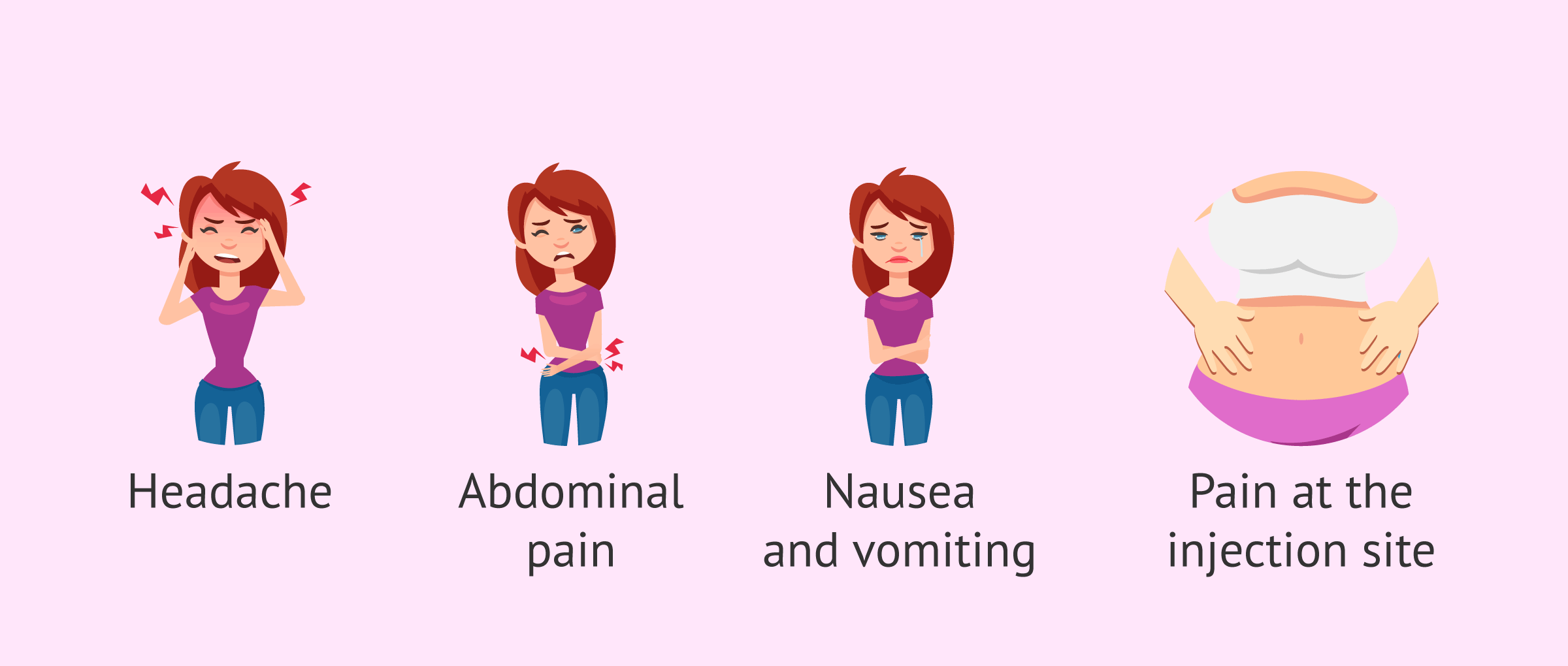
Side Effects Of High Hcg Levels
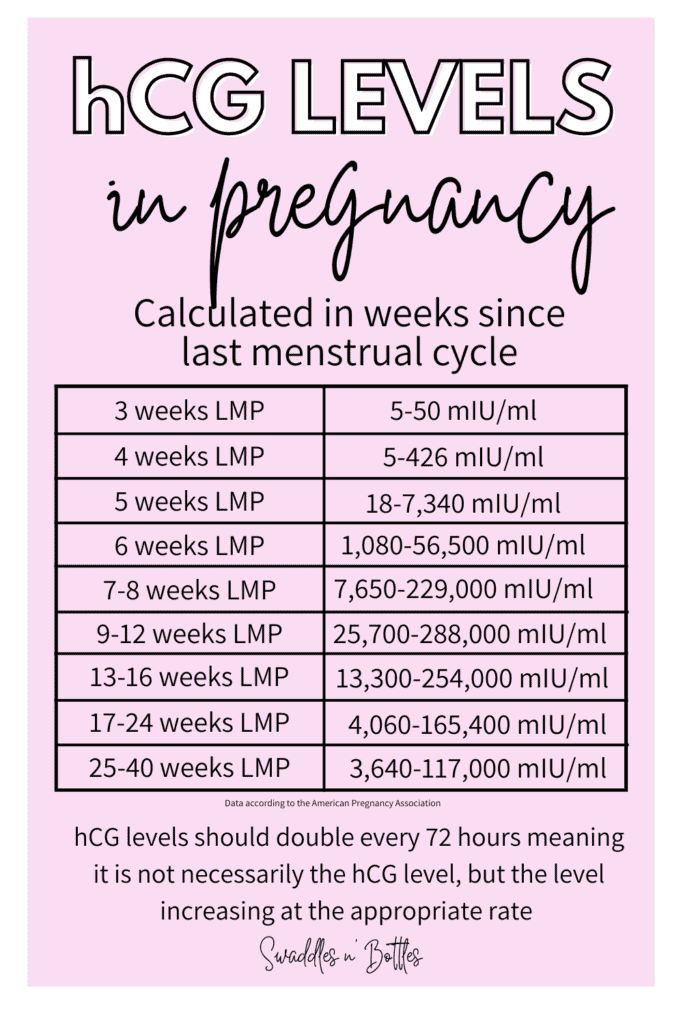
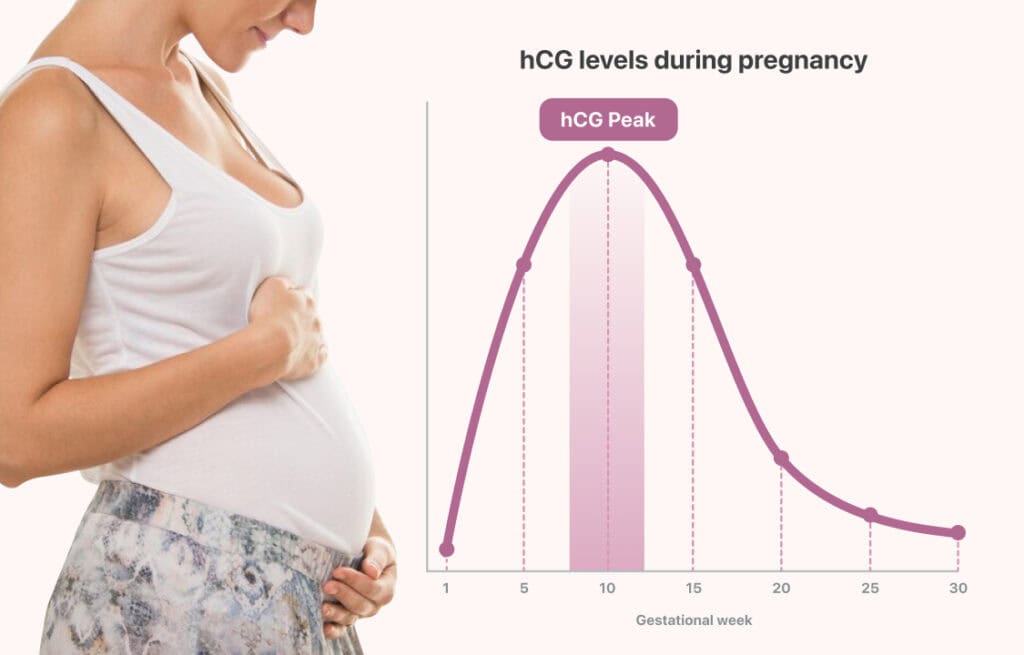
Learn about the side effects of HCG (chorionic gonadotropin (hcg)), from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. The placenta produces hCG hormone after the fertilized egg implants in the uterine lining, and the levels of hCG continue to rise up until the first 8 to 10 weeks of pregnancy. Rising hCG is a key indicator of a progressing pregnancy, and it often comes with physical symptoms like breast tenderness, nausea, and fatigue among others.

