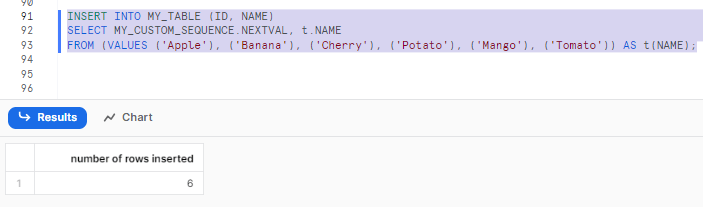
Snowflake From Values
In the SELECT statement, the VALUES subclause of the FROM clause lets you specify a set of constants to form a finite set of rows. For information about the VALUES clause in the INSERT statement, see the documentation for the INSERT statement. Snowflake supports VALUES clause: In the SELECT statement, the VALUES sub.

The VALUES clause can specify literal values or expressions to be used in the FROM clause. This clause can contain table and column aliases (not shown in the diagram above). For more details about the VALUES clause, see VALUES.

How to Retrieve Values from a Snowflake View Using Left Joins - YouTube
The SELECT clause in Snowflake offers more than just basic column selection. Master exclusion, renaming, and value manipulation to craft concise and informative queries. Snowflake is a great cloud data warehouse software that offers a variety of SQL use cases and keywords that every data developer loves to use.

In this article, we will briefly go through the VALUES keyword, whose use cases are among the best. Reference SQL command reference Query syntax SELECT SELECT SELECT can be used as either a statement or as a clause within other statements: As a statement, the SELECT statement is the most commonly executed SQL statement; it queries the database and retrieves a set of rows. As a clause, SELECT defines the set of columns returned by a query.

Snowflake User-Defined Functions (UDFs) - ThinkETL
See also: Query syntax Syntax The following sections. Learn how to use subqueries in Snowflake to perform complex queries and get more out of your data. With subqueries, you can easily filter data, join tables, and calculate aggregated results.

This comprehensive guide will teach you everything you need to know to use subqueries effectively in Snowflake. Reference Function and stored procedure reference Semi-structured and structured data GET Categories: Semi-structured and structured data functions (Extraction). In Snowflake Scripting, you can use variables in expressions, Snowflake Scripting statements, and SQL statements.
Snowflake Data Types: 6 Essential Types You Should Know | Estuary
Returning the value of a variable This example declares a variable named my_var for use in a Snowflake Scripting anonymous block and then returns the value of the variable.