Elements By Rarity
The abundance of the chemical elements is a measure of the occurrences of the chemical elements relative to all other elements in a given environment. Abundance is measured in one of three ways: by mass fraction (in commercial contexts often called weight fraction), by mole fraction (fraction of atoms by numerical count, or sometimes fraction of molecules in gases), or by volume fraction. Everyone is probably familiar with the more common elements on the periodic table, such as Hydrogen, Gold, and Oxygen, but the rare elements on this list aren't talked about often outside of the scientific community.

Essentially all of the rarest elements on Earth are radioactive and don't have commercial/practical uses. Element abundance in the Earth's crust refers to the relative quantities of different chemical elements that make up the solid outer layer of our planet. This composition plays a crucial role in the formation of minerals, the availability of natural resources, and various geological and industrial processes.
Rarity: The Element of Generosity by AnimatedOne on DeviantArt
List of chemical elements in order of abundance on earth. Learn when the elements in periodic table discovered and list atomic numbers and chemical symbols. These rare elements often have unusual properties, high value, or important uses in technology, medicine, or research.

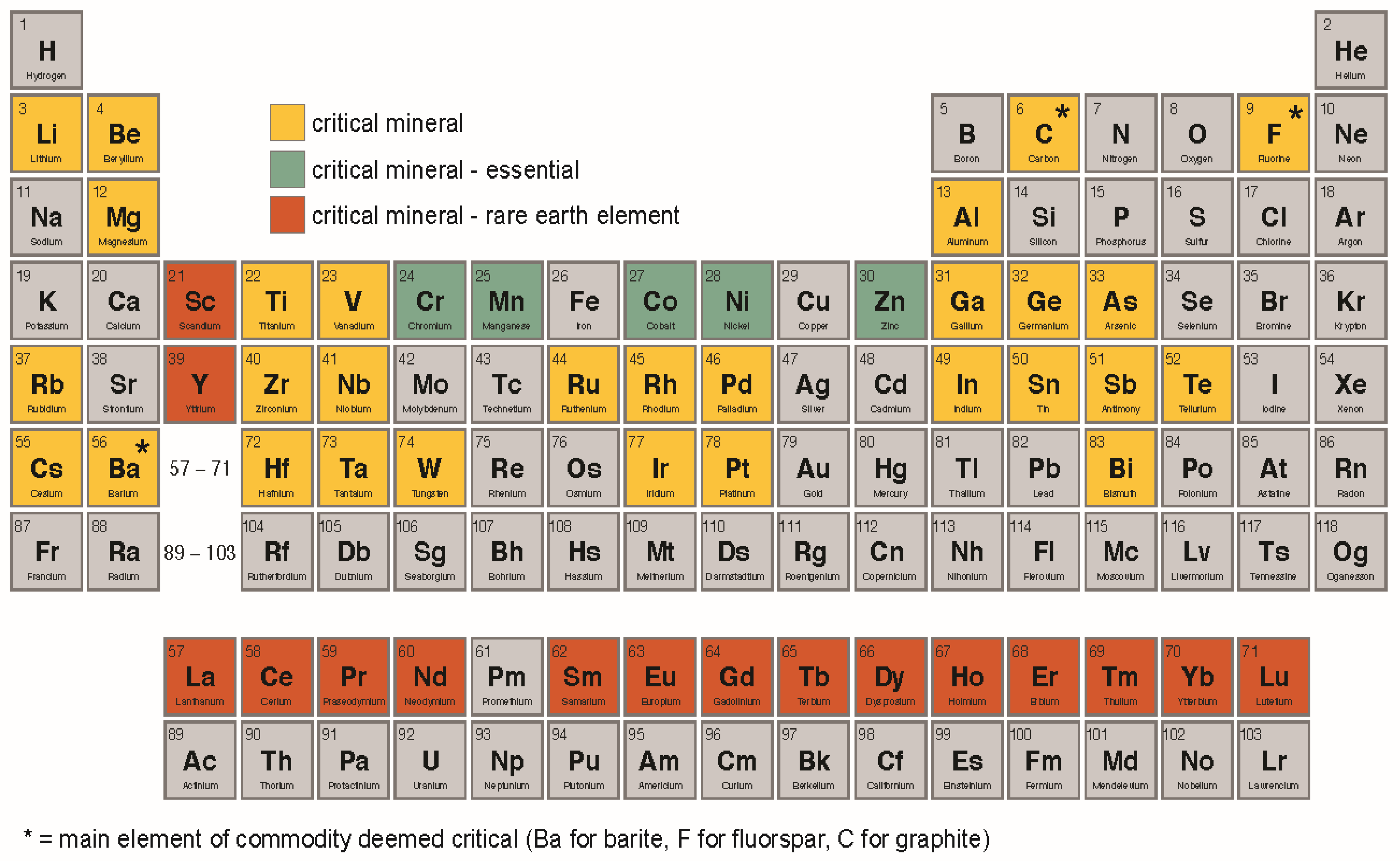
In this article, we'll explore some of the rarest elements on the periodic table and what makes them so special. These critical elements include rare earth elements, precious metals, and even some that are essential to life, like phosphorus. How Do Endangered Elements Relate to Green Chemistry? Endangered elements in the chemical enterprise face critical supply risks, making sustainable management of their extraction, use, reuse and dispersion essential.