2. What Is Considered "High hCG"? "High hCG" means your hCG level is above the normal range for your gestational age. Your doctor will usually do several hCG tests 2-3 days apart, not just one test.
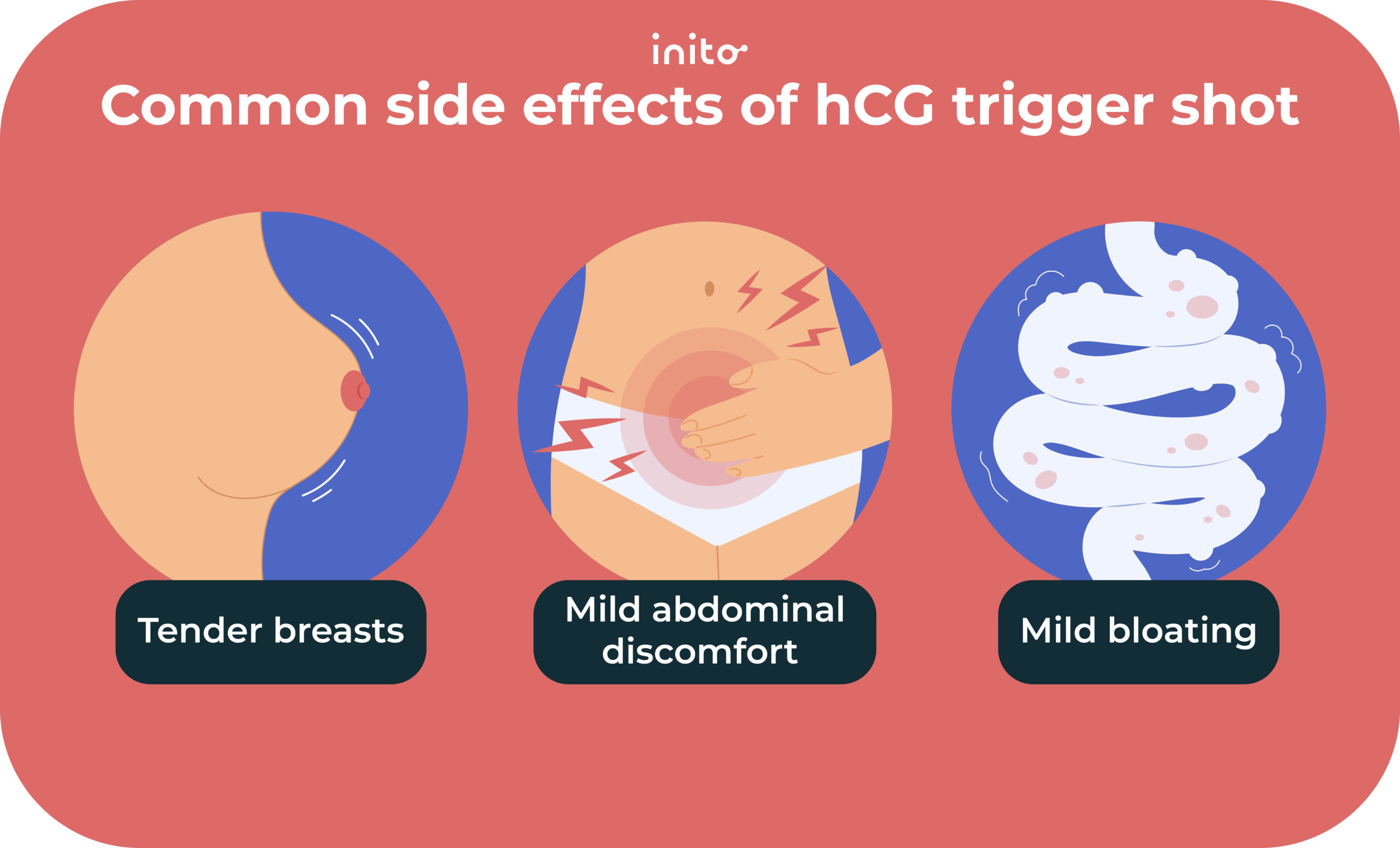
