Horse Hoof Colors
