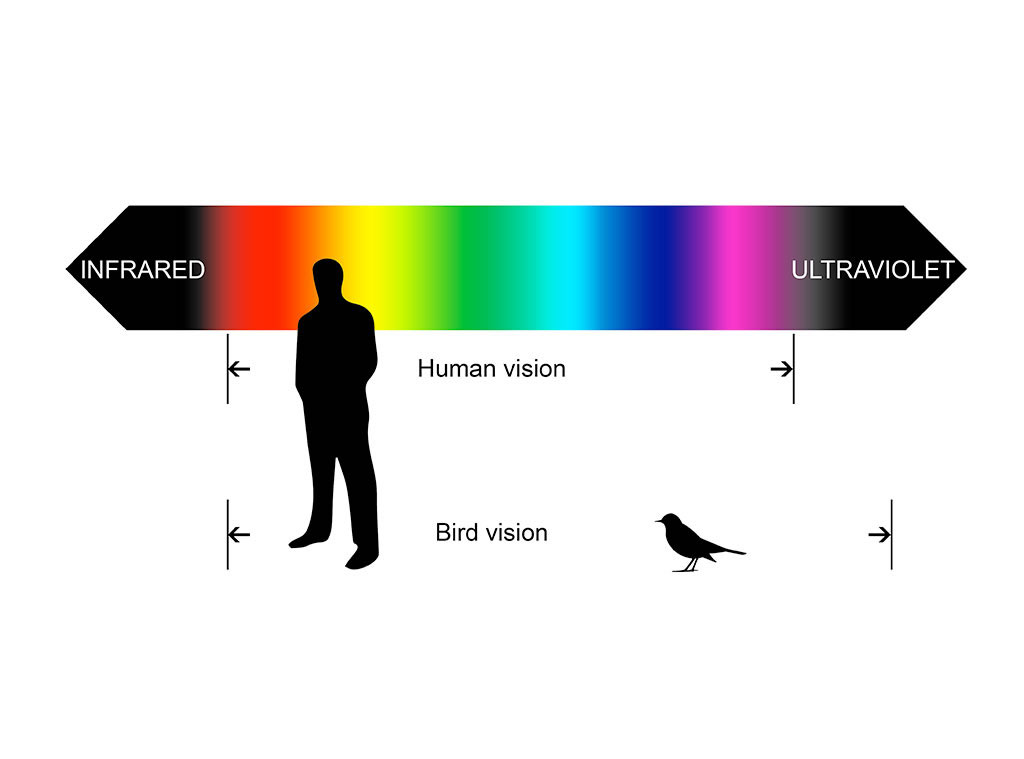
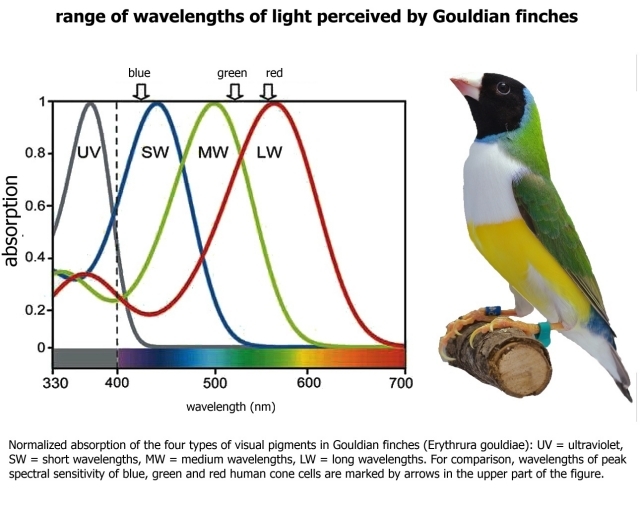
Bird Colour Vision
True Colors: How Birds See the World Thanks to UV vision, birds see the world very differently than we do Cynthia Berger Animals Jul 19, 2012 IN THE EARLY 1970s, A RESEARCHER testing the ability of pigeons to discriminate colors discovered by accident that the birds can see ultraviolet (UV) light. The finding was deemed curious but not too important. "It was natural for scientists to assume.