Six Common hCG Trigger Shot Mistakes to Avoid - Inito
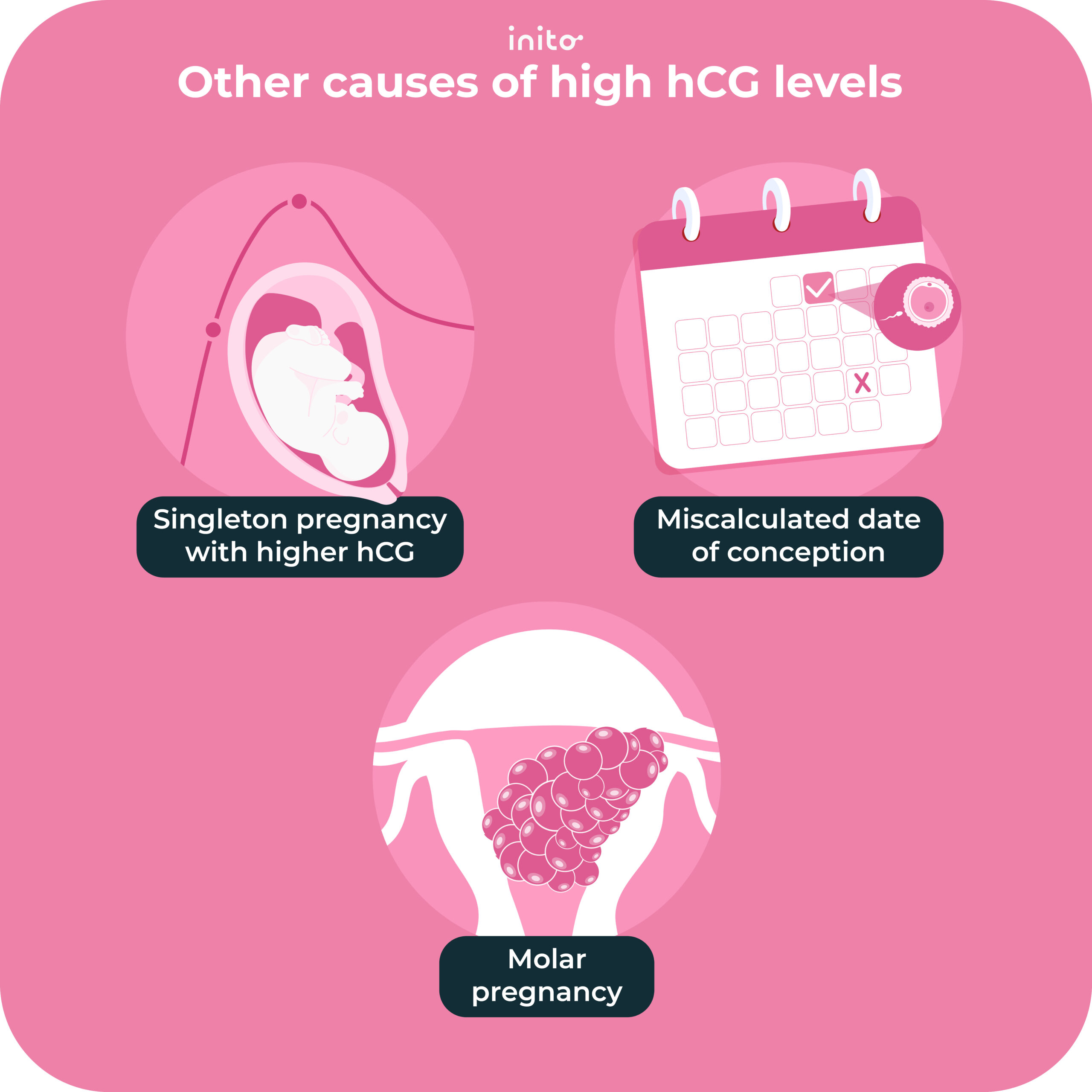
This is because hCG varies a lot between pregnant women. Some women with high hCG still have completely normal pregnancies. Sometimes, the hCG is high just because the pregnancy is further.
