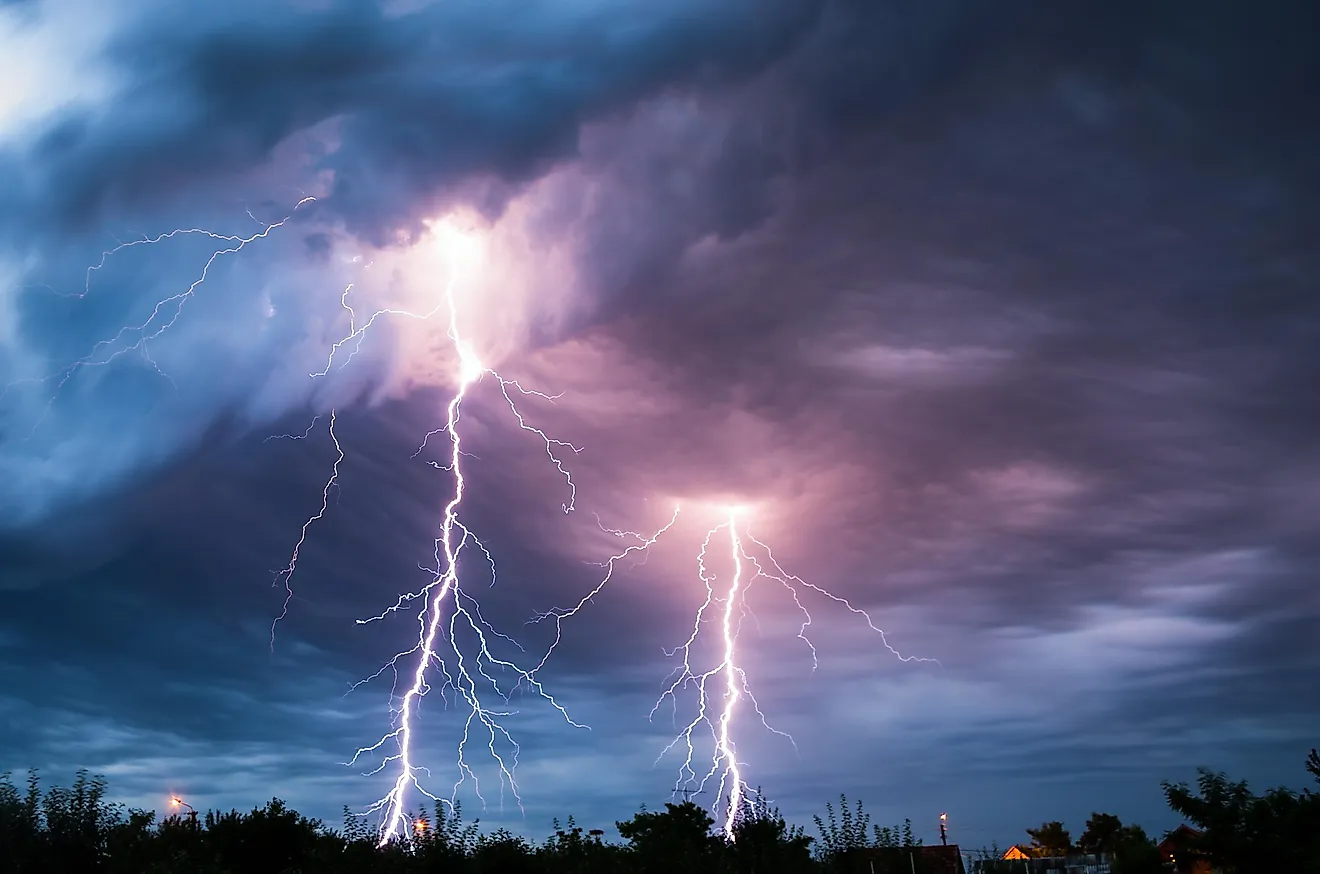
Color May Vary Due To Lightning
We use something like this: "We try to make sure that the photos of our items accurately reflect the actual color of the item in person. However, due to the differences in monitor and device settings (brightness, contrast, saturation, etc) there may be a slight difference in color between what is shown on the site and the final product. Lightning, a powerful natural phenomenon, often captivates observers with its dramatic flashes across the sky.

