Pond Habitat
Learn about the diverse wildlife that depends on ponds, from aquatic insects and amphibians to birds and bats. Discover the features, history and importance of this freshwater habitat and how to protect and create more ponds. Learn about the fascinating features and functions of pond habitats, from their size and salinity to their microbial communities and ecological importance.

Discover how ponds are vital for many plants and animals, but also face many challenges from human activities and climate change. Learn about the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of pond habitats, and how they support diverse life forms and ecosystem services. Explore the zones, interactions, and seasonal changes of these miniature ecosystems, and how to manage them for optimal balance.

Design and Construction of a Thriving Pond Habitat | Pond habitat, Pond landscaping, Habitat garden
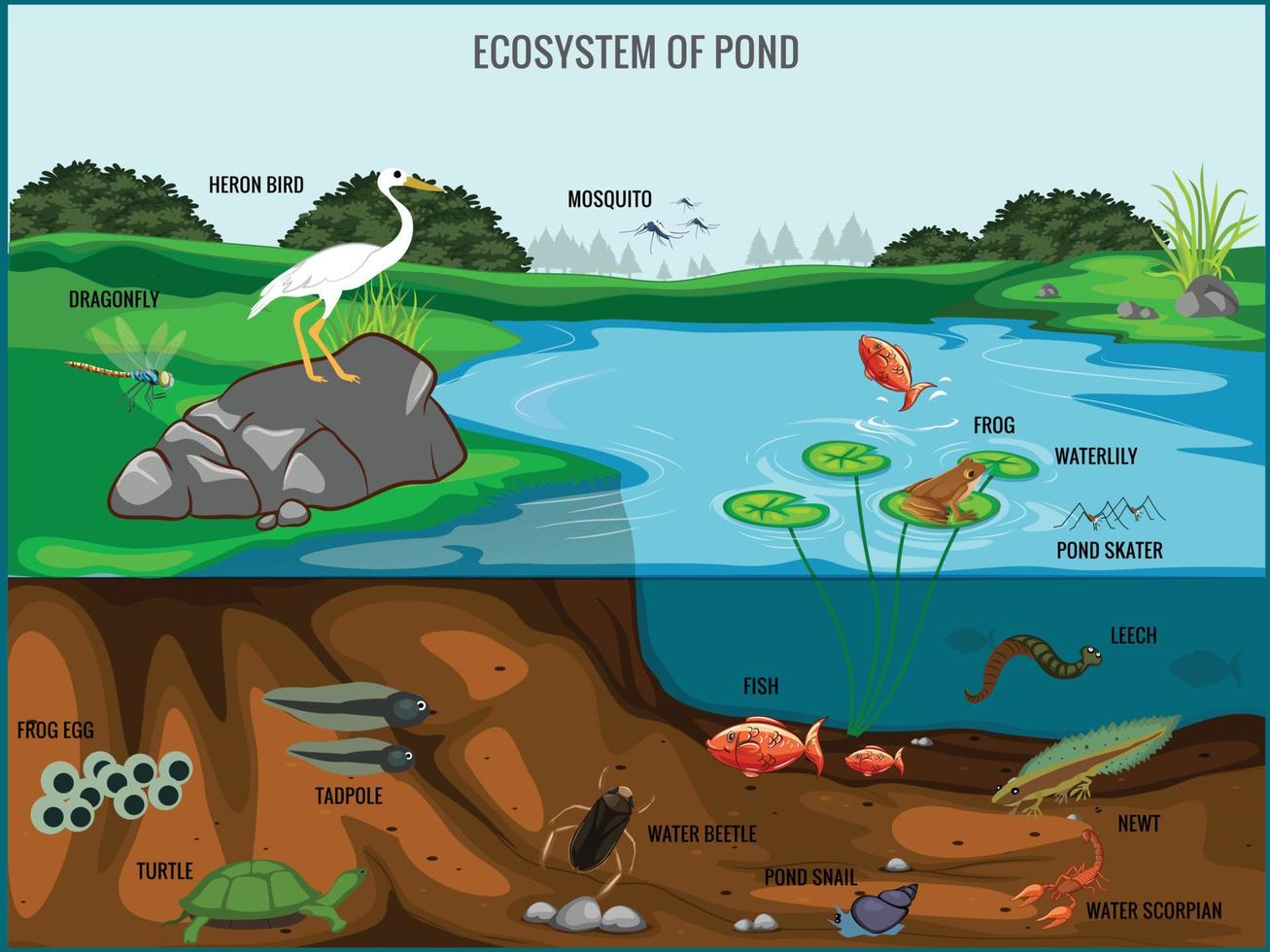
Learn about the different organisms that live in ponds, from algae and plants to fish and mammals. Find out how ponds are ecosystems and how they support many types of living things. Ponds have three main characteristics: stagnant water, either natural or artificial boundaries surrounding it.

