Heart Color Organ
The human heart is an incredibly complex and vital organ that plays a crucial role in circulating blood throughout the body. But have you ever wondered - what color is the human heart? Understanding the color and appearance of the heart can provide insight into its anatomy and function. In this article, we will explore the reasons behind the characteristic color of the human heart.

What color is the human heart? This question often brings to mind the bright red, stylized symbol seen everywhere from Valentine's Day cards to health campaigns. That widely recognized emblem, however, diverges significantly from the organ's biological reality. The actual color of a living human heart might surprise many, prompting a deeper understanding of this vital organ beyond its.

Humans anatomy and internal organs concept with a color drawing of a medical model of the human ...
Heart, organ that serves as a pump to circulate the blood. It may be as simple as a straight tube, as in spiders and annelid worms, or as complex as the four-chambered double pump that is the center of the circulatory system in humans, other mammals, and birds. about the heart in this article.
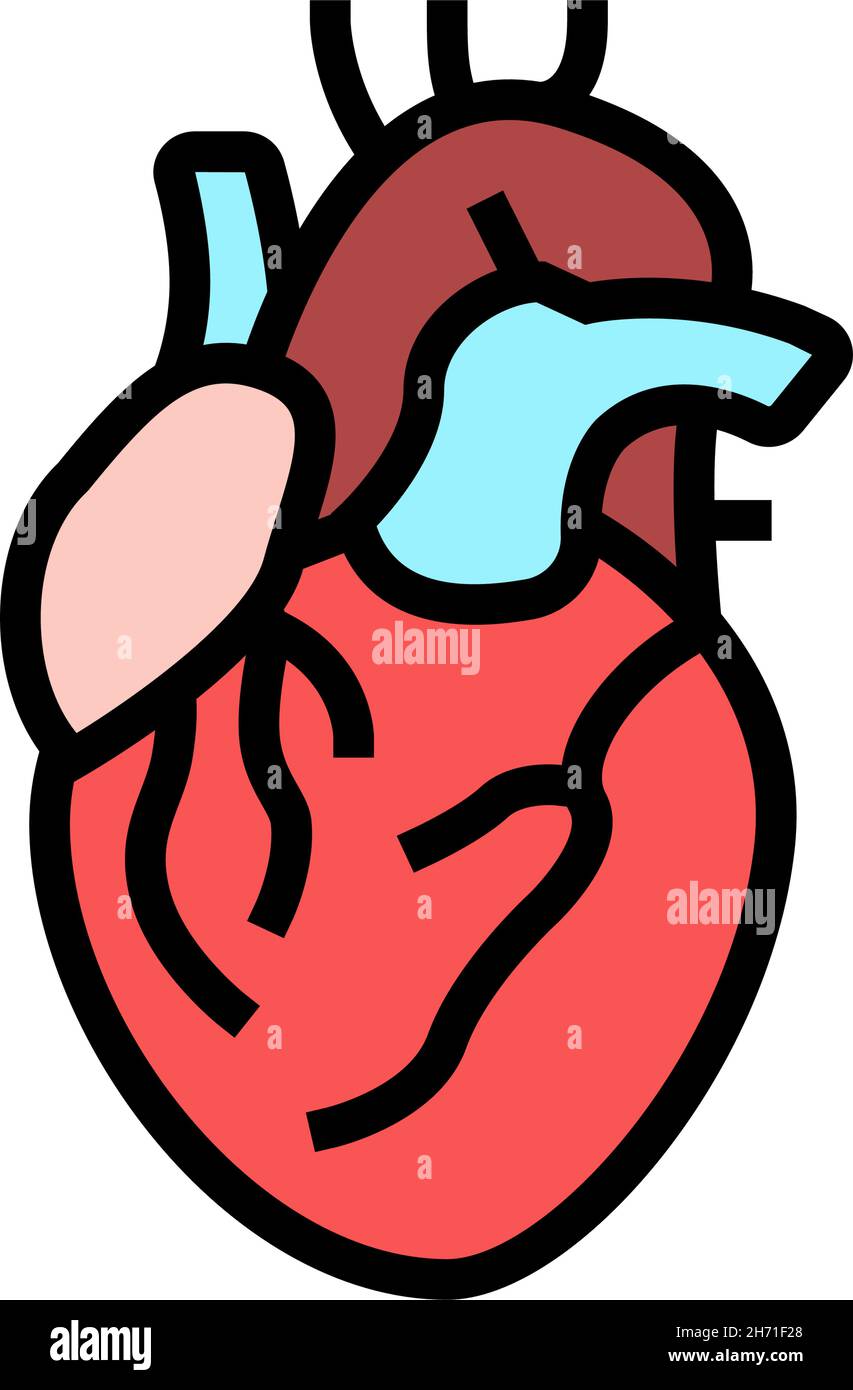
The human heart is a complex organ that serves as the center of the cardiovascular system. It is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body via a vast network of blood vessels. But what happens when you remove the blood from this vital organ? What color does the heart become without the red oxygenated blood flowing through it? This clear and comprehensive anatomical illustration presents the fundamental structures of the human heart with precise labeling and color-coding.