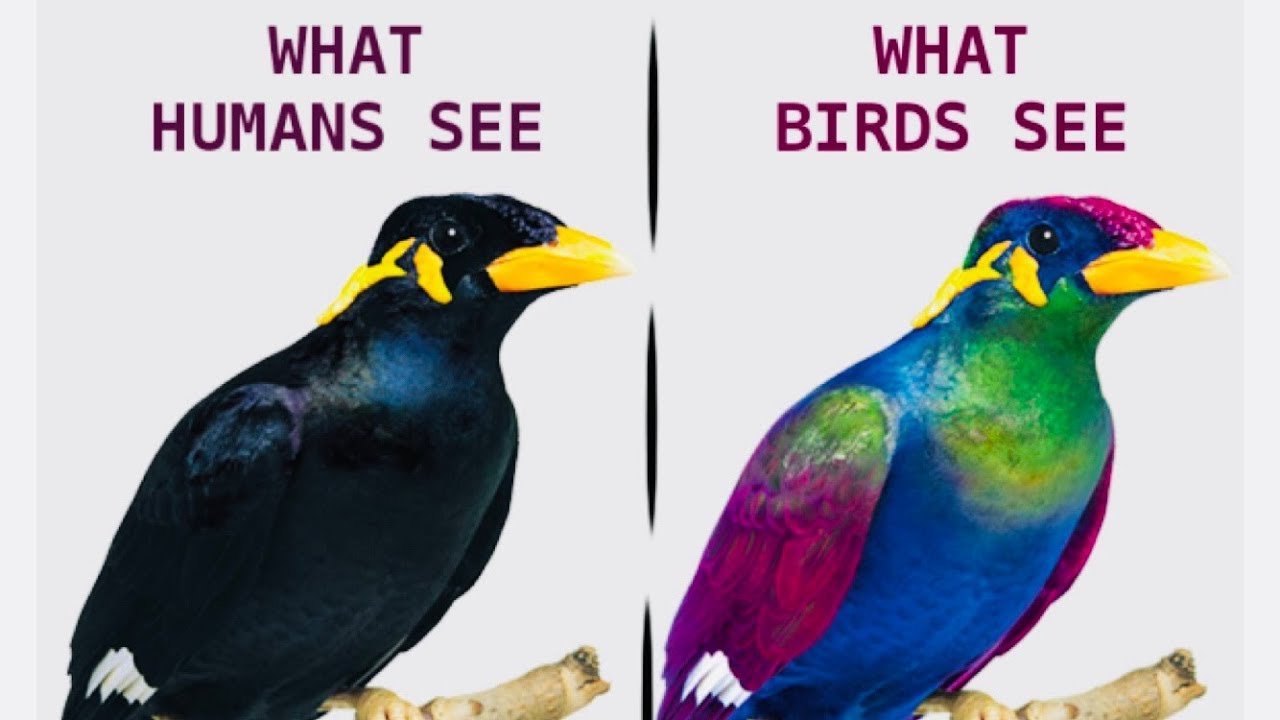
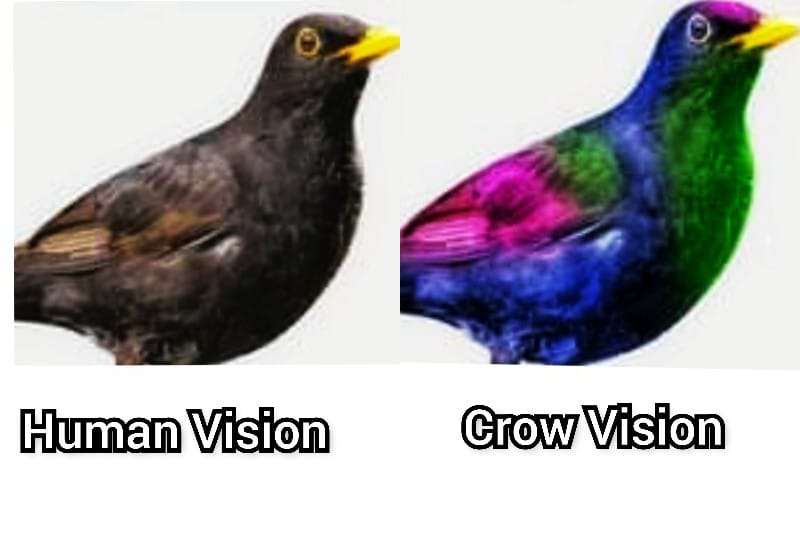
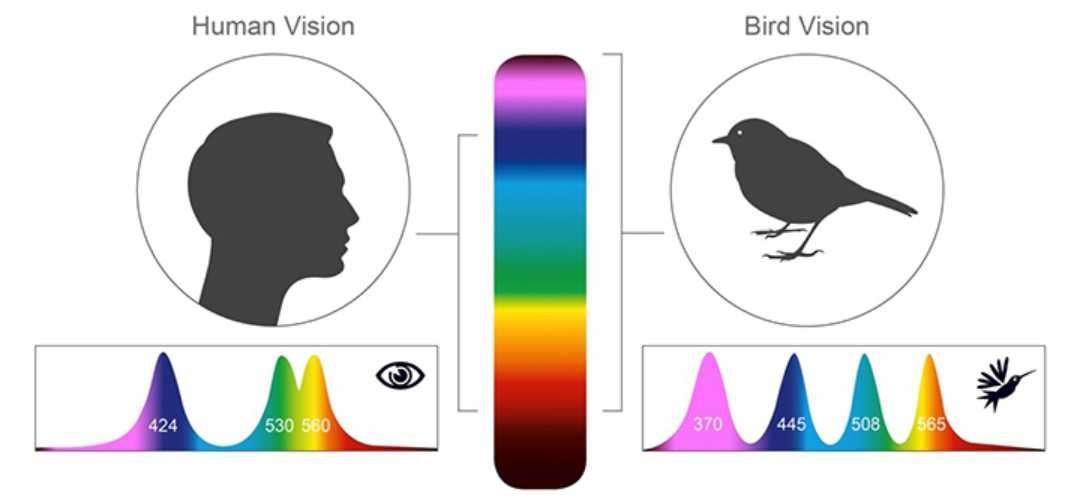
Birds use spectral information for circadian control, magnetic orientation and phototaxis but most importantly for discriminating the colours of important objects such as food items or mates. Their tetrachromatic colour vision is based on four types of single cones expressing four opsin. This is called spectral filtering and results in distinguishing between colors.
