Moon Color Nasa
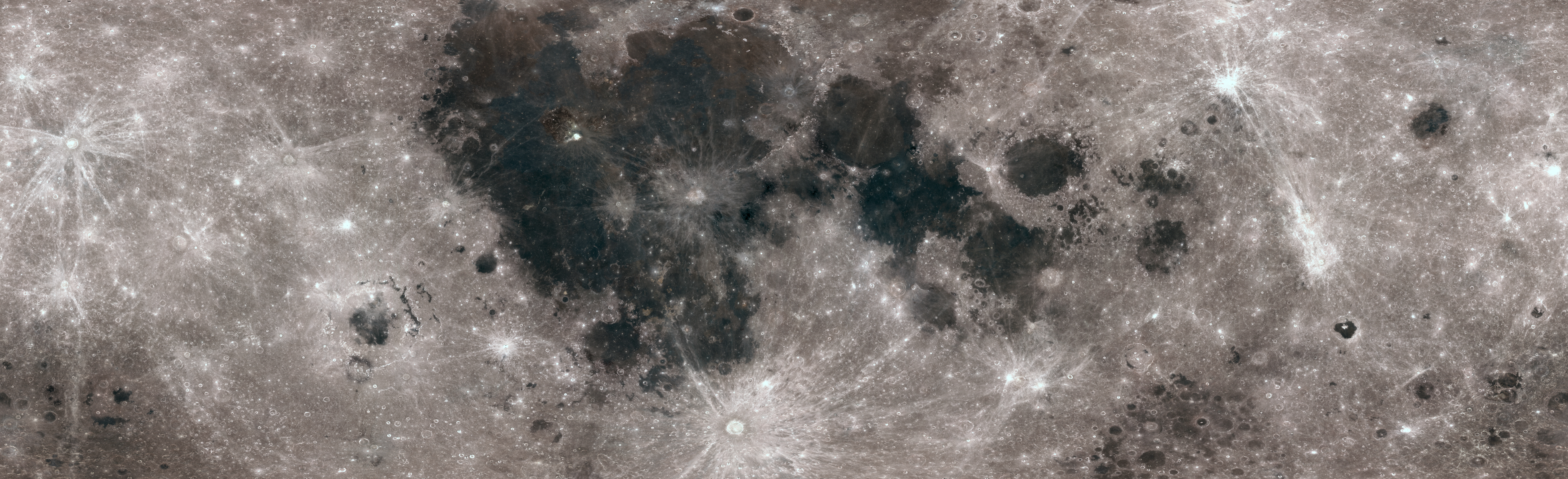
Lunar Surface in Color NASA/Goddard/Arizona State University October 9, 2017 A color composite mosaic showing most of the Moon's surface, based on images from NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, photometrically normalized. Note that small "holes" in the mosaic are due to shadows or saturation in the original observations. The color map tells the software how to paint the surface, and the displacement map tells it how to add the shape details that define the lunar terrain.

Without them, the Moon model is just a smooth, monochrome ball. What color is the Moon? The actual color of the Moon is a combination of various shades of gray. We know this from the days of the NASA missions.

What NASA's Technicolor Mosaic Images of the Moon Can Teach Us About the Lunar Surface
Photographs, lunar rocks, and soil samples were taken by Apollo Astronauts while on the surface of the Moon. If gray is its primary color, why do we see so many different colors of the Moon? Why is it called the Blue Moon, Harvest Moon, or the. The Moon's True Hue The Moon's inherent color, when viewed without interference from Earth's atmosphere or specific lighting conditions, is primarily various shades of gray, brown, and tan.
