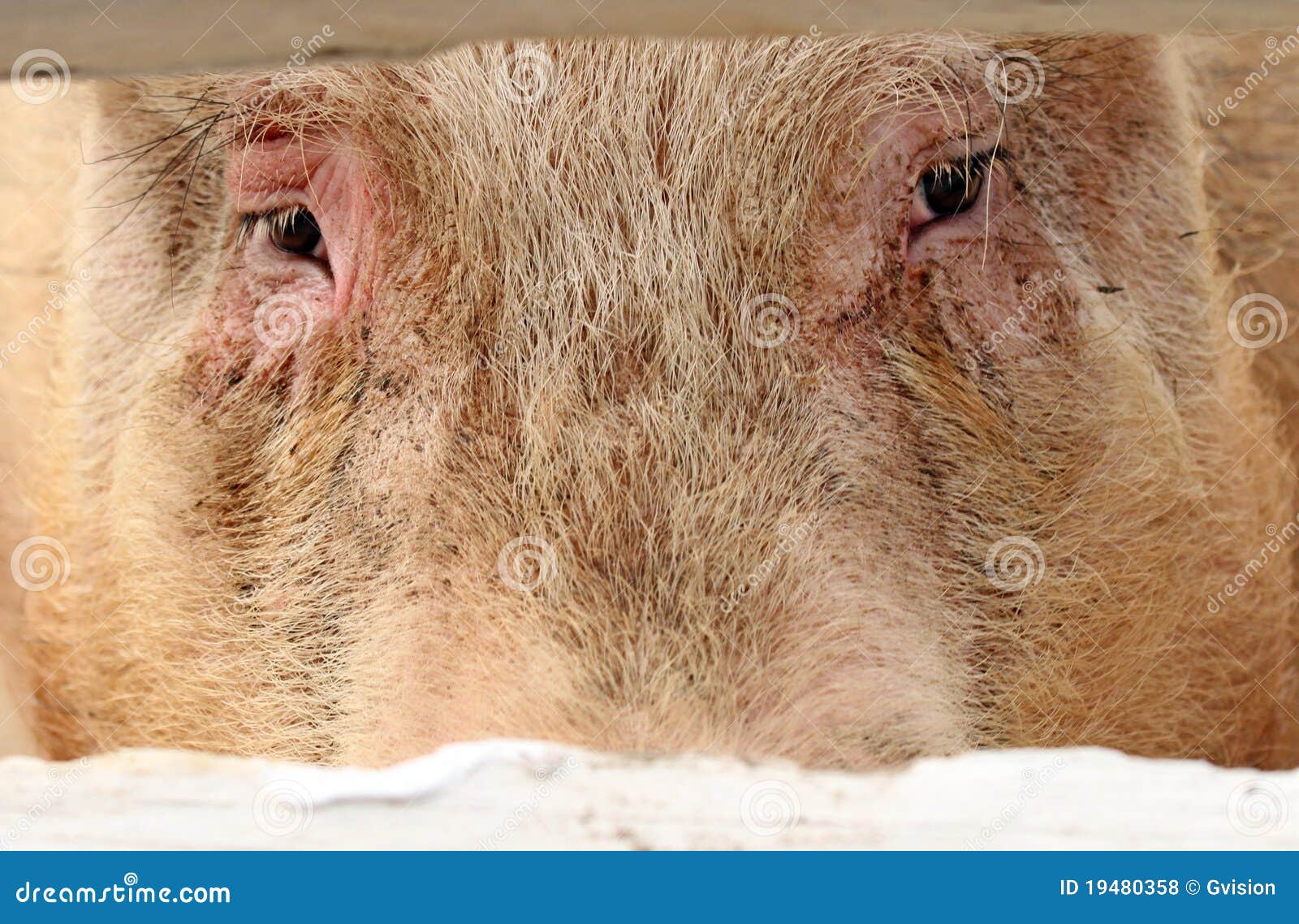
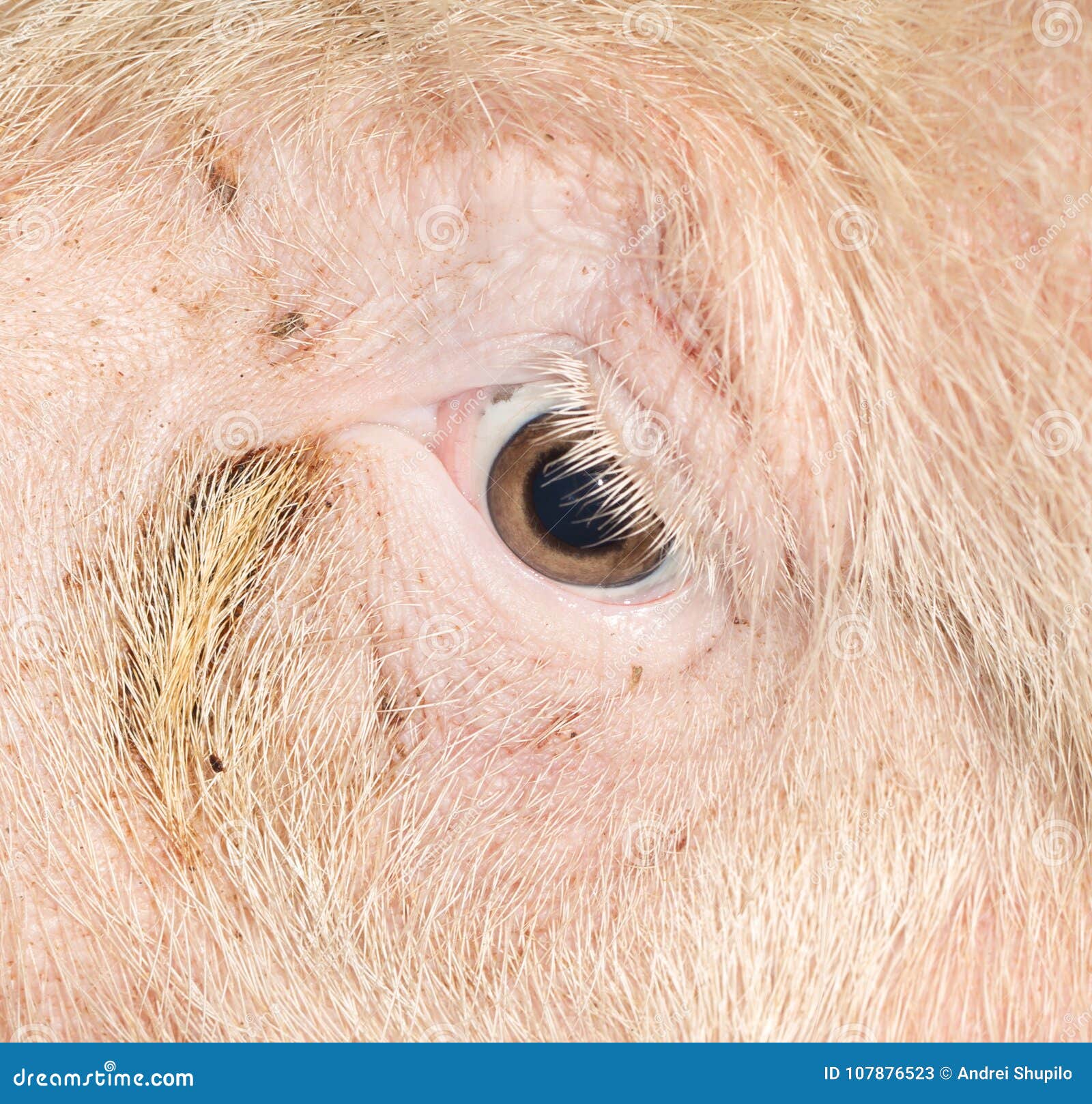
Pig Eye Colors
Certain colors are more prevalent than others, depending on the breed and the eye color of their parents, much like in people. Typically, pigs are seen with darker eye colors such as brown or black. However, some breeds may also have individuals with blue or red/pink eyes, which result from a lack of pigment.

