Are Tigers Colorblind
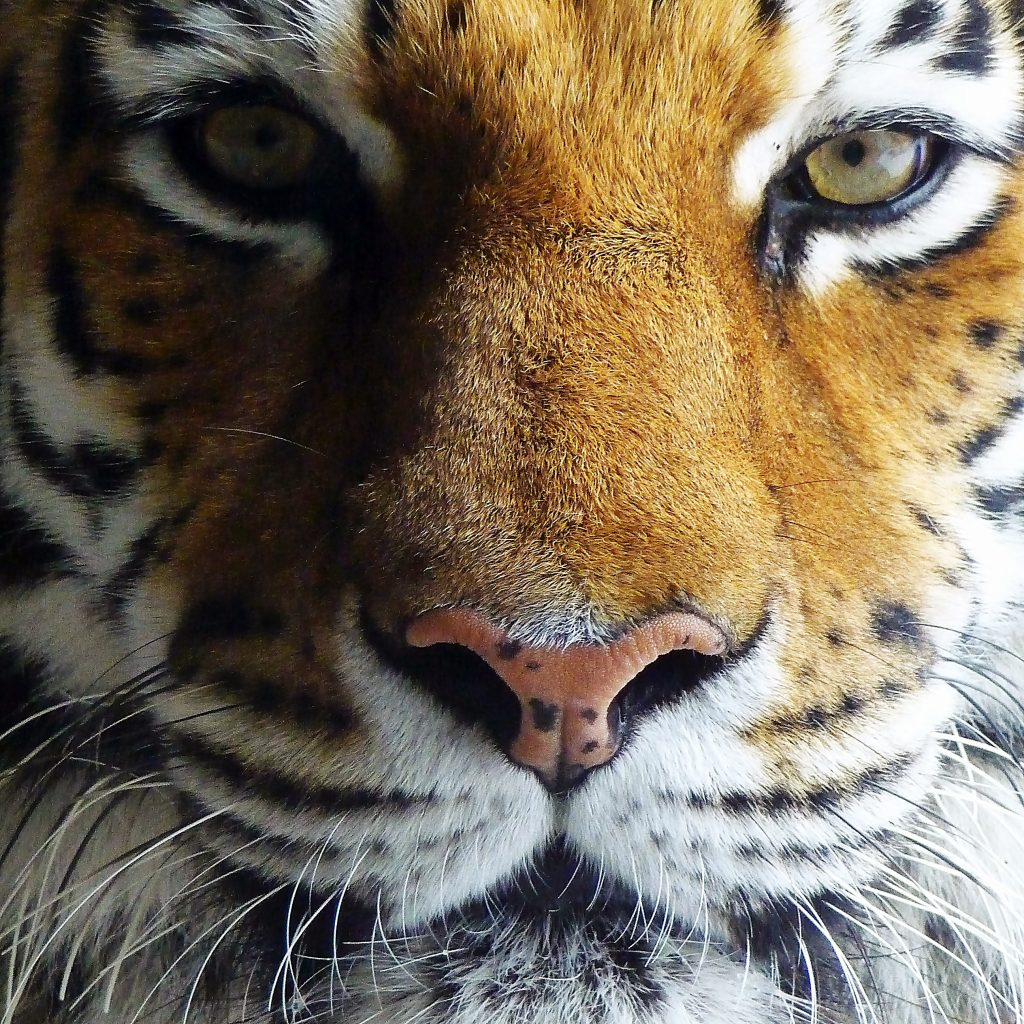
Tigers are known for their astonishing visionary power for hunting animals and prey. With the brightest eyesight, they can also perceive a wide range of colors. Some may anticipate tigers are color blind.

