Heart Dye Ct Scan
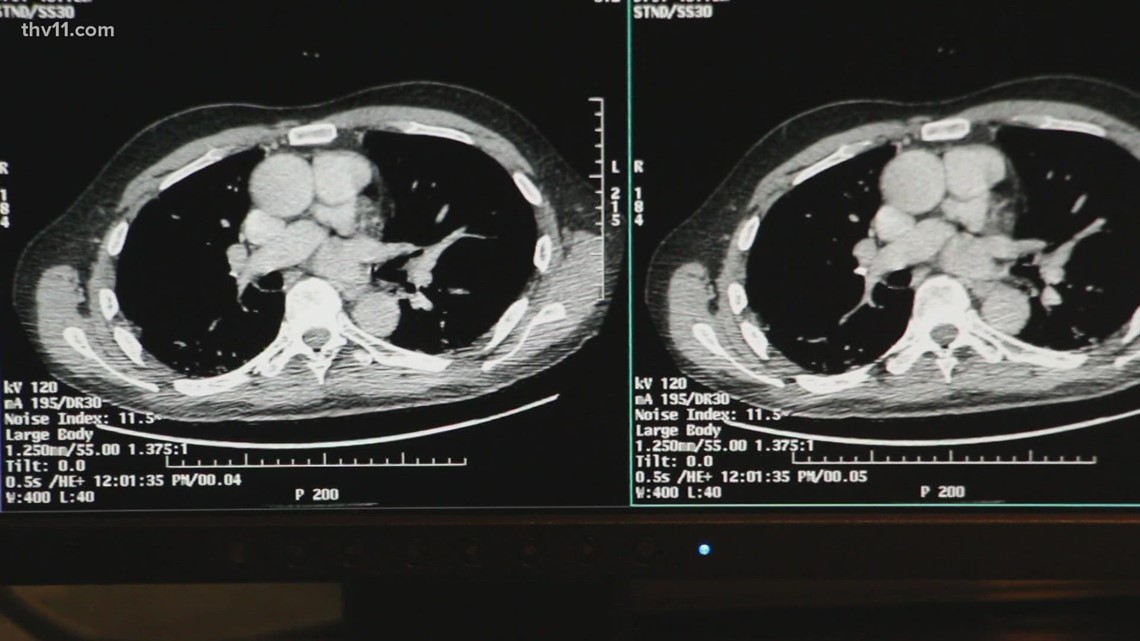
A heart CT scan creates high-resolution images of your heart to assess for heart, valve, coronary artery, aorta and other diseases. A heart, or cardiac, CT scan is used to view your heart and blood vessels. During the test, a specialized dye is injected into your bloodstream.
Heart scans with dye, known as contrast-enhanced imaging, help visualize blood flow and detect abnormalities in the heart. Understanding Heart Scans with Dye Heart scans utilizing dye, or contrast agents, play a pivotal role in modern cardiovascular diagnostics. These scans enhance the visibility of cardiac structures and blood vessels, allowing healthcare professionals to diagnose various.
Cardiac CT Scans: Essential for Identifying Heart Disease Early - Modern Heart and Vascular
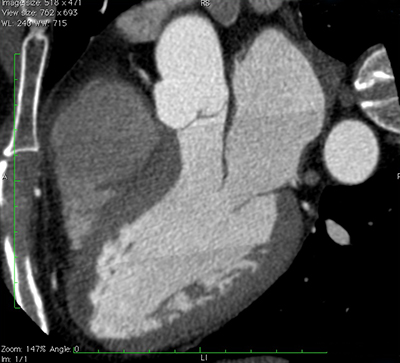
What is a cardiac CT scan? A cardiac CT scan is a non-invasive imaging test that uses X-ray technology to create detailed 3D images of the heart and its surrounding blood vessels. Doctors use CT scans to look for anomalies and diagnose heart conditions, such as coronary artery disease, blockages in the heart's blood vessels, and heart valve problems. They're also used as an alternative to.

A heart CT scan uses X. The contrast dye used in heart CT scans can contain iodine, which is flushed from the body through the kidneys. If you've previously had a negative reaction to contrast dye, you may be at a greater risk of an allergic or adverse reaction in the future.

2000.01.16 - Second Cardiac Computed Tomography (CT)
from WebMD about high-tech tests for heart disease, including CT scans, PET scans, total body CT scans, calcium-score screening, and coronary CT angiography. CT contrast (also known as contrast dye) is used to better visualize blood vessels and internal organs on a CT scan. How does it work? And, are there any side effects or risks? A heart CT scan involves potential risks related to radiation exposure and contrast dye.
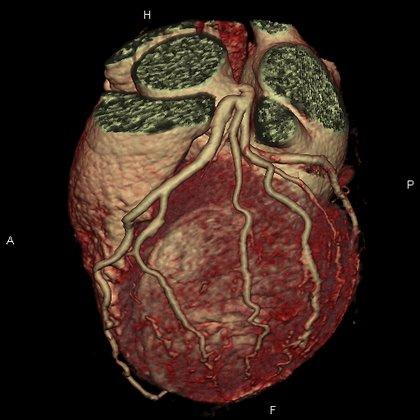
The procedure uses X-rays, meaning there is a small amount of radiation exposure. The American Heart Association explains Cardiac Computed Tomography, multidetector CT, or MDCT.