Here, we have explained, "What colors do pigs see," along with answering other relevant queries on pigs.. In addition, pigs have more rods than cones in their eyes, enhancing their ability to see in low light. This makes them adaptable, especially in dim conditions.

Pin by Belle MyMichele on Precious Little Things | Cute piglets, Cute pigs, Pet pigs
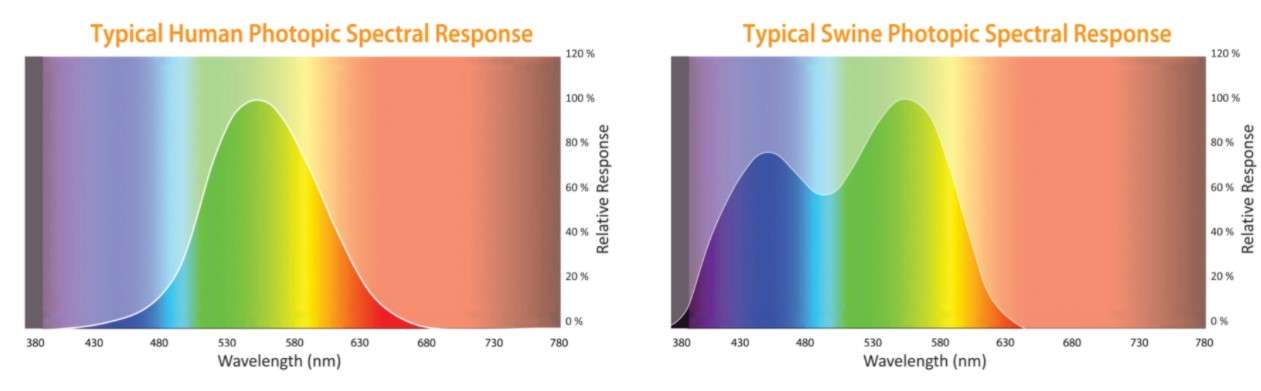
Comparison with Human Vision Humans have trichromatic vision, with three types of cones sensitive to red, green, and blue light. This allows us to see a wider spectrum of colors and shades. Can pigs distinguish between different shades of blue and yellow? Why can't pigs see all the colors of the rainbow? How does pig vision affect their behavior? What are some tips for enriching a pig's environment considering their limited color vision? In this study, we analysed eye colour variability in a Large White pig population (n = 897) and report the results of GWASs based on several comparisons including pigs having four main eye colour categories (three with both pigmented eyes of different brown grades: pale, 17.9%; medium, 14.8%; and dark, 54.3%; another one with both eyes.

Pigs exhibit dichromatic vision, meaning their eyes contain two types of cone cells sensitive to blue and green-yellow wavelengths of light. Their color perception peaks around light blue and yellowish-green, and they are largely unable to distinguish red from green, perceiving red as a shade of gray. Pigs eyes come in various colors.
23,357 Pig eyes Images, Stock Photos & Vectors | Shutterstock
They are mainly dark, such as black, brown or blue. The eyes can also be red, pink, or dark with a ruby hue. Pigs cannot perceive sharp lines, but they do see color.

Our study identifies two candidate genes for eye colors variation, and establishes a genetic link between iris and plumage color, two traits that vary widely in the evolution of birds and other. In contrast, the pig's eye, while structurally similar in some respects, possesses key differences that shape their visual perception. The human eye is designed to see a wide spectrum of colors and high levels of detail and clarity.

Super Realistic Pig Eye Illustration Stock Illustration - Illustration of character, design ...
The pig eye, while still capable of visual processing, is structured and geared for a slightly different purpose. Color Perception Pigvision Institute studies showed that pigs see primarily red, green and blue wavelengths. When these colors are combined - for example, in a multicolored pig food with red, green and blue pellets.