Octant In 3d
An octant in solid geometry is one of the eight divisions of a Euclidean three-dimensional coordinate system defined by the signs of the coordinates. It is analogous to the two-dimensional quadrant and the one-dimensional ray. [1].

Learn what an octant is in 3D geometry with clear definitions, sign conventions, visual representation, and solved examples. Understand how to identify points in different octants easily. This 3D simulation shows all different octant of Euclidean three.

Octants – ToolNotes
Position vectors in 3D space are still represented by arrows that begin at the origin and end at the point in question. The diagram above shows a point, P, located in the front, lower, right octant. 🚀 Welcome to our journey through the Eight Octants of Space! 🌌 In this video, we explore the three-dimensional (3D) coordinate system and its eight octants.

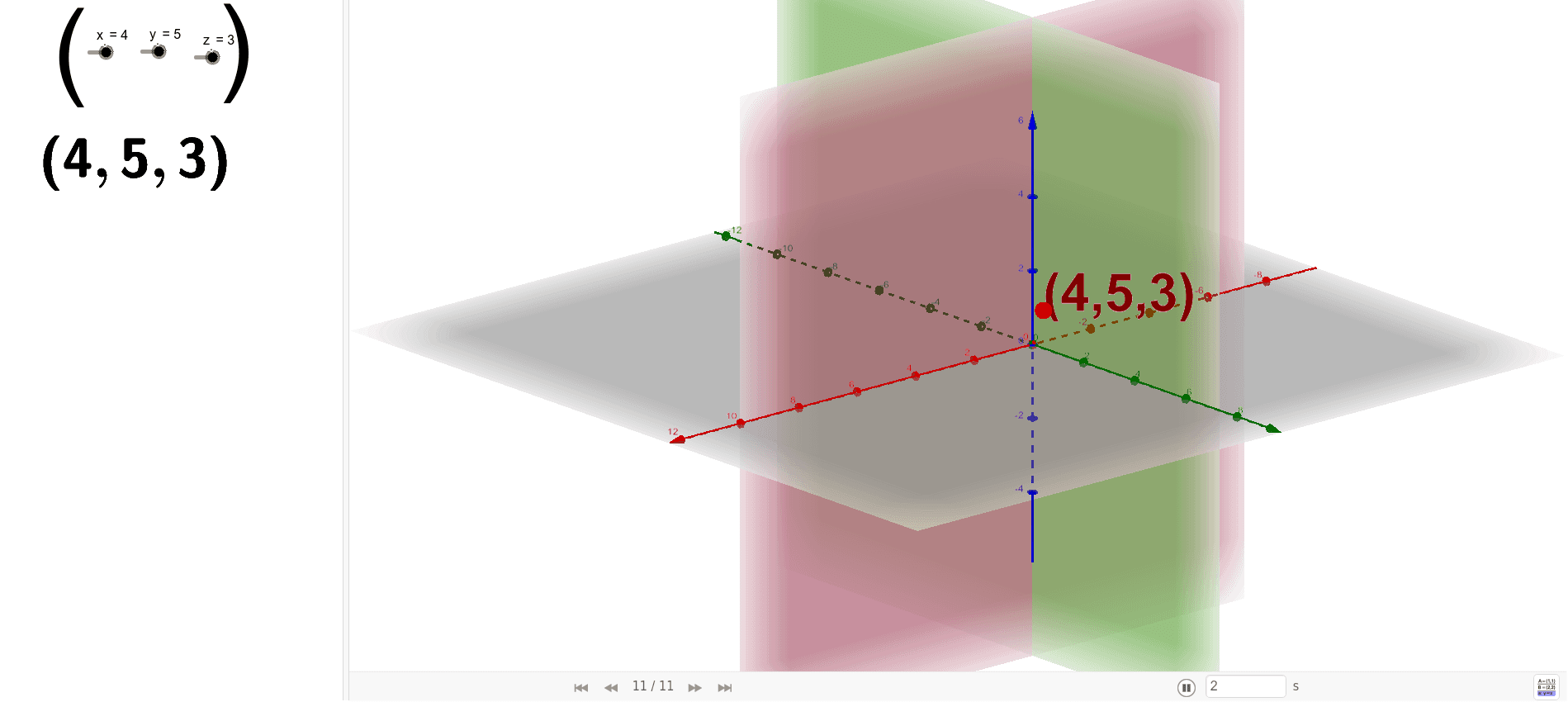
Perfect for understanding 3D. The first octant is the region where $x \ge 0$, $y \ge 0$ and $z \ge 0$. Unlike in the plane, there is no standard numbering for the other octants.
Octant in 3D Geometry: Definition, Sign Conventions, Representation & Examples
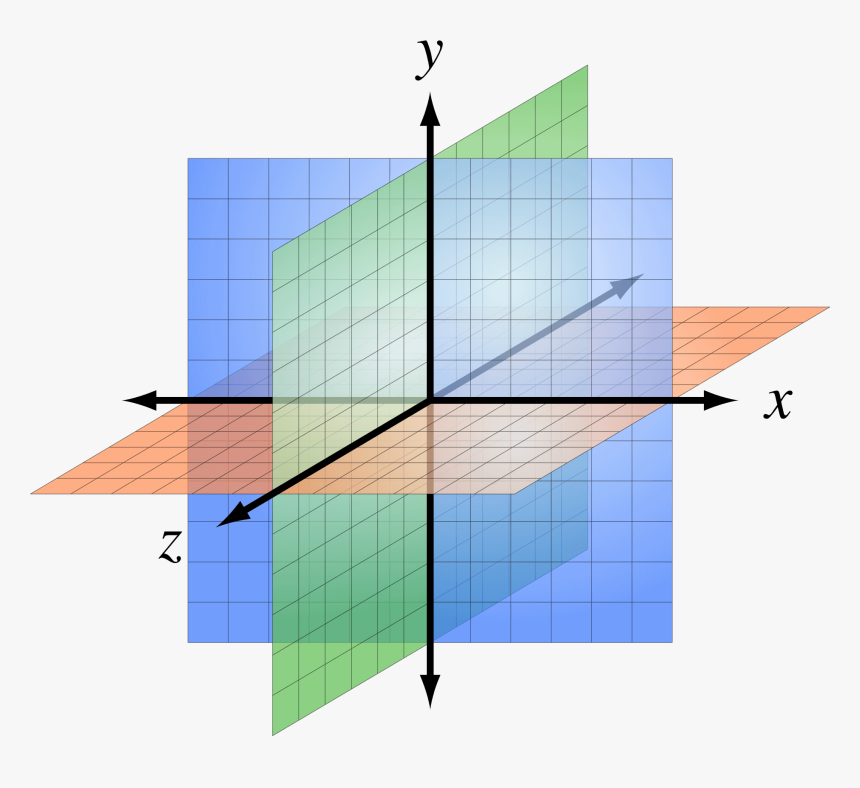
We usually think of the $x$-$y$ plane as being horizontal, with the $x$ axis pointing East, the $y$ axis pointing North, and the $z$ axis pointing straight up. This is described by the right hand rule. One of the eight regions of space defined by the eight possible combinations of signs (+/-,+/-,+/-) for x, y, and z.