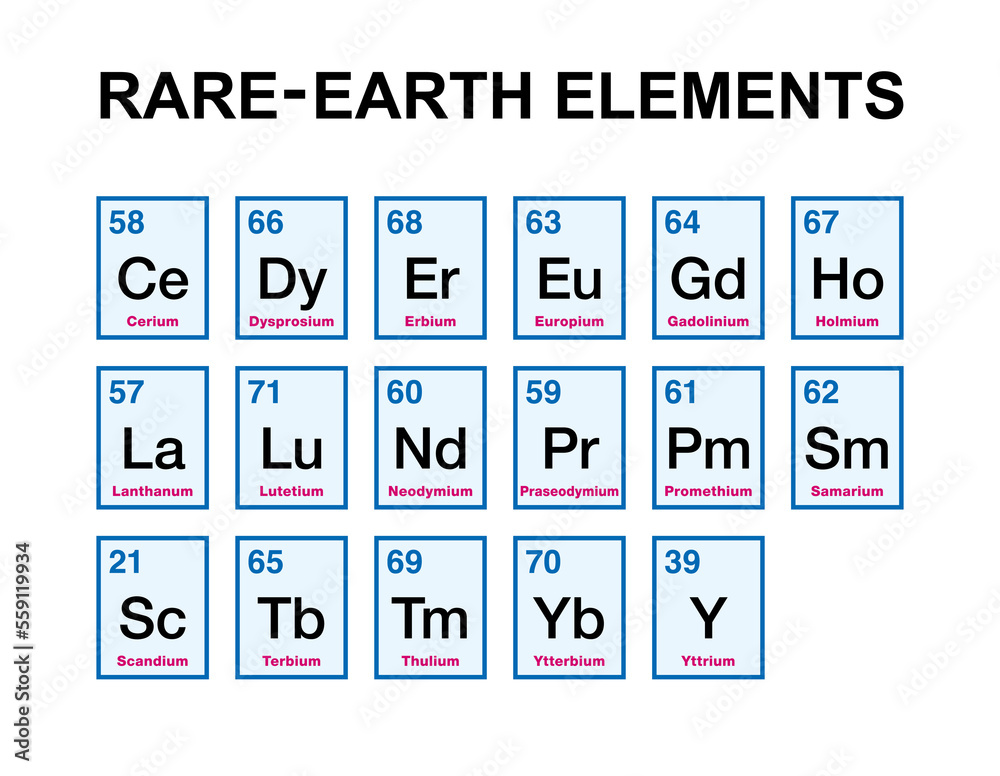
Rare Earth Elements – A Subset of Critical Minerals | netl.doe.gov
Its rarity makes francium largely impractical for any technological use. However, it represents one of the most extreme examples of element scarcity and remains a fascinating focus for physicists interested in the behavior of atoms near the edge of stability. The Natural History Museum states the rarest elements in the Earth's crust are platinum group metals, existing up to 3000 km underground.