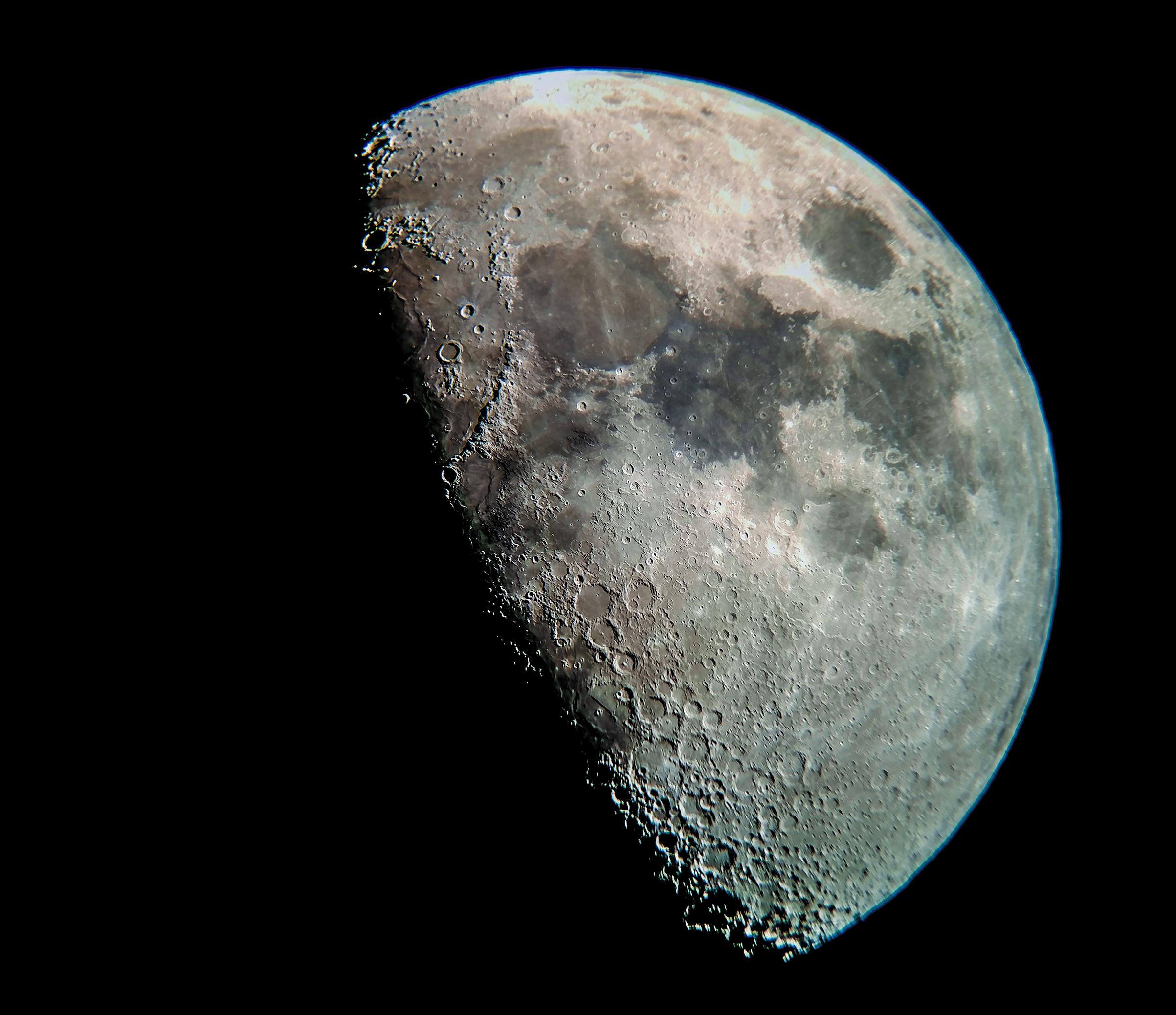
This is due to the composition of its surface material, known as regolith, a dusty, rocky substance covering the entire lunar surface. Moon - Lunar Color AS08-14-2432 (December 1968). This is a near vertical photograph of the lunar surface taken with a telephoto lens during the Apollo 8 lunar orbit mission.

Nasa Colors
The photographed area is approximately 20 miles on a side and is located within a large, unmanned 100 mile diameter crater on the farside of the moon. The Moon's color depends on the light the Moon reflects, which in turn depends on the Moon's surface and its features, having for example large darker regions. In general, the lunar surface reflects a brown-tinged gray light.