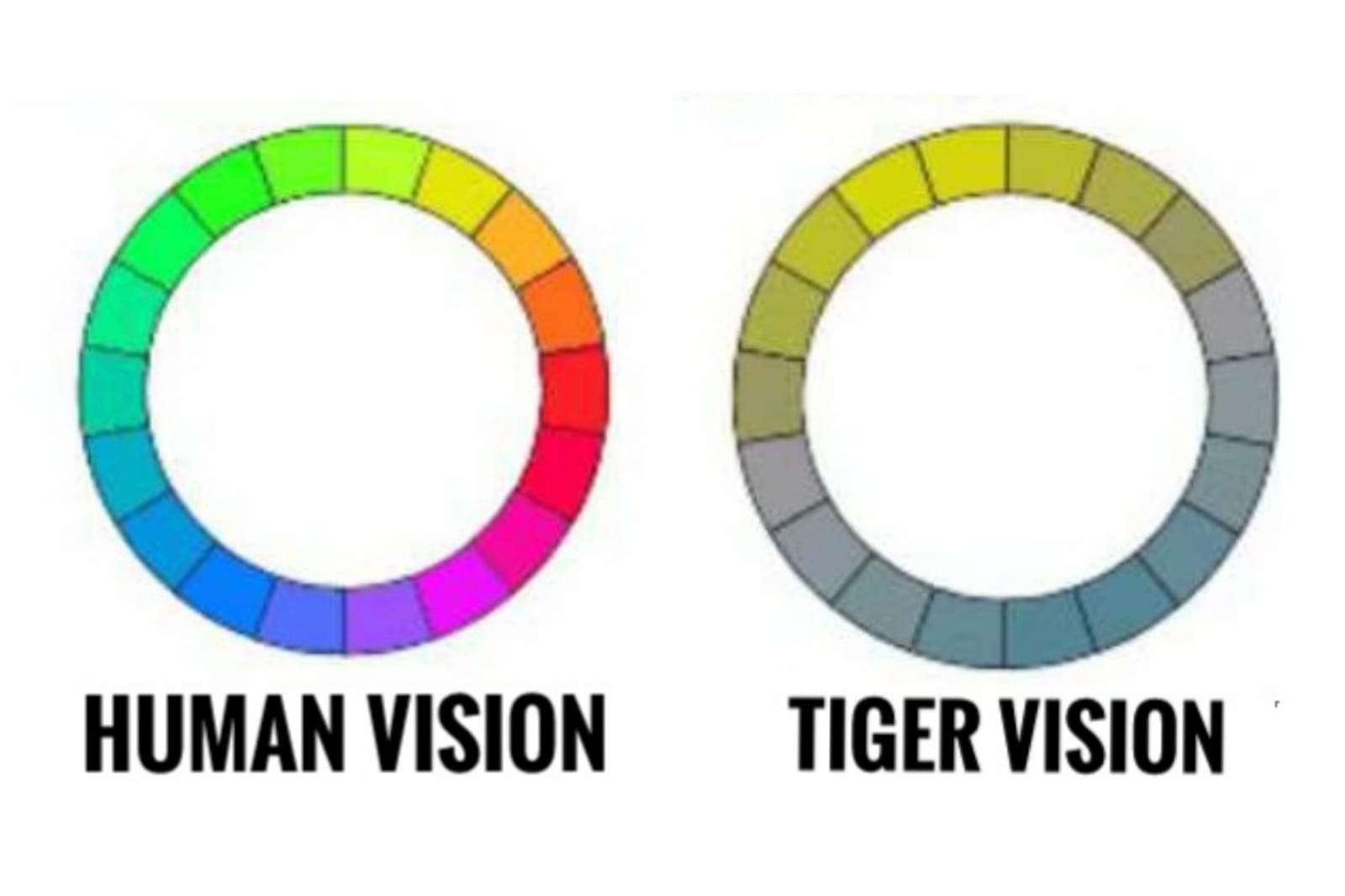
But in reality, tigers have cons as light receptive cells in their eyes that they use for their color. Tiger Vision and Color Perception Tigers are not entirely colorblind, but their vision differs significantly from that of humans. These big cats exhibit dichromatic vision, meaning their eyes possess two types of cone photoreceptor cells, unlike humans who have three.
post processing - How to set tint if one is colour blind? - Photography Stack Exchange
Are tigers colorblind or can they see in color like humans? One of the most majestic creatures on earth, tigers are known for their beautiful striped coats and fierce hunting abilities. But what about their vision? Are tigers colorblind? Many people wonder if these impressive animals see the world in the same way humans do, or if they perceive colors differently. To answer this question, we.