17+ Heart Diagram Templates - Sample, Example, Format Download
The diagram effectively distinguishes between oxygenated (red) and deoxygenated (blue) blood pathways, while showcasing the heart's chambers, valves, and major vessels in an easy. The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. Without blood, the heart appears pale or light pink in color.
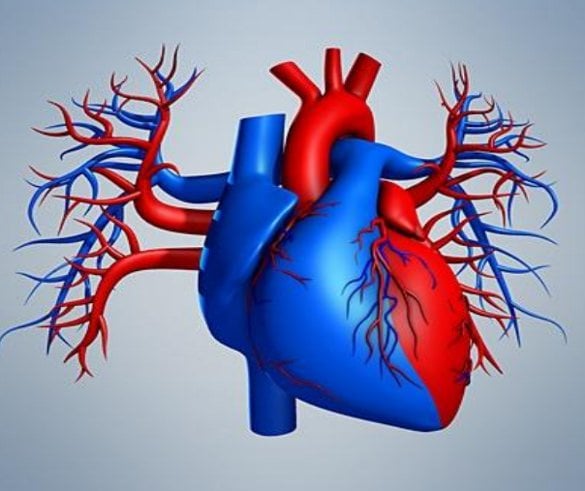
This is because the color of the heart is mainly attributed to the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood present within its chambers and vessels. Oxygenated blood appears bright red due to its interaction with oxygen, while deoxygenated blood is darker in color. A heart diagram colored red and blue is a visual representation of the human heart, portraying the flow of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood within the organ.

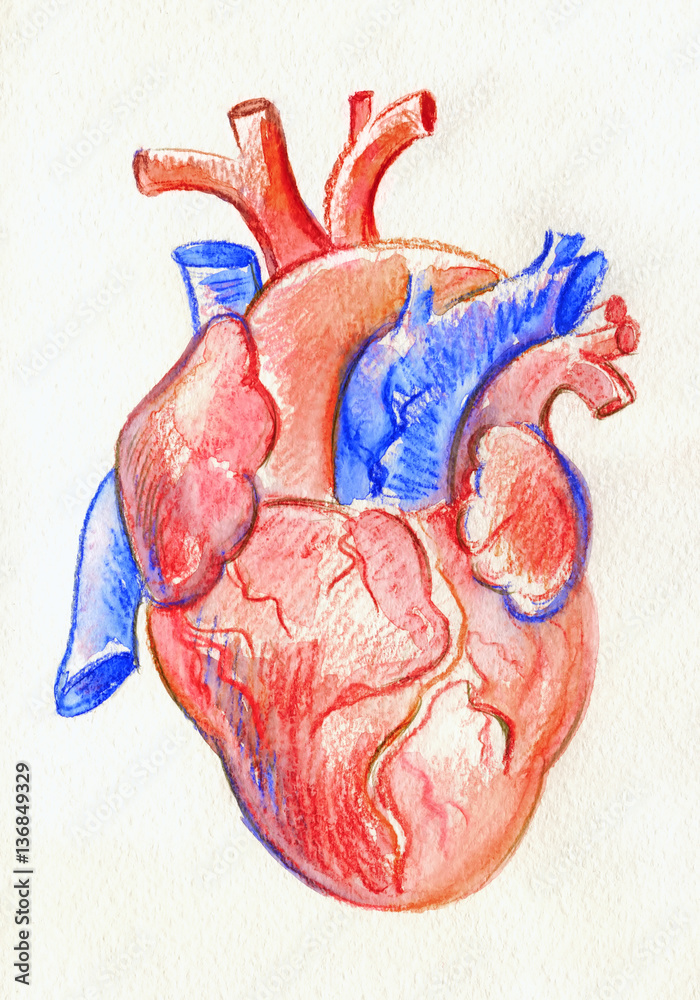
Hand drawing sketch anatomical heart. Colored watercolor pencil. Stock Illustration | Adobe Stock
The red color signifies oxygenated blood, while the blue color represents deoxygenated blood. The real human heart is generally a deep red, reddish-brown color. This is due to the muscle tissue, blood vessels, and connective tissues that often form the organ's visible surface.
The color of a healthy heart may range from a bright, dark red to a dark brown, depending on the age, sex, and race of the individual. Human organs obviously have color, that is, the liver is brown, the heart is red, bones are white, and so on. They are crucial for protection, metabolism, sexual behavior, and communication.

The Heart Without Blood When blood is drained from the heart, the organ takes on a different color and appearance: The epicardium appears pale gray, yellowish, or tan. The myocardium is a dark brownish-gray color. The endocardium may retain a faint pinkish hue.

Without blood, the true color of the heart muscle and tissues is revealed.