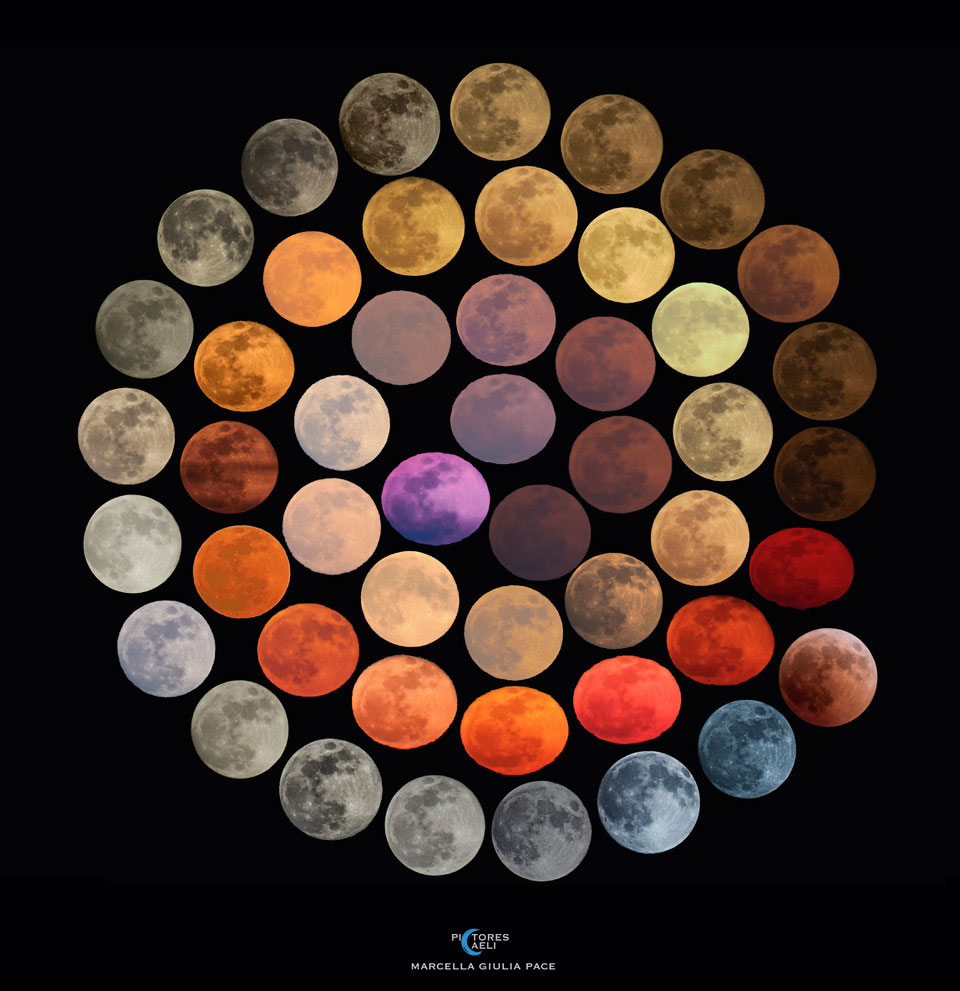

[221]. Viewed from inside the Earth's atmosphere, though, the moon can appear quite different. The featured image highlights a collection of apparent colors of the full moon documented by one astrophotographer over 10 years from different locations across Italy.