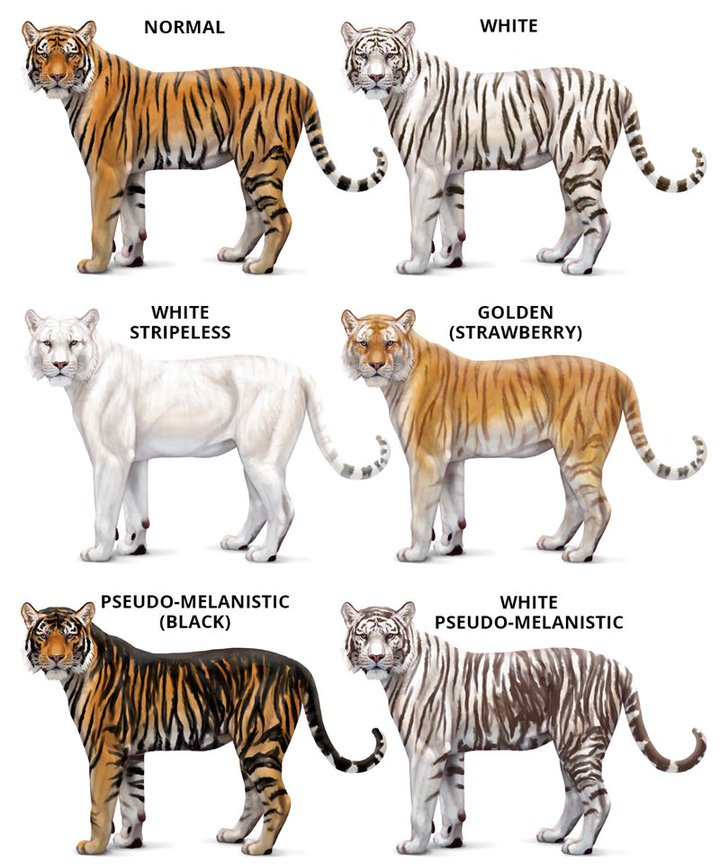
Researchers from the University of Bristol found that deer see the predator as green because they are colourblind. Instead of seeing tigers as humans do (right) they see a green blur instead (left). Tigers are the largest species of feline on the planet and one of the most fearsome predators in the world.

