Original England Flag
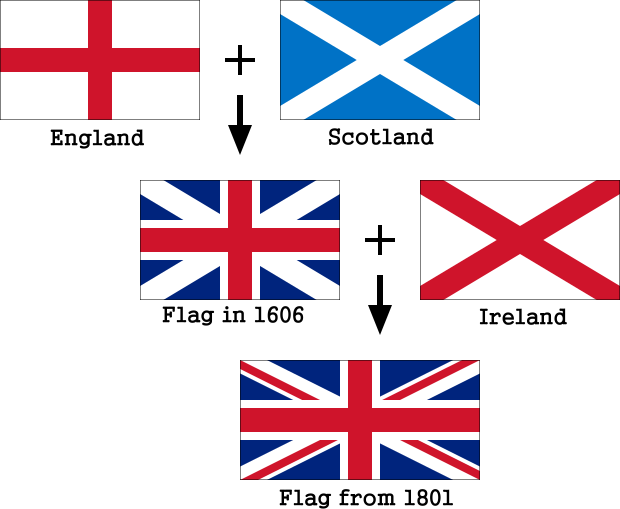
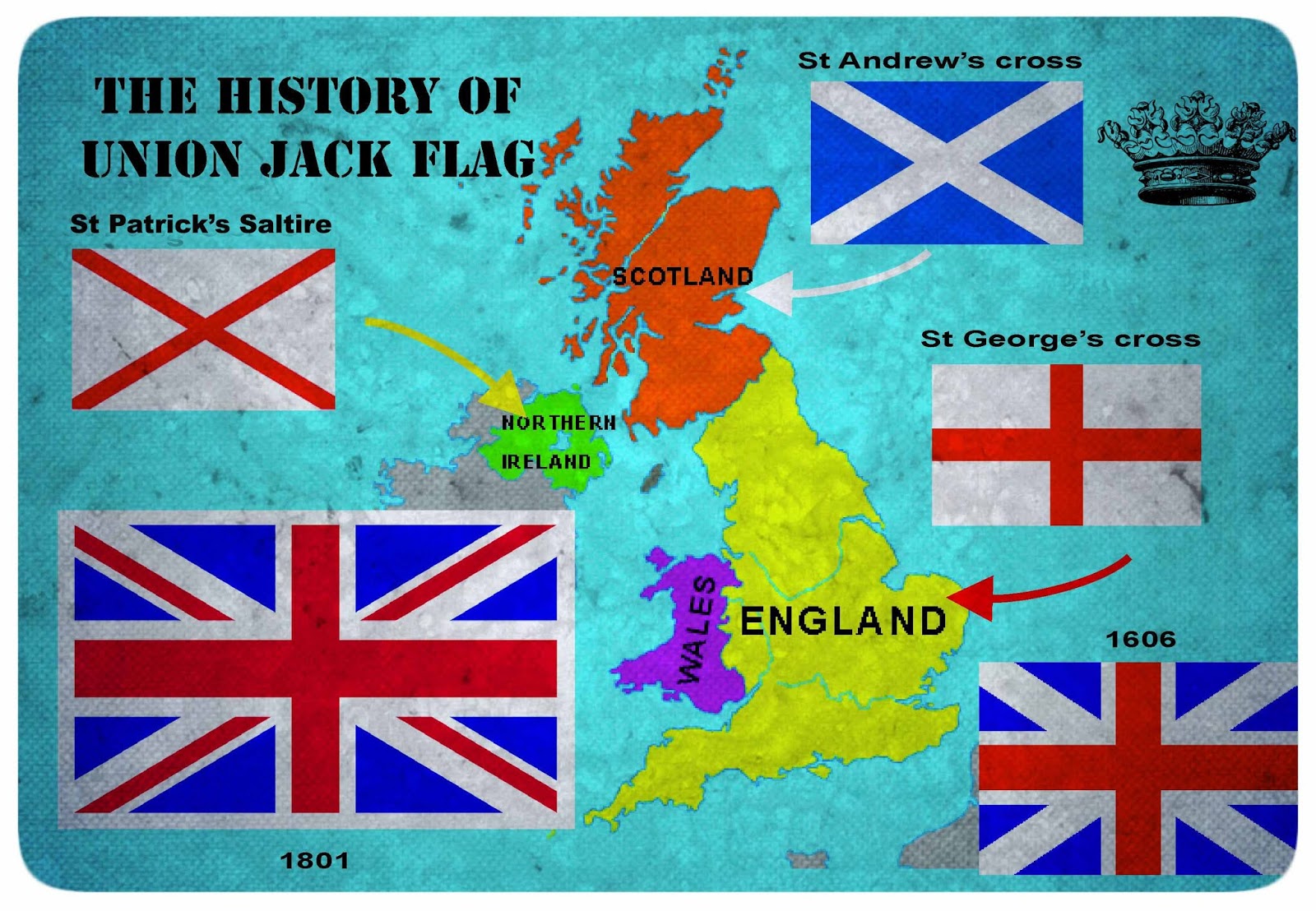
The flag of England is the national flag of England, a constituent country of the United Kingdom. It is derived from Saint George's Cross (heraldic blazon: Argent, a cross gules). The association of the red cross as an emblem of England can be traced back to the Late Middle Ages when it was gradually, increasingly, used alongside the Royal Banner.

Flag of a constituent unit of the United Kingdom, flown subordinate to the Union Jack, that consists of a white field (background) with a red cross known as the Cross of St. George.The origin of the flag, its association with St. George (the patron saint of England), and its adoption by England all.

Hoist Up the Flag: The British Red Ensign
Learn about the history of the St George's flag, the flag of England. The flag is a red centred cross on a white background. One of the most easily recognizable flags in the world is the flag of England.

Meaning and history behind the flag is quite an interesting subject. Read on, to know more about the flag of England, its meaning, and its history. What was the original flag of England? The St George's flag is the flag of England and is derived from the St George's cross which dates back to the Middle Ages.
British/English Flag History. Every flag of England and UK 927-2021. - YouTube
The flag is a red. The cross of St George, not the Union Jack, is the flag of England. It is a red cross on a white field.

The official proportions for the national flag of England is 3:5, with the cross being 1/5. The flag of England consists of a white field with a red cross at its center. This red cross is known as the St.

Original British Flag
George's Cross. The cross is a symbol of Saint George, who is the patron saint of England. The flag has a simple yet bold design, which makes it easily recognizable.

The dimensions of the flag are not fixed, but it is commonly seen in a ratio of 3:5 or 1:2. Find definitive artwork, specification and history for the England Flag. The flag went out of use in 1649 when England became a commonwealth but was restored for use in the king's ships after the restoration in 1660.

The flag became 'the ensign armorial of the United Kingdom of Great Britain' as one of the provisions of the Act of Union in 1707, when the kingdoms of England and Scotland were united.