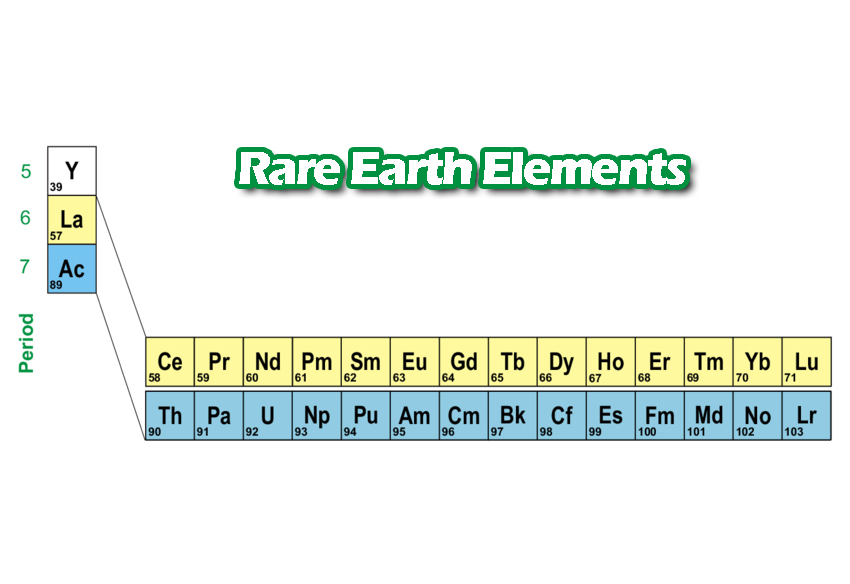
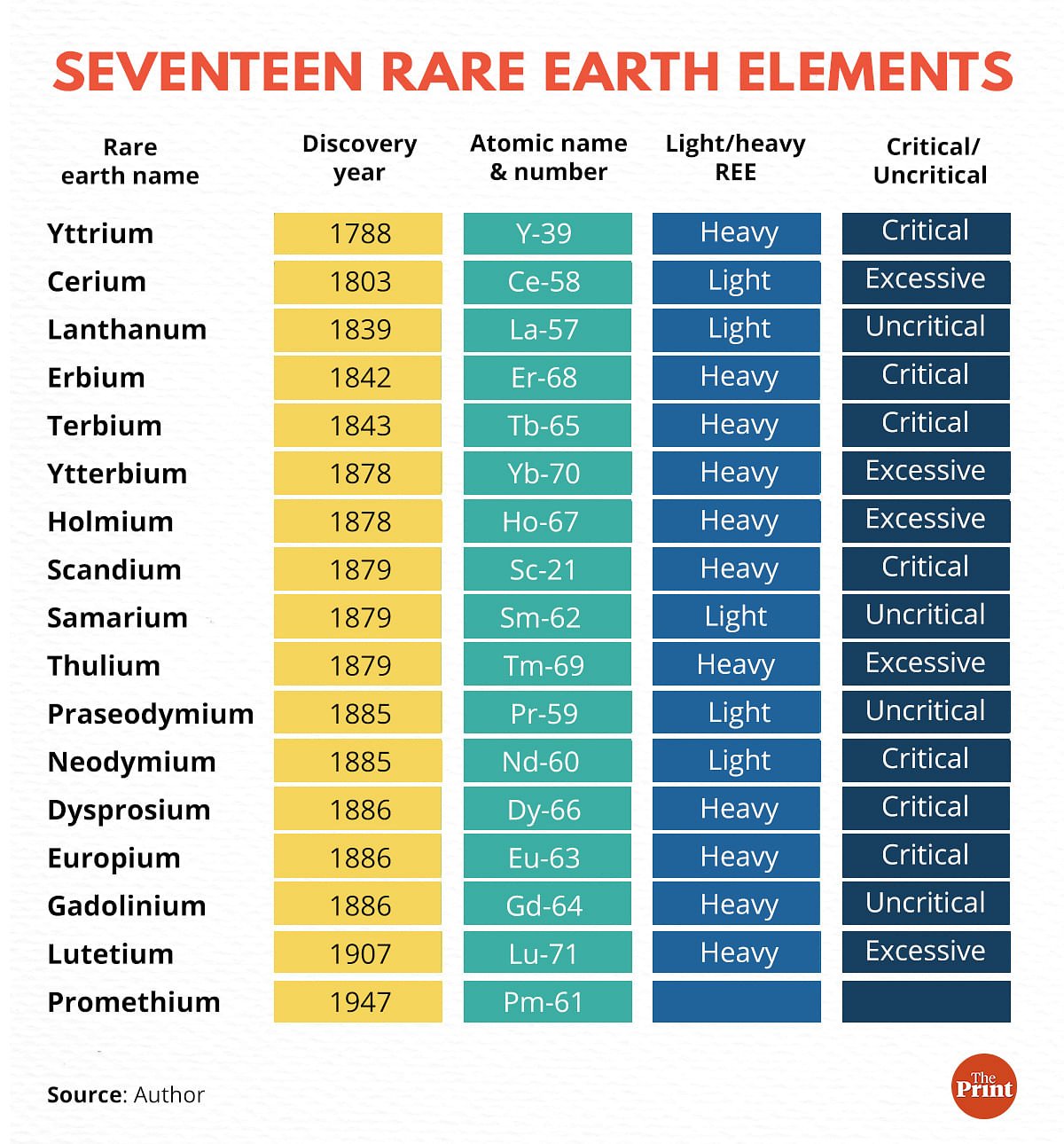
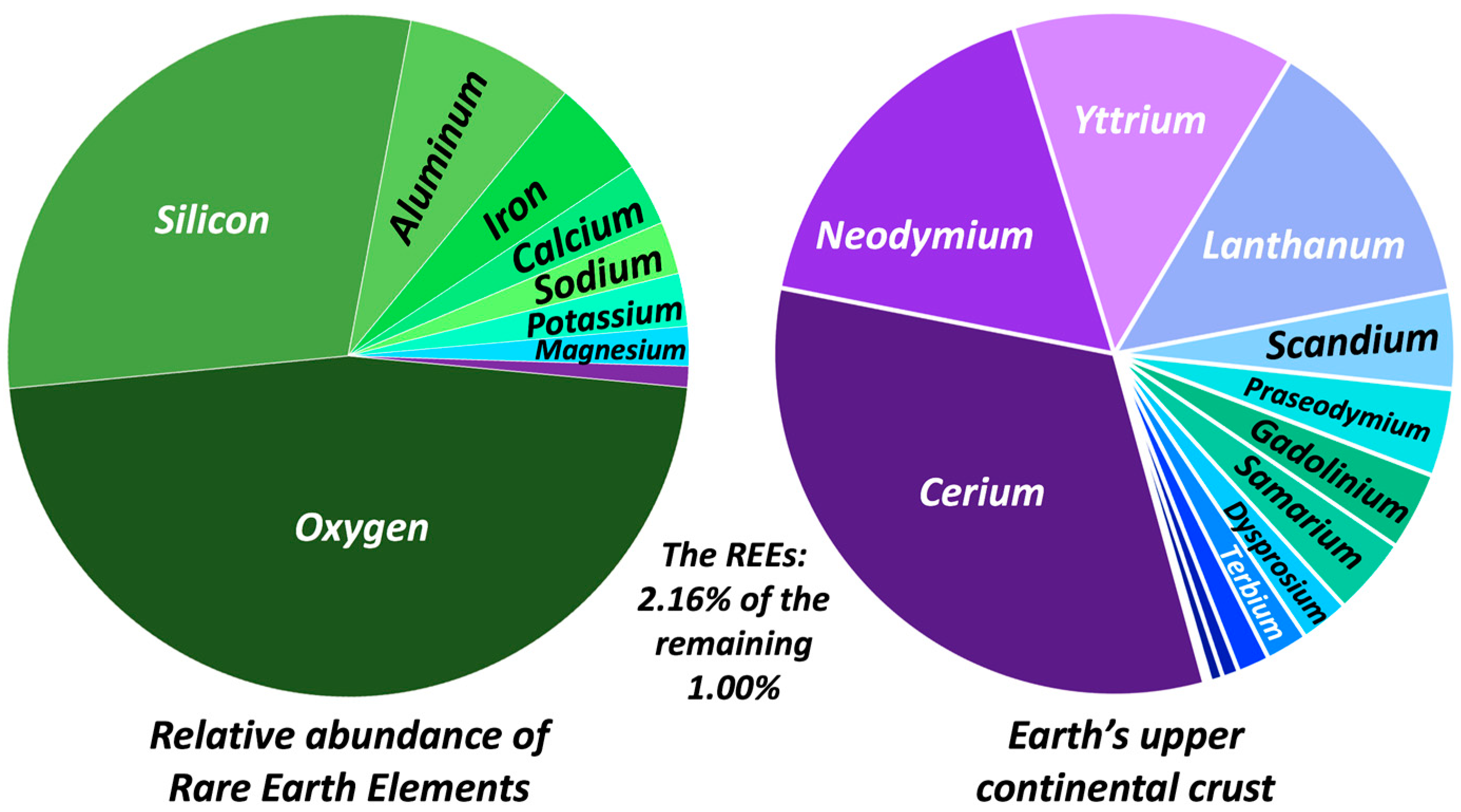
The principal economic sources of rare earths are the minerals bastnasite, monazite, and loparite and the lateritic ion-adsorption clays. The rare earths are a relatively abundant group of 17 elements composed of scandium, yttrium, and the lanthanides. The elements range in crustal abundance from cerium, the 25th most abundant element of the 78 common elements in the Earth's crust at 60 parts.