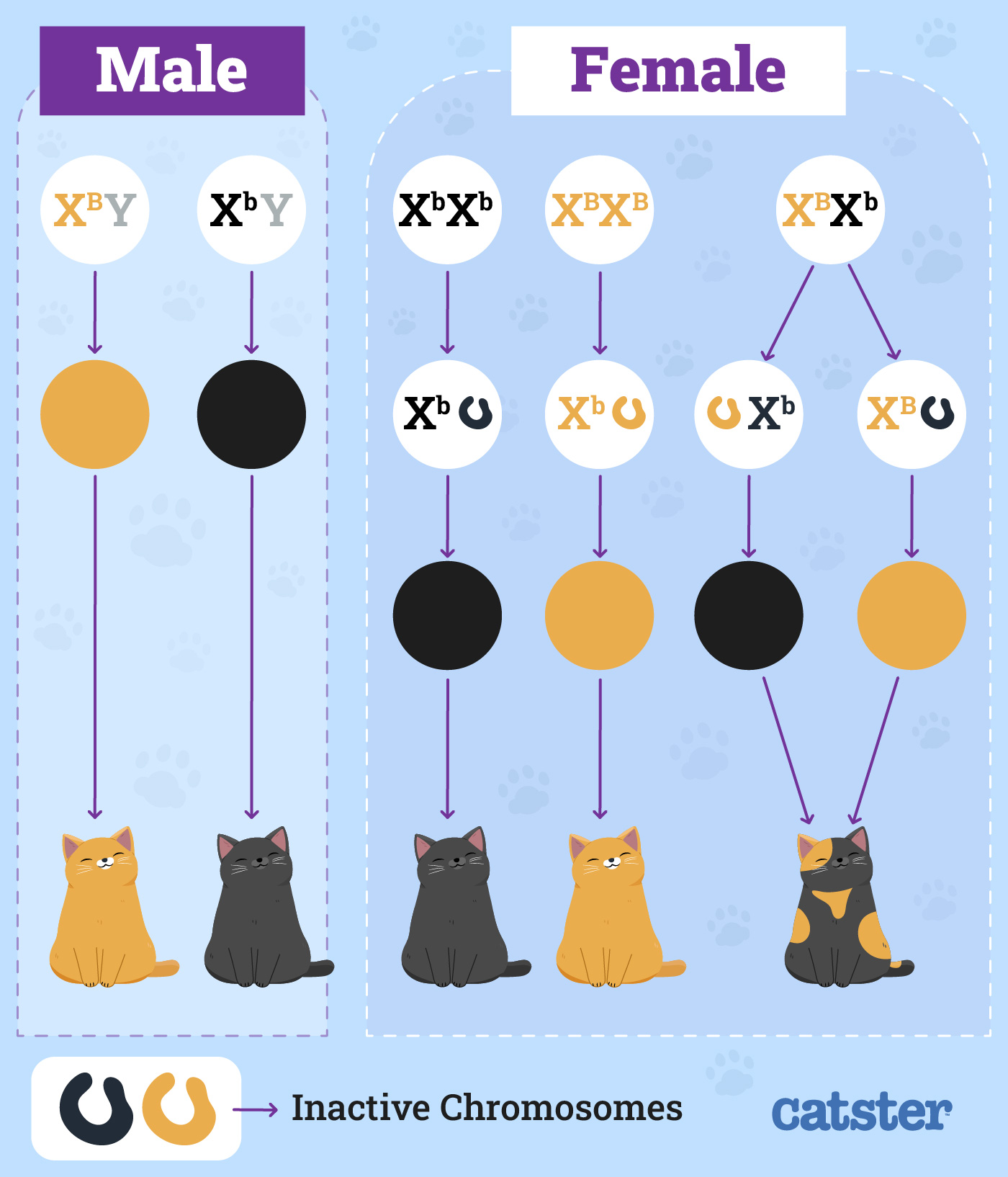
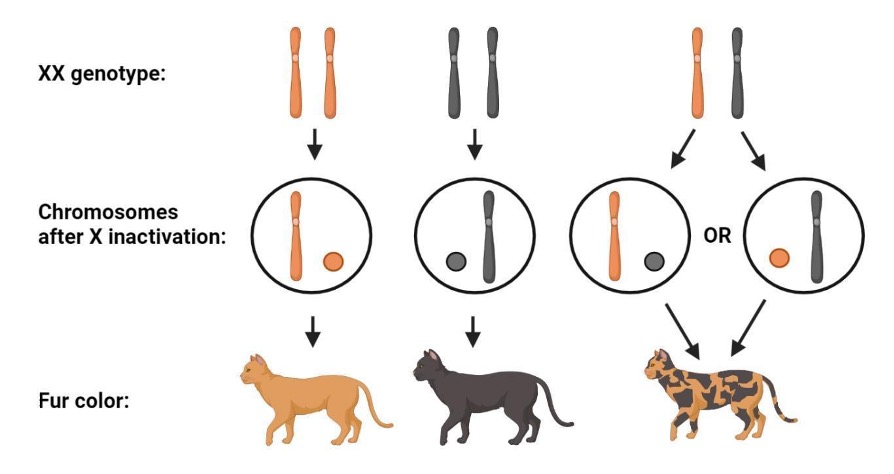
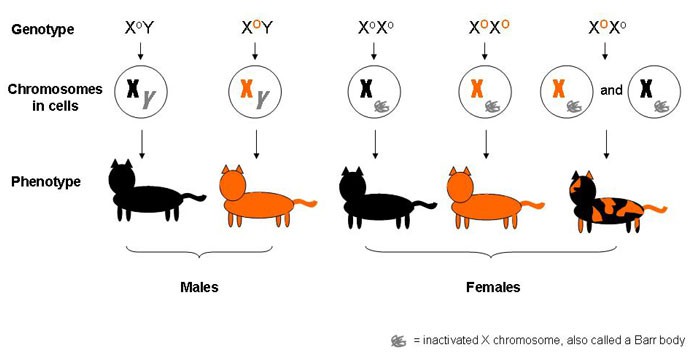
Male cats only have one X chromosome, so they can only be either orange or black, but not both. Female cats, on the other hand, have two X chromosomes, which allows for a mix of orange and black fur. Females have two X chromosomes; if both X chromosomes carry the Red gene, then the cat will be Red.