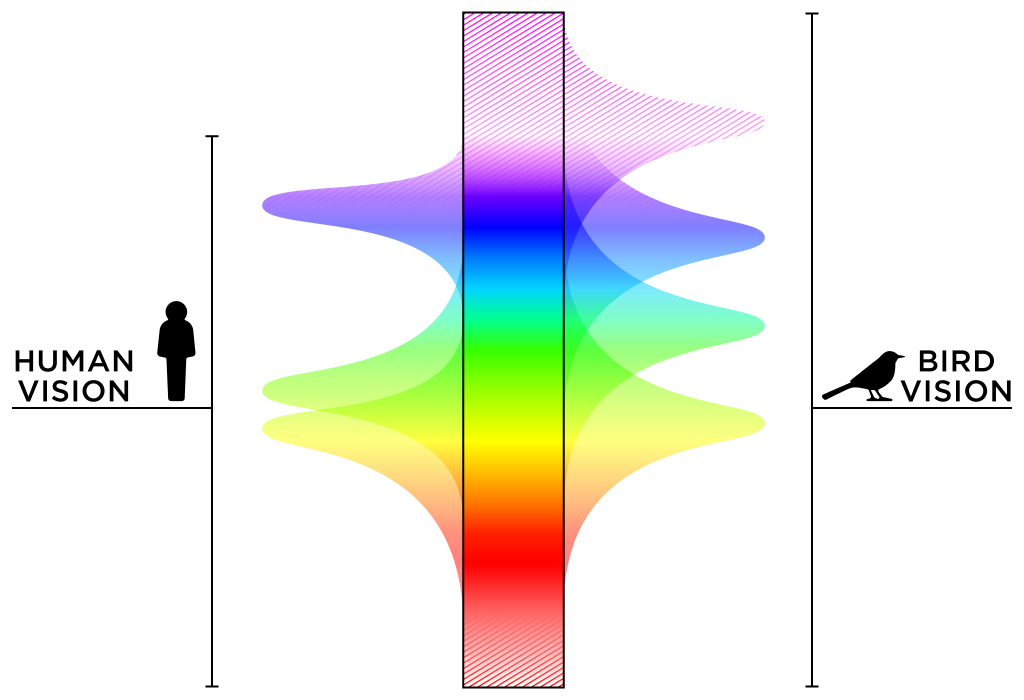
Unveiling the World of Avian Vision: How Birds See Color?
Overall, the oil droplets in birds' eyes play a crucial role in their exceptional color vision. They help to channel light and fine-tune the color perception of the cone cells, allowing birds to distinguish a wider range of colors than humans. Discover how birds perceive a world of vibrant colors, including UV light, and how their advanced vision differs significantly from human sight.