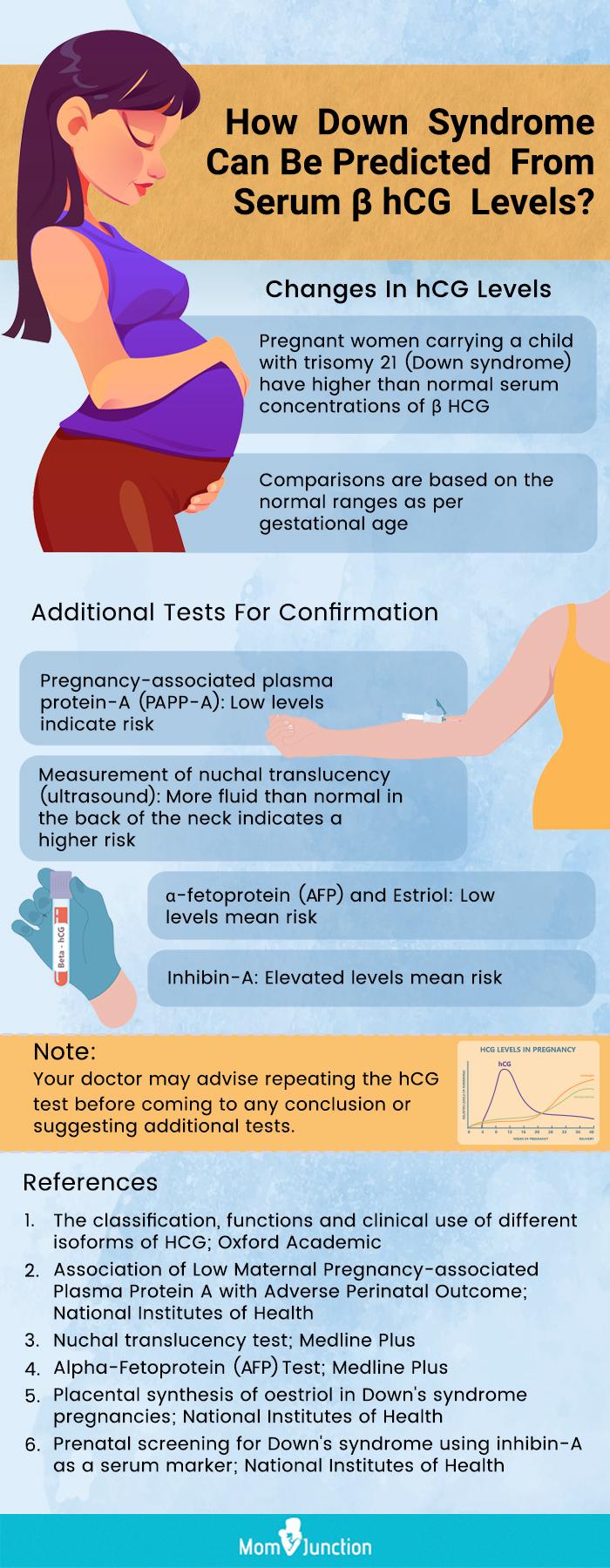
The human chorionic gonadotropin (hcg) level is routinely measured to diagnose and monitor pregnancy. In addition, because hCG can be elevated in females with trophoblastic disease, germ cell tumors, and other malignancies, it is often used as a prognostic marker and for disease monitoring. 1 These days, more women, even those in perimenopause and menopause, are having their hCG levels.