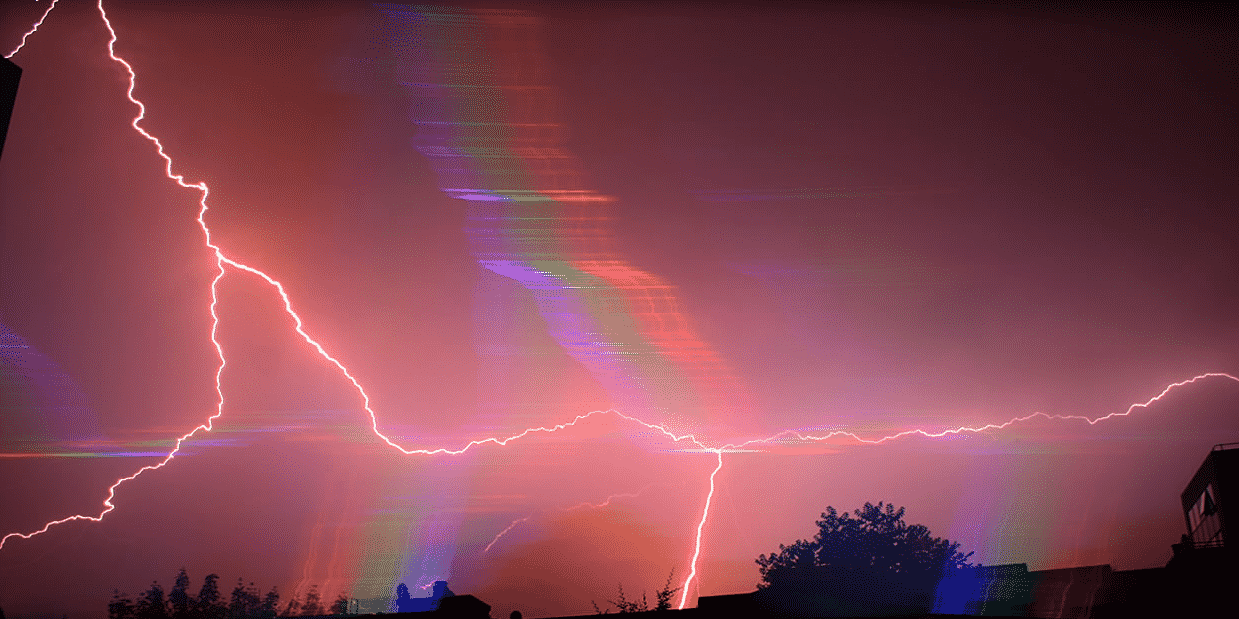
While commonly depicted in popular media as stark white or bright yellow, the actual color of a lightning bolt can vary significantly. This range of hues sparks curiosity about what causes these visual differences in such a fleeting event. Rare Genetic Phenomenon) Q: Can lightning be different colors at different altitudes? A: Yes, the color of lightning can vary depending on the altitude at which it occurs.
VINTAGE SOFT SKORT COLOR MAY VARY DUE TO LIGHTNING, Women's Fashion, Bottoms, Skirts on Carousell
For example, lightning that occurs at high altitudes may appear more blue-violet, while lightning that occurs at lower altitudes may appear more yellow or orange. Most lightning occurs within clouds due to the attraction between positive and negative charges. If the Earth's surface becomes highly charged, the interaction between negative charges at the cloud's base and positive charges on the Earth's surface can cause cloud-to-ground lightning.

If these positive charges pass through objects like buildings, trees, or people, lightning may strike them. This unique coloration is primarily due to the presence of nitrogen in the atmosphere, which emits blue light when excited by electrical discharge. The green color of lightning is caused by the excitation of oxygen atoms, which is an extremely rare occurrence.
Why Isn’t All Lightning White? The Science Behind Nature’s Colorful Spark - Weather Geeks
The atmospheric conditions impacting blue lightning are essential to its formation. One of the underlying factors that gives lightning its color is temperature. When anything gets really hot, it will glow in a range of colors from red to blue.

Effects of different lightning colors on surrounding objects While the immediate danger from lightning lies mostly in its intense electrical current, the color of lightning may have varying effects on surrounding objects. For example, white lightning may cause more severe burns due to its higher temperature, while blue lightning may indicate an increased presence of impurities, which could. When lightning strikes, different particles will scatter this light and cause the strike to appear as blue, pink, purple, white or even a brown.

The colours of lightning – Waterfront Media Halifax
Explore how different lighting conditions dramatically affect color perception, from natural daylight variations to artificial light sources. Understand key concepts like color temperature, metamerism, and color constancy, and their practical implications in design, photography, and everyday life. Discover how lightning gets its dazzling colors-and what each hue reveals about atmospheric conditions, temperature, and storm intensity.


.jpg)