Chapter 13: Modern Understanding of Inheritance ppt download
However, many females carry the Red gene on only one chromosome, which allows the black. They have one orange X chromosome and one black X chromosome, making them female - except for rare genetic abnormalities that can result in a male tortoiseshell. Approximately 80% of orange cats are boys, since a male only needs to inherit one orange X chromosome to be ginger.

Related reading: What Color Is a Cat's Water Breaking Look Like? X chromosome Inactivation Science Project: Investigate whether X chromosome inactivation is random or predetermined by looking at coat color patterns in tortoiseshell cats. Female cats have two X chromosomes, allowing them to inherit two different color genes. This combination leads to the beautiful mix of colors found in calico patterns.

X Marks the Spot: How X Chromosome Inactivation Gives Females an Advantage · Frontiers for Young ...
The interaction between X-linked and autosomal genes ultimately shapes each cat's unique appearance. Role Of X Inactivation In Coat Color X inactivation balances gene expression between males and females by silencing one X chromosome in each cell. In calico cats, this process dictates which pigment.
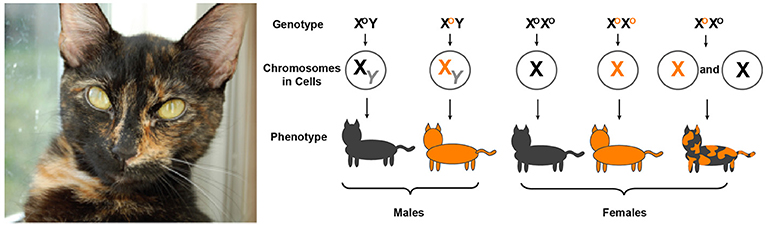
It turns out that one of the several genes that determine a cat's color is located in the X chromosomes, and since males have only one X chromosome, the expression of their fur's color is straightforward.



.jpg)