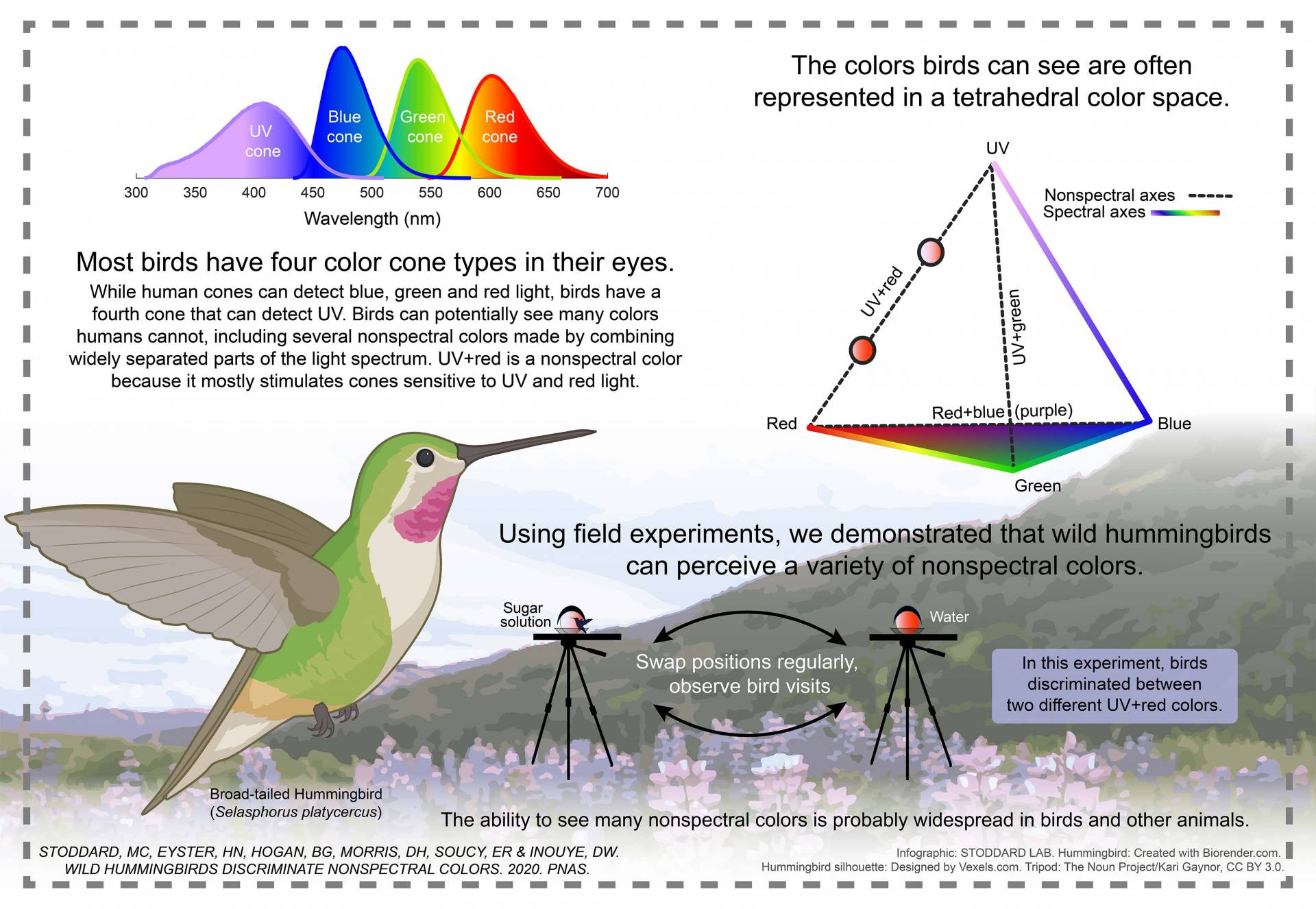
Birds have excellent color vision compared to humans. Their retinas contain four types of cone cells that allow them to see ultraviolet light in addition to the red, green, and blue light that humans can see. This gives birds a richer visual experience and allows them to distinguish colors that humans cannot.
What colors can Birds see? Birds Vision Explained 2023 - HowitSee
Understanding what colors birds see best can provide insights into how they find food. Without color vision, their fancy feathers would be meaningless since they help birds recognize members of their species and gather important information like the age, sex, and fitness of other individuals. Color vision also plays an essential role in finding food and prey and in detecting danger.
Birds are known for their remarkable vision, which plays a crucial role in their survival and behavior. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of bird vision, including their color perception, evolutionary adaptations, visual acuity, and visual communication. We will delve into the differences between bird and human vision, the types of colors birds can perceive, and how color.

How Bird Vision Is Different Than Human Vision
Explore the fascinating world of avian vision and discover how birds see color with their tetrachromatic ultraviolet vision. Key Takeaways Exceptional Color Vision: Birds possess an advanced color vision system, utilizing four or more types of cone receptors, allowing them to see ultraviolet light and a broader spectrum than humans. Enhanced Discrimination: Birds can distinguish between colors and subtle shades that are indistinguishable to humans, aiding in tasks like identifying ripe fruits and potential mates.

Other Ways Birds Use Color While keen vision and color are critical for birds finding food, color also plays other roles in their survival. Brighter feathers can indicate healthier, stronger potential mates, allowing birds to choose the best partners to improve their chances of passing along their genes to the next generation.