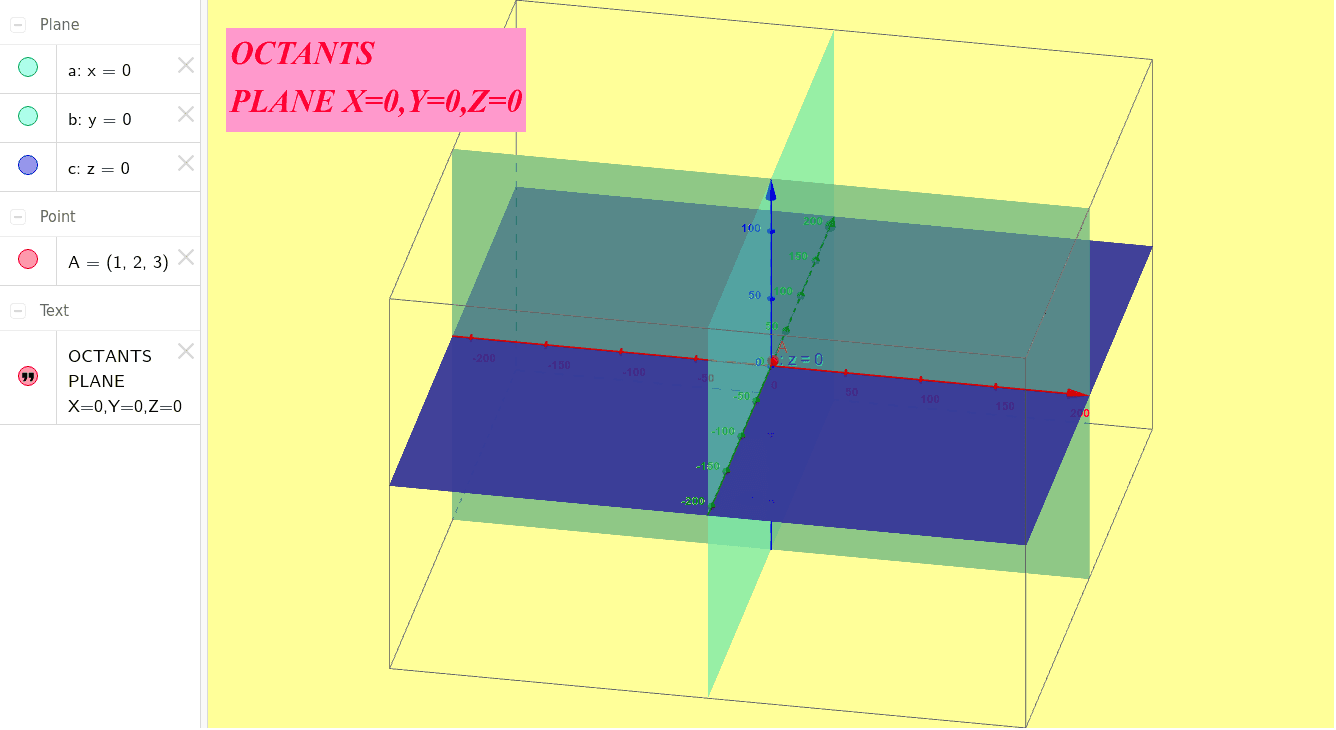
Octant Classification via Cartesian Coordinates 07 Oct 2024 Tags: Computer Graphics Computer Science Geometric Modeling CSG Representation of Octants Popularity: ⭐⭐⭐ Octant Determination in CSG This calculator determines the octant of a point in 3D space using its x, y, and z coordinates. Explanation Calculation Example: In CSG, an octant is a region of 3D space defined by the signs of. What is the first octant of a graph? The three planes all intersect in one point, the origin (located at (0,0,0)), and divide 3 space into 8 octants (similar to the 4 quadrants in 2 dimensions).
Octant | 3D | 3 Dimensional Geometry | Partitions - YouTube
The octant in which all three coordinates are positive is called the first octant. It happens to be the intersection of the two vertical planes. Any point in this space can now be identified with three coordinates with respect to these three axes.

Rotate the planes below and see that that the whole space is divided into 8 distinct portions. These are called octants. The first octant has points all whose coordinates will be.