The pond ecosystem exhibits three habitats at different levels: decomposers and scavengers live in pond bottoms, where fish dominate and prey in mid-water, and on the pond surface, where animals breathe through their gills, skin, or lungs. Learn about ponds, small waterbodies that support two-thirds of all freshwater species and help tackle environmental issues. Find out how to create, protect and manage ponds, and explore our projects and resources.

Ponds - Freshwater Habitats Trust
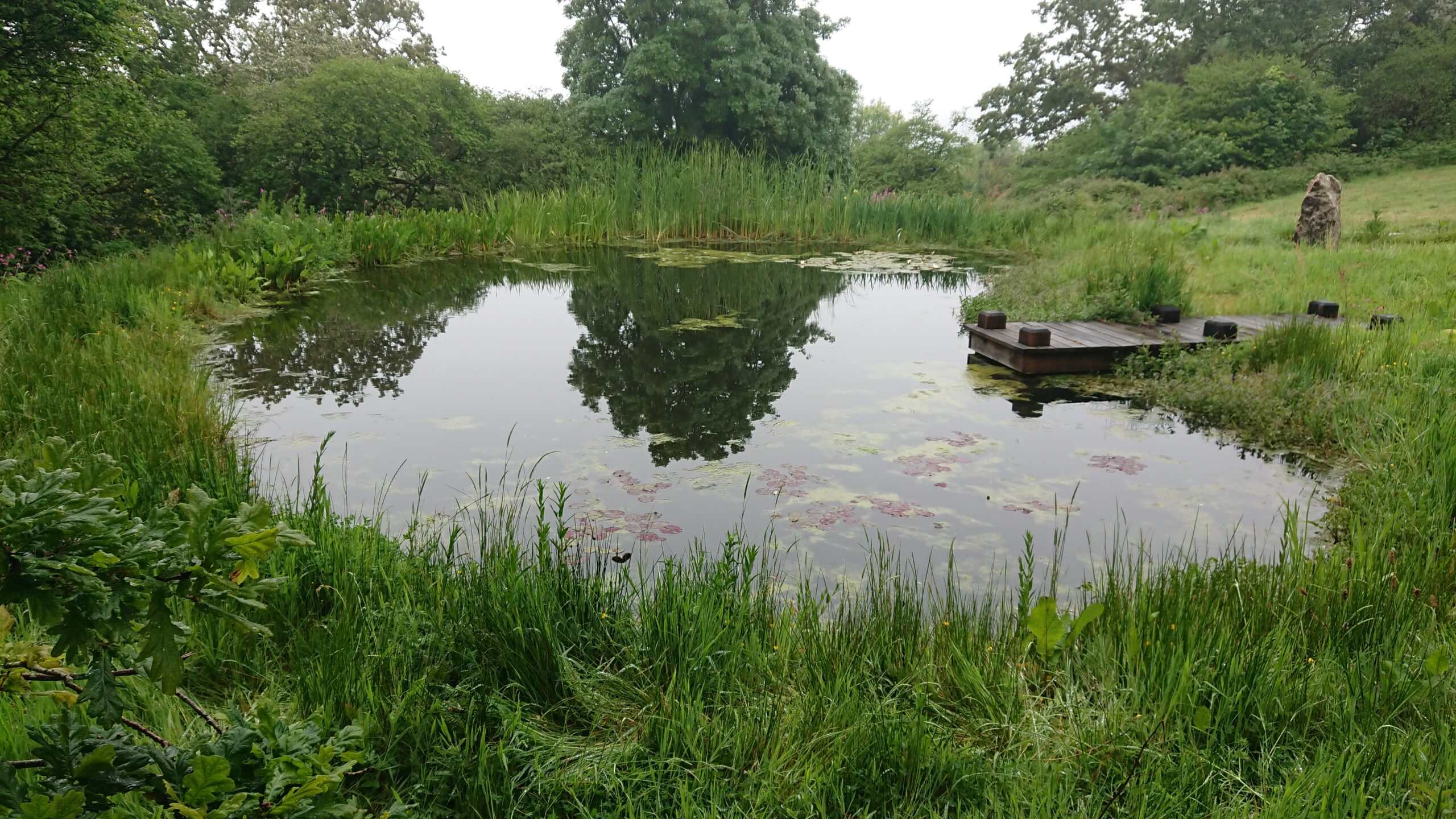
A pond ecosystem represents a natural system where living organisms interact with their non-living environment. This community includes diverse plant, animal, and microscopic life within a defined body of water. All the plants and animals in a pond form its habitat.
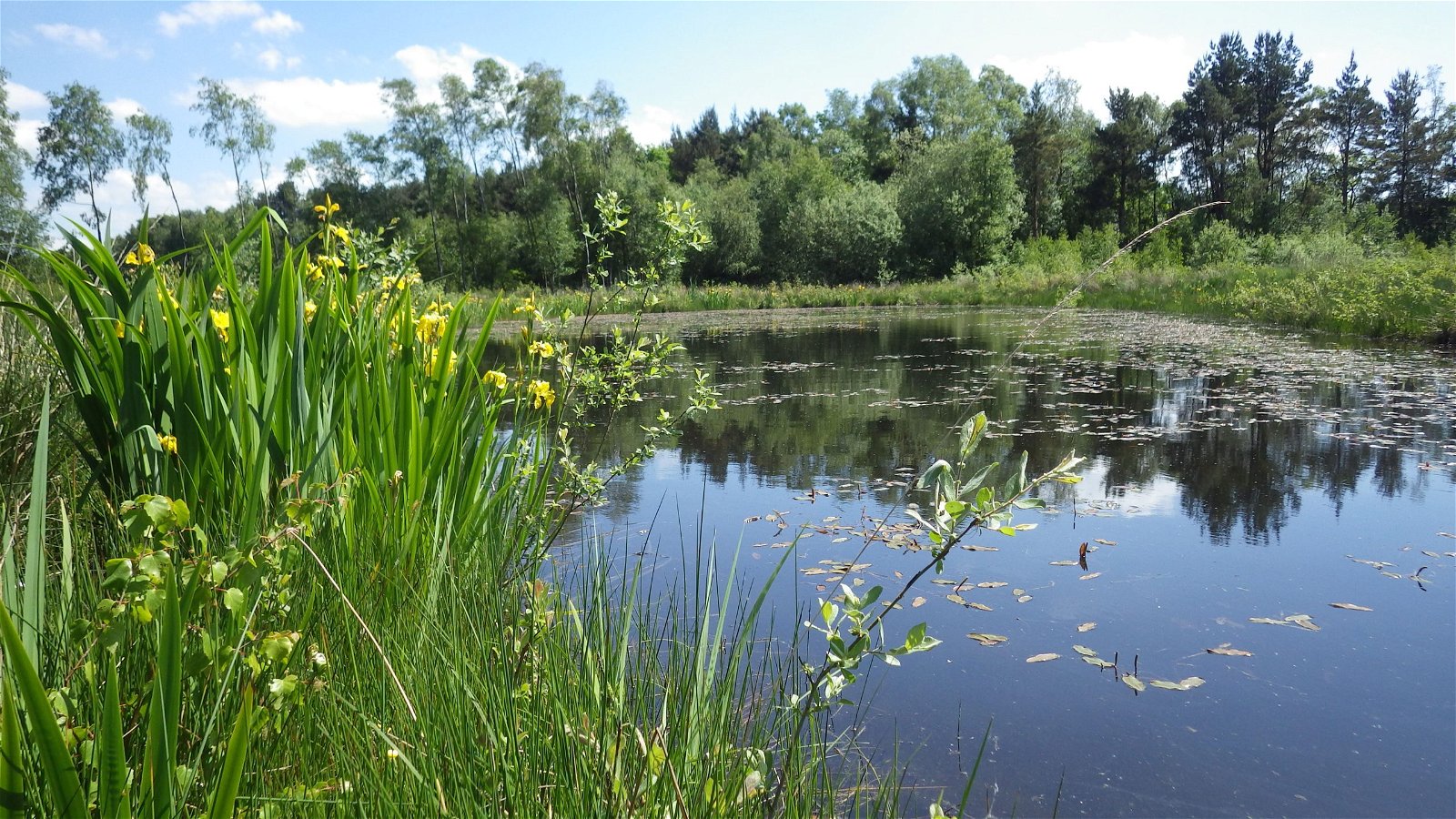

The area around a pond includes water-loving plants and shelter for the birds and wildlife. In a healthy pond's waters, plants, fish and other animals thrive in their aquatic ecosystem. Learn about the different types of pond ecosystems, their characteristics, and the food chain that supports them.

341 best Little Raindrop - Pond Habitat images on Pinterest | Forests, Pond habitat and Nature
Find out how ponds are formed, what plants and animals live in them, and what benefits they provide. Pond biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms that exist within pond ecosystems, encompassing plants, animals, and microorganisms. This diversity is critical for maintaining ecological balance and health.

The dynamic interactions between these organisms contribute to the resilience of the ecosystem. A rich biodiversity promotes water quality, provides habitats, and supports various.