Solid Wikipedia
In software programming, SOLID is a mnemonic acronym for five design principles intended to make object-oriented designs more understandable, flexible, and maintainable. The forces between the atoms in a solid can take many forms. For example, a crystal of sodium chloride (common salt) is made up of ionic sodium and chlorine, which are held together by ionic bonds.
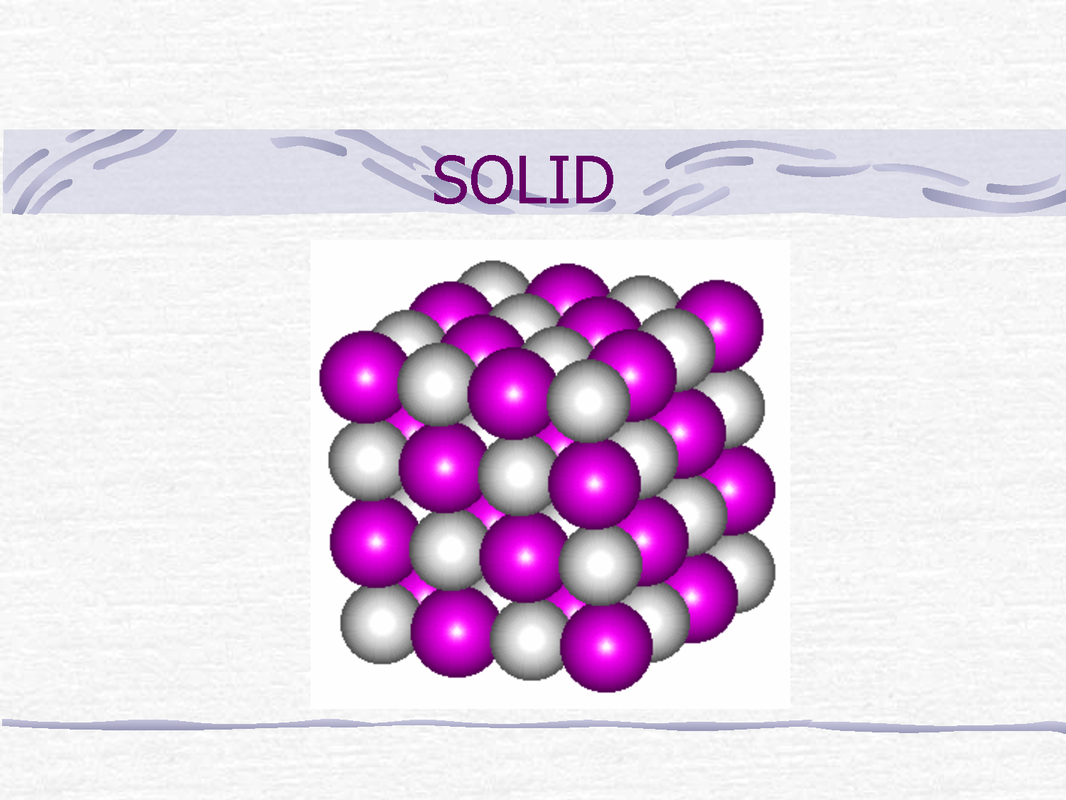
In diamond or silicon, the atoms share electrons and make covalent bonds. In metals, electrons are shared in metallic bonding. Some solids, like most organic compounds, are held together with "van.

