Coco Format Example
The "COCO format" is a specific JSON structure dictating how labels and metadata are saved for an image dataset. Many blog posts exist that describe the basic format of COCO, but they often lack detailed examples of loading and working with your COCO formatted data. This post will walk you through: The COCO file format.

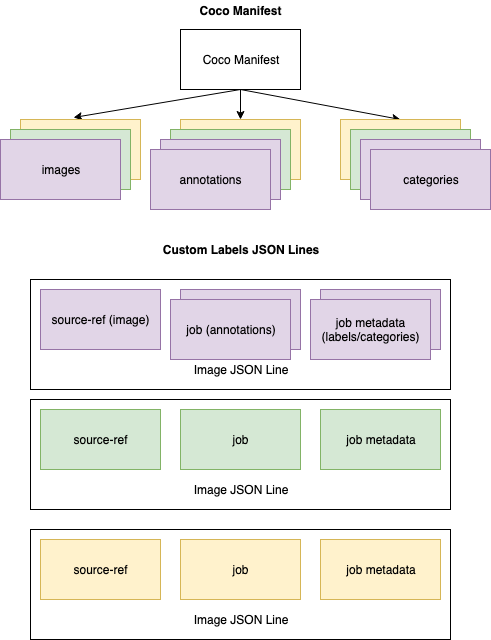
This tutorial will teach you how to create a simple COCO. To create a Custom Labels manifest, you use the images, annotations, and categories lists from the COCO manifest file. The other sections (info, licences) aren't required.
How to Filter the COCO Dataset by Category — Immersive Limit
The following is an example COCO manifest file. COCO is a common JSON format used for machine learning because the dataset it was introduced with has become a common benchmark. COCO format Familiarize yourself with the supported formats in the Tenyks platform 1.

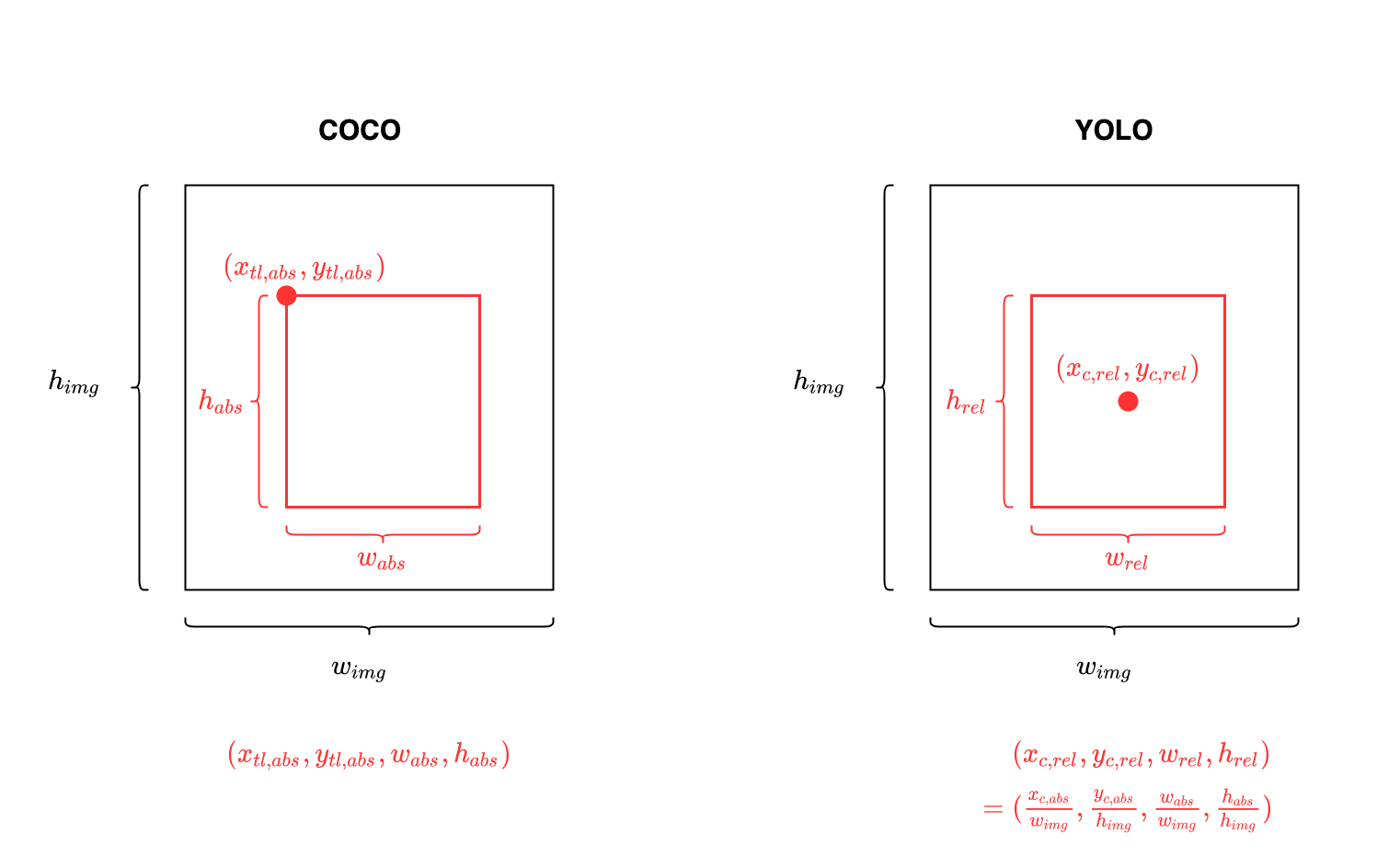
COCO format 1.1 What is the COCO format? The COCO (Common Objects in Context) format is a standard for organizing and annotating visual data to train and benchmark computer vision models, especially for object detection, instance segmentation, and keypoint. COCO Object Detection Format Overview COCO (Common Objects in Context) is a large. Sample Images and Annotations The COCO dataset contains a diverse set of images with various object categories and complex scenes.

Sample mitotic figure COCO format annotation C. Proposed DL Models ...
Here are some examples of images from the dataset, along with their corresponding annotations: Mosaiced Image: This image demonstrates a training batch composed of mosaiced dataset images. Mosaicing is a technique used during training that combines multiple images. We have partnered with the team behind the open-source tool FiftyOne to make it easier to download, visualize, and evaluate COCO FiftyOne is an open.

How COCO annotations are structured and how to use them to train object detection models in Python.