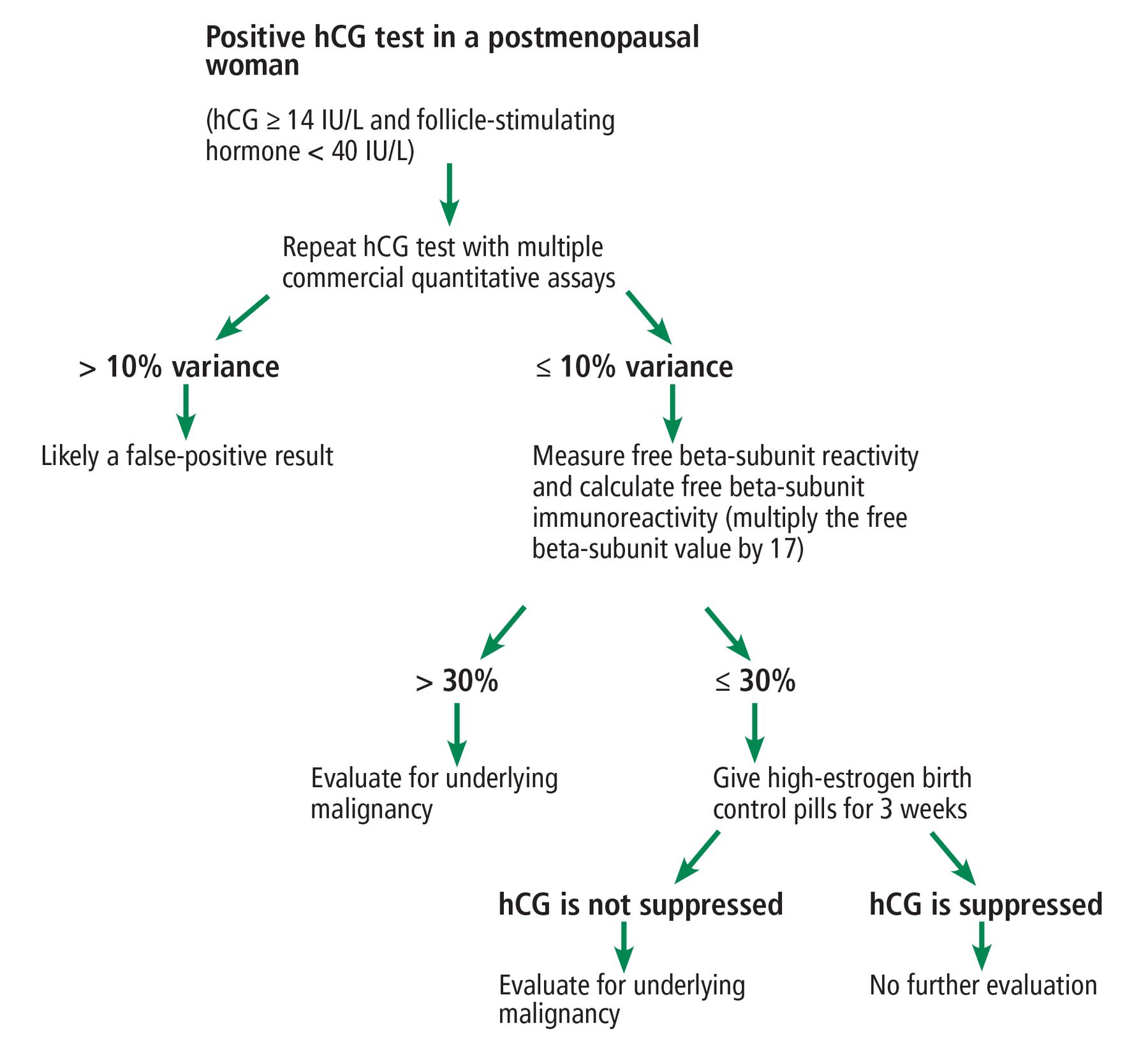
Molar Pregnancy Hcg Levels Chart - Ponasa
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone produced by the placenta during pregnancy. It helps thicken your uterine lining to support a fetus and tells your body to stop menstruating. HCG levels rise after conception and continue to rise until about 10 weeks in pregnancy.
In this article, we look at hCG in detail - including normal ranges during pregnancy, what happens when levels fluctuate, and how doctors use the measurements to identify underlying health. Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) is a hormone associated with pregnancy. It serves as a marker in pregnancy tests, confirming conception and monitoring early gestation.
Effects Of Hcg On Heart
Understanding HCG levels provides insight into pregnancy progression. HCG's Role in Pregnancy HCG is a hormone produced by trophoblast cells that surround a developing embryo, eventually forming the placenta after. Understanding HCG: The Basics Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) is a hormone produced by the placenta shortly after a fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining.

This hormone plays a crucial role in maintaining pregnancy and is often measured to confirm pregnancy and monitor its progression. Understanding HCG levels can provide valuable insights into reproductive health, making it. The hCG hormone is usually a sign of pregnancy, but it can also indicate an ectopic pregnancy, where a fertilized egg implants itself somewhere other than the uterus.
How are hCG levels detected in pregnancy? HCG production starts right after implantation, but the levels are very low at first. They increase rapidly in the first few weeks, and home pregnancy tests can typically detect hCG in. The body usually produces hCG to support a healthy pregnancy, so high levels in other people may point to a health condition.