Particle Diagram Solid
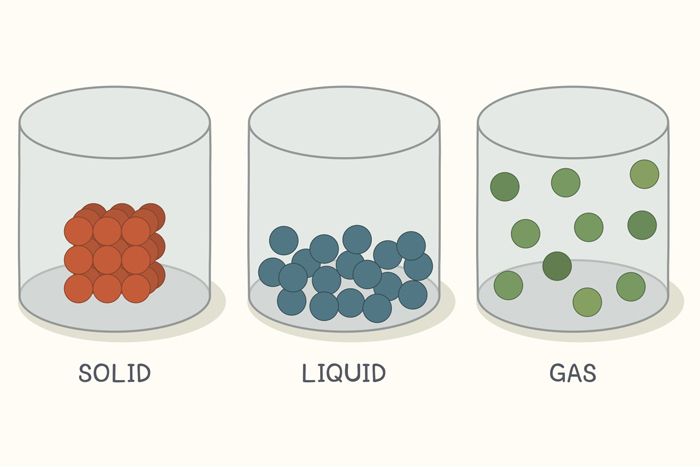
In physics, a state of matter or phase of matter is one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Different states are distinguished by the ways the component particles (atoms, molecules, ions and electrons) are arranged, and how they behave collectively.

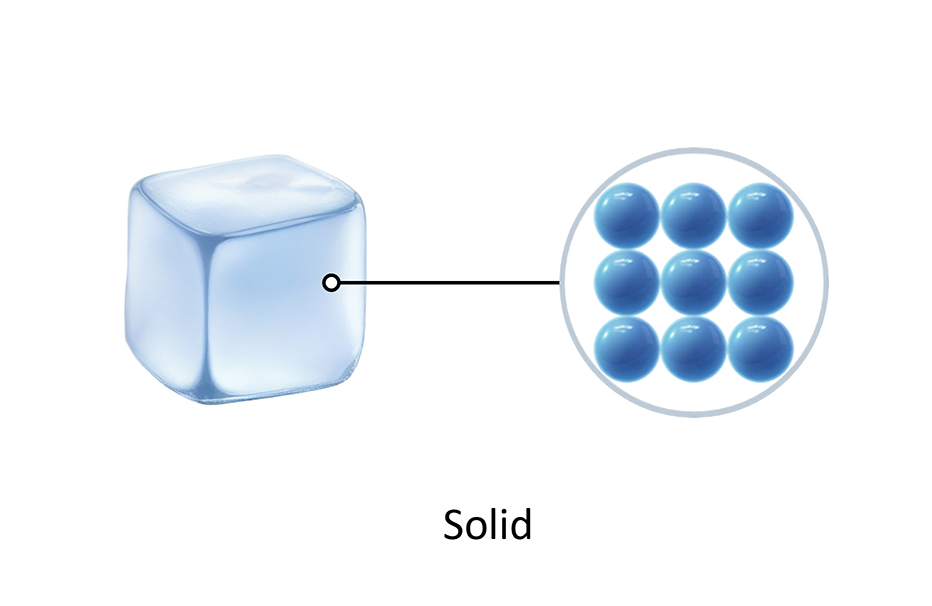
In a solid, the particles are tightly packed. Solid-state physics is the study of rigid matter, or solids, through methods such as solid-state chemistry, quantum mechanics, crystallography, electromagnetism, and metallurgy. Solid (abbreviation from Social Linked Data) [1] is a web decentralization project led by Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web, originally developed collaboratively at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
.PNG)
Platonic solid - Wikipedia
SOLID is often used with systems that use an object-oriented design. [source?] SOLID was promoted by Robert C. Martin but the name itself was created by Michael Feathers.

[1][better source needed] In essence, SOLID principles guide developers towards creating code that is more maintainable, flexible, and reusable. Solid is a term that can refer to different things in various fields, such as matter, plumbing, biology, computing, and arts. This page lists the possible meanings of solid and provides links to the related articles.

What is a solid? - Twinkl
Solid, one of the three basic states of matter, the others being liquid and gas. A solid forms from liquid or gas because the energy of atoms decreases when the atoms take up a relatively ordered, three. The geometry in solid modeling is fully described in 3‑D space; objects can be viewed from any angle.
Solid modeling (or solid modelling) is a consistent set of principles for mathematical and computer modeling of three-dimensional shapes (solids). Solid modeling is distinguished within the broader related areas of geometric modeling and computer graphics, such as 3D modeling, by its. solid (plural solids) (chemistry) A substance in the fundamental state of matter that retains its size and shape without need of a container (as opposed to a liquid or gas).