Can Tigers See Colors Or Are They Colorblind? | MedShun
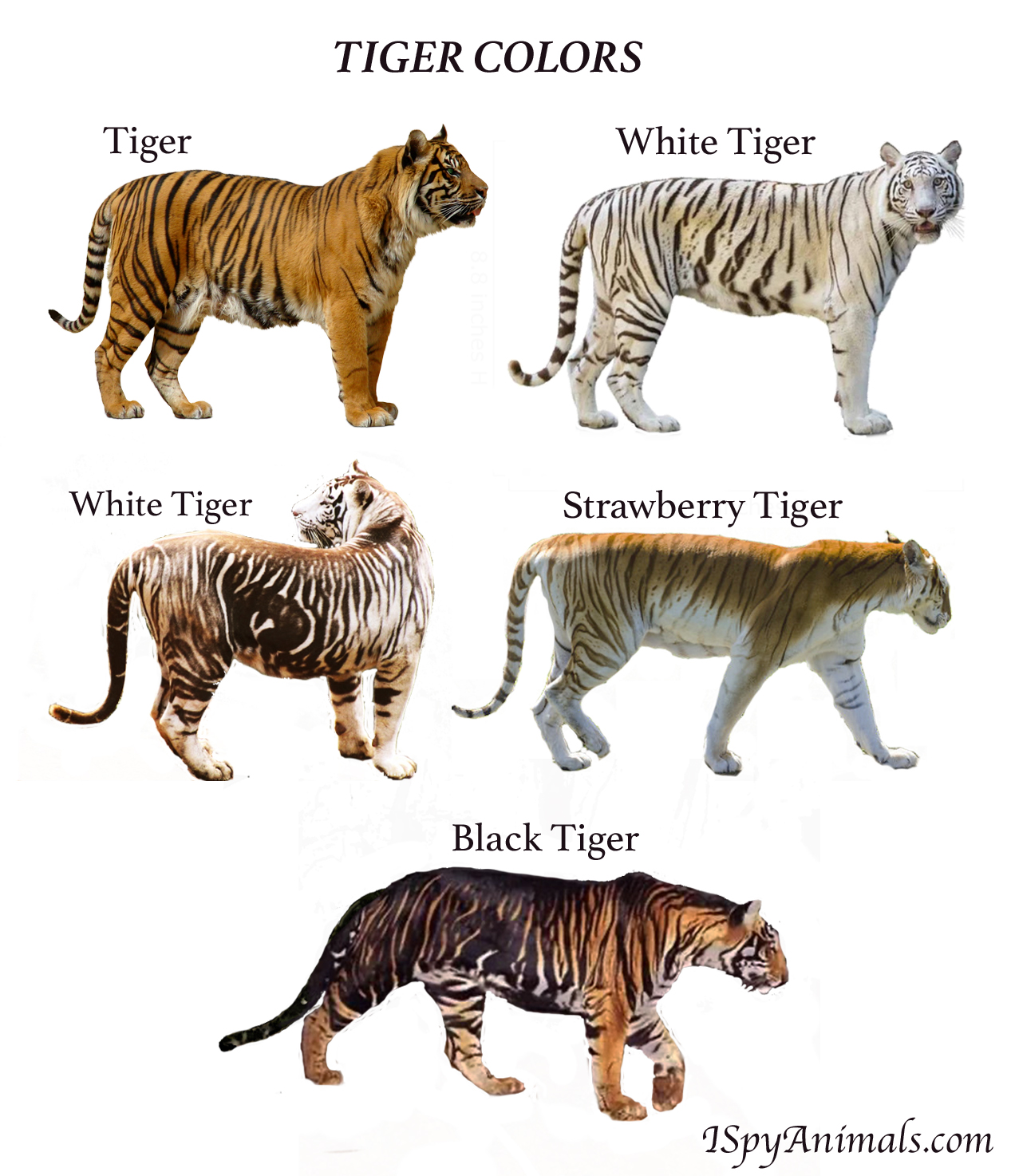
They are known for their very recognizable striped red-orange fur, a coloration that is. Tigers are dichromatic animals, which implies that only small (blue) and medium (green) wavelength colors may be perceived by the cones in their eyes. Only the color red renders them colorblind.

Humans, on the other hand, are trichromatic, which means that the receptors in our eyes are reactive to the colors blue, green, and red. Are Tigers Color Blind? Tigers are renowned for their exceptional hunting skills, which rely heavily on their incredible eyesight. Many wonder if these magnificent predators have the ability to perceive a wide range of colors, or if they are, in fact, color blind.

Are Tigers Colorblind? ???? Can They See Green? - WildLifeFAQ
This article explores the fascinating truth behind tigers' vision and explains why they are classified as dichromats. Are tigers and lions color-blind? Lions are not colorblind. Like humans, they have color vision and are able to see a range of colors.

However, their ability to see in low light is particularly well-developed, which is an advantage for their nocturnal hunting behavior. Why are most animals color-blind while humans are not? Tigers generally appear orange to humans because most of us are trichromats, however, to deer and boars, among the tiger's common prey, the orange color of a tiger appears green to them because ungulates are dichromats. A tiger's orange and black colors serve as camouflage as it stalks hoofed prey.

The mammals they prey on, such as deer and boar, also have dichromatic vision. This means they see the tigers' orange coloring as shades of green, making it harder to detect the big cats and allowing tigers to better camouflage themselves in the forest. This gives tigers a greater chance of successfully securing a meal.