Lunar Surface in Color - Moon: NASA Science
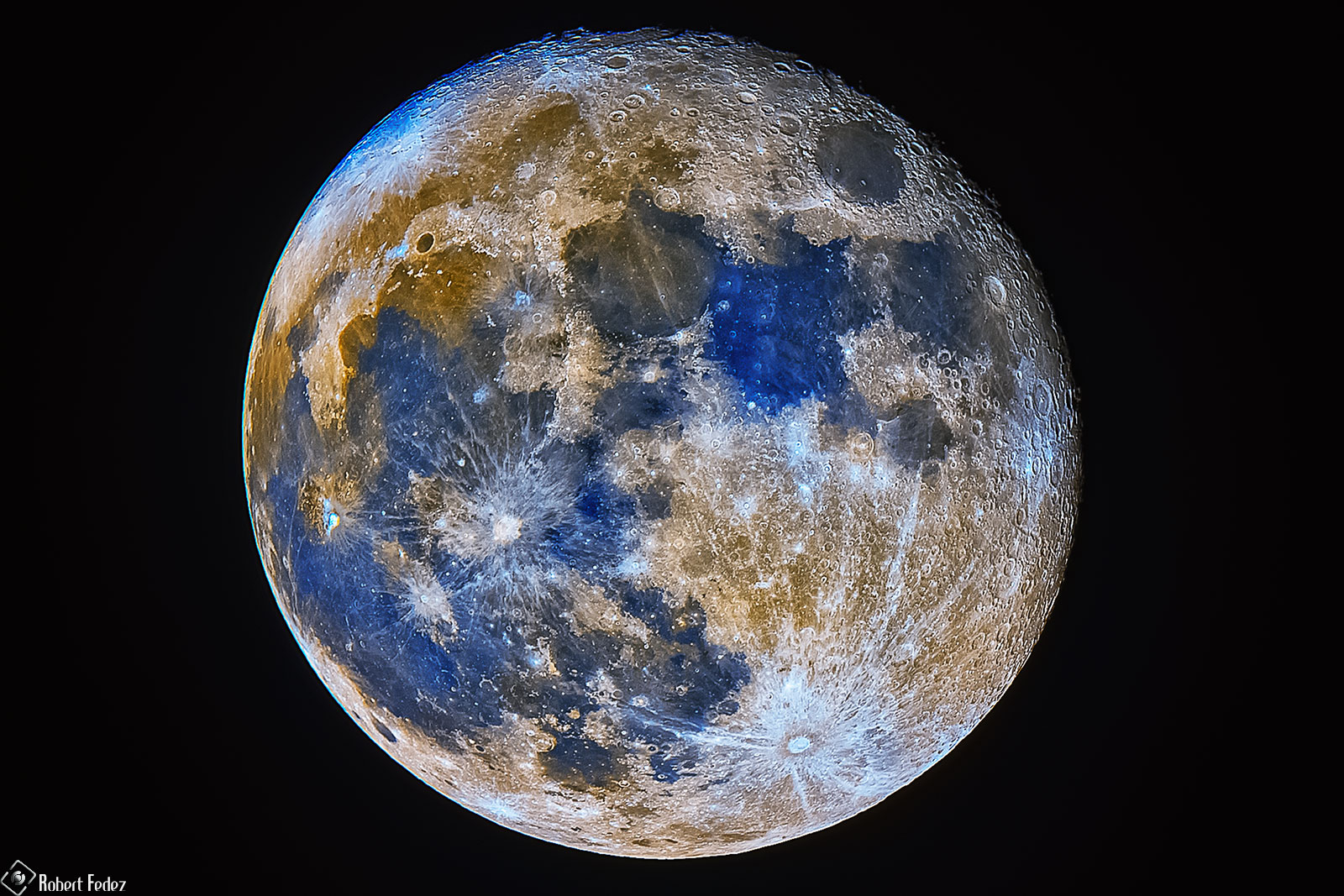
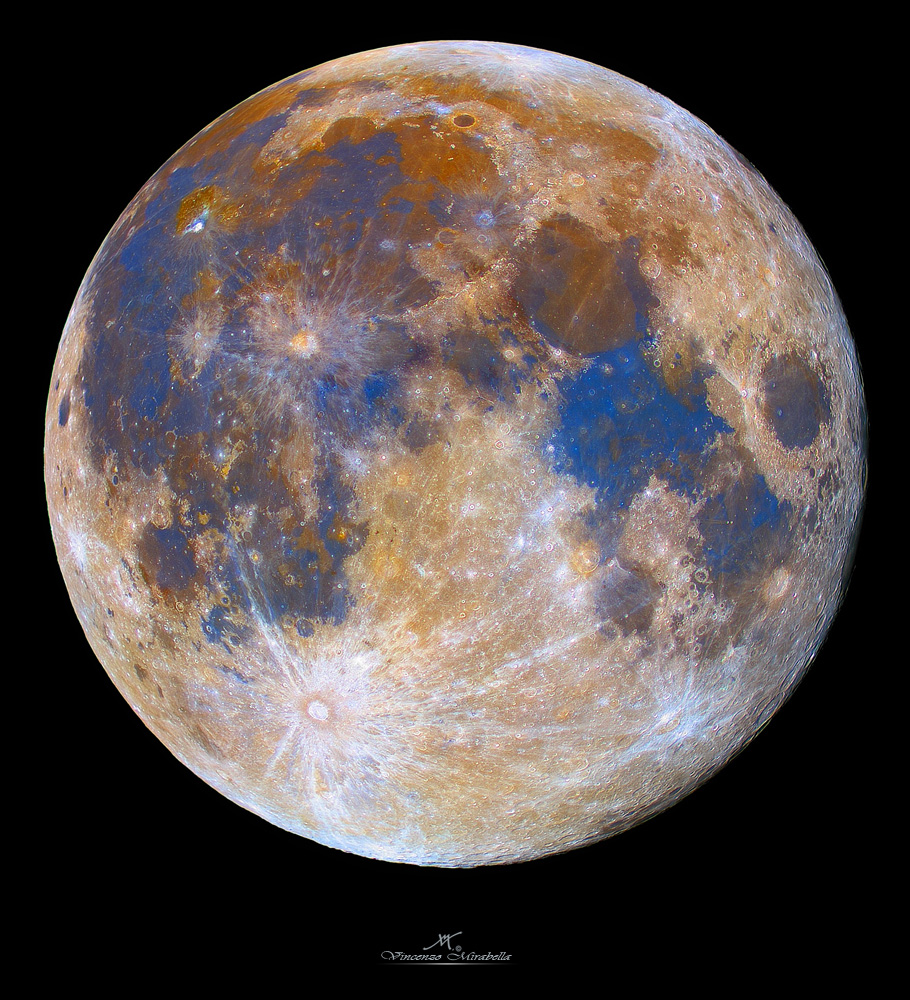
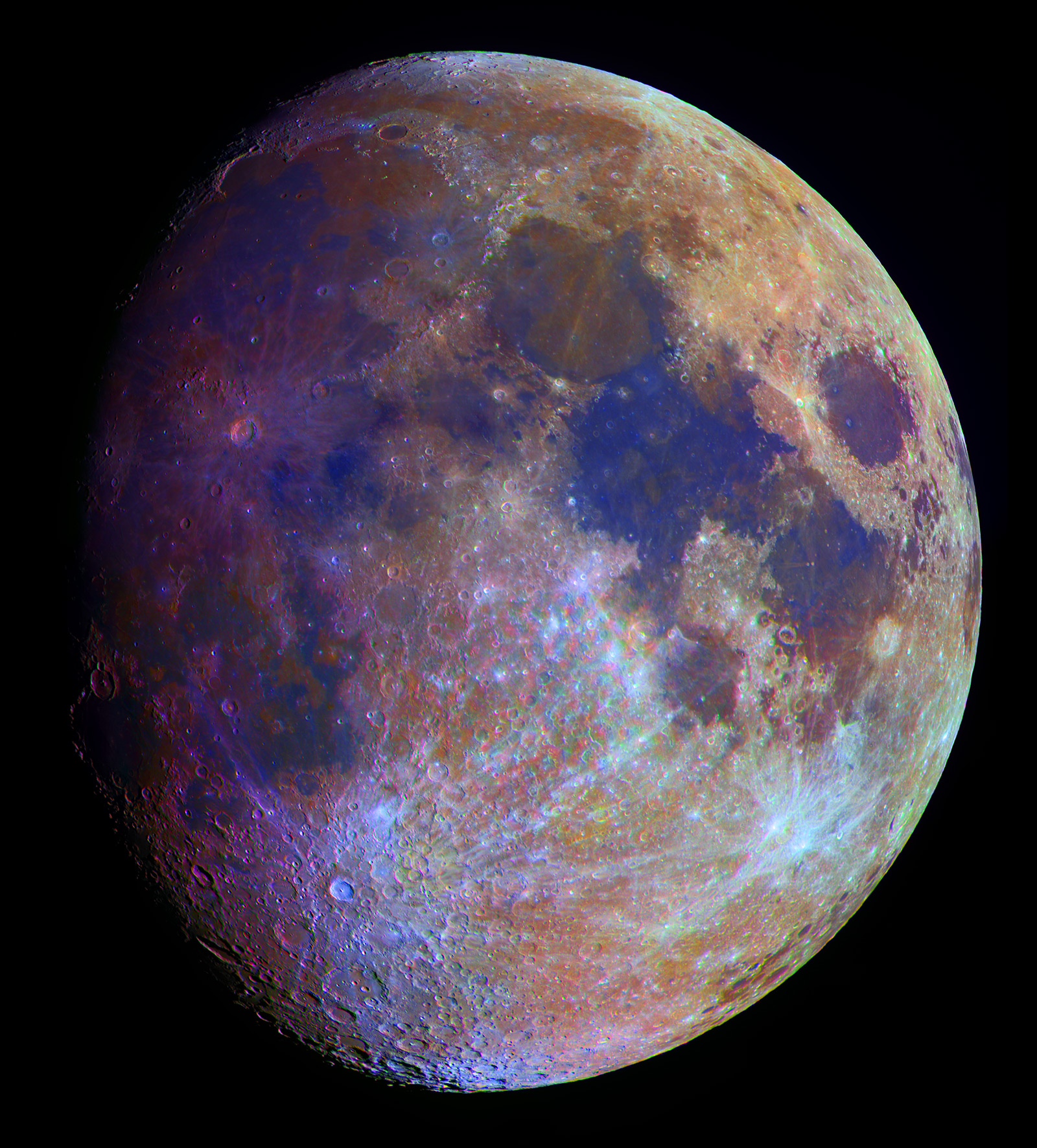
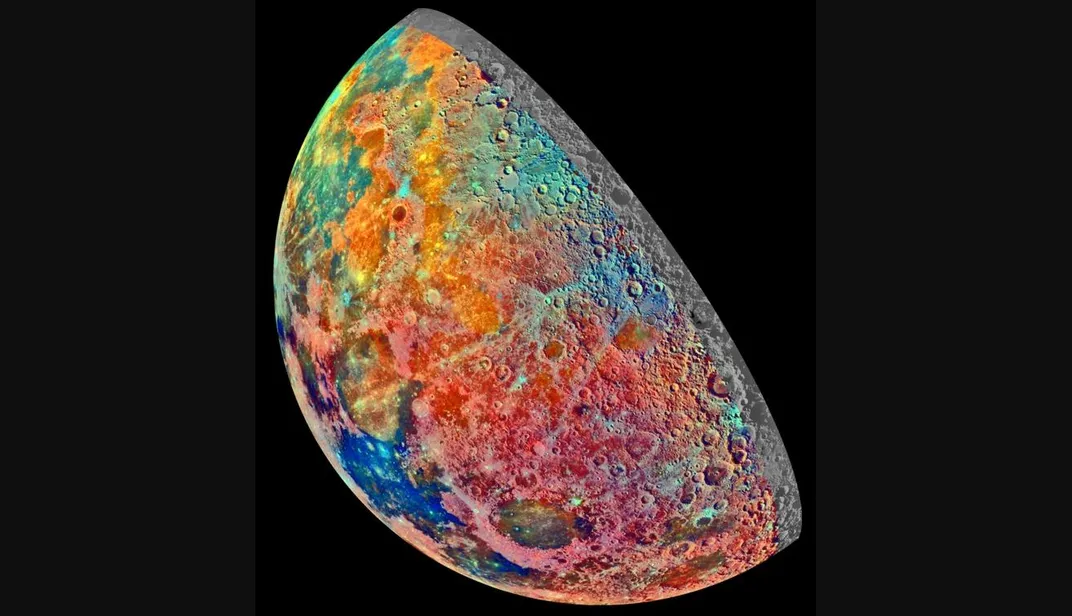
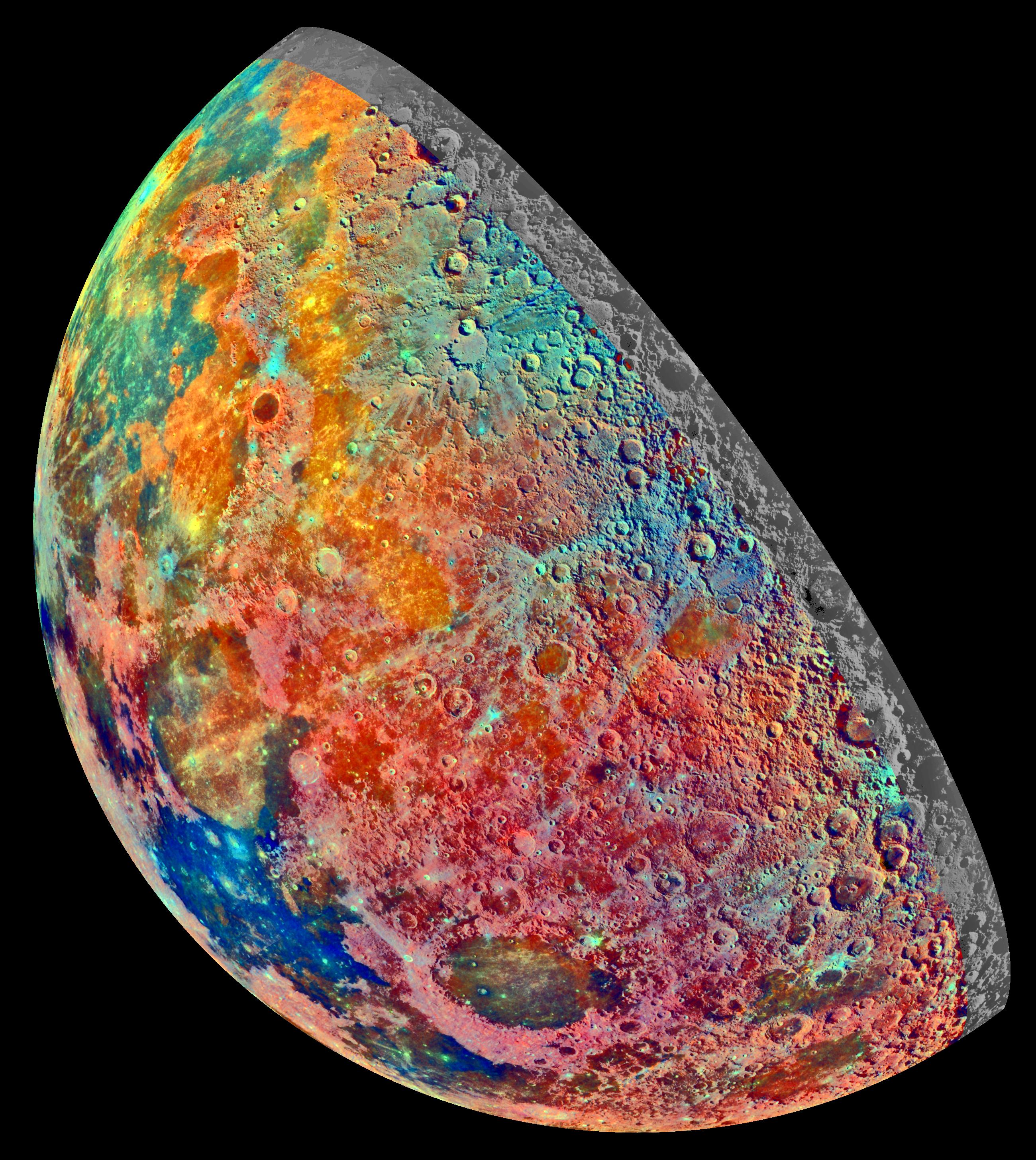
A red or yellow colored moon usually indicates a moon seen near the horizon. This false-color photograph is a composite of 15 images of the Moon taken through three color filters by Galileo's solid-state imaging system during the spacecraft's passage through the Earth-Moon system on December 8, 1992. When this view was obtained, the spacecraft was 262,000 miles (425,000 kilometers) from the Moon and 69,000 kilometers 43,000 miles (69,000 kilometers) from Earth.
The. These color visualizations of the Moon were obtained by NASA's Galileo spacecraft as it left the Earth after completing its first Earth Gravity Assist. The images were acquired Dec.

8-9, 1990. Explanation: Earth's Moon is normally seen in subtle shades of grey or yellow. But small color differences have been greatly exaggerated to make this dramatic mosaic image of the Moon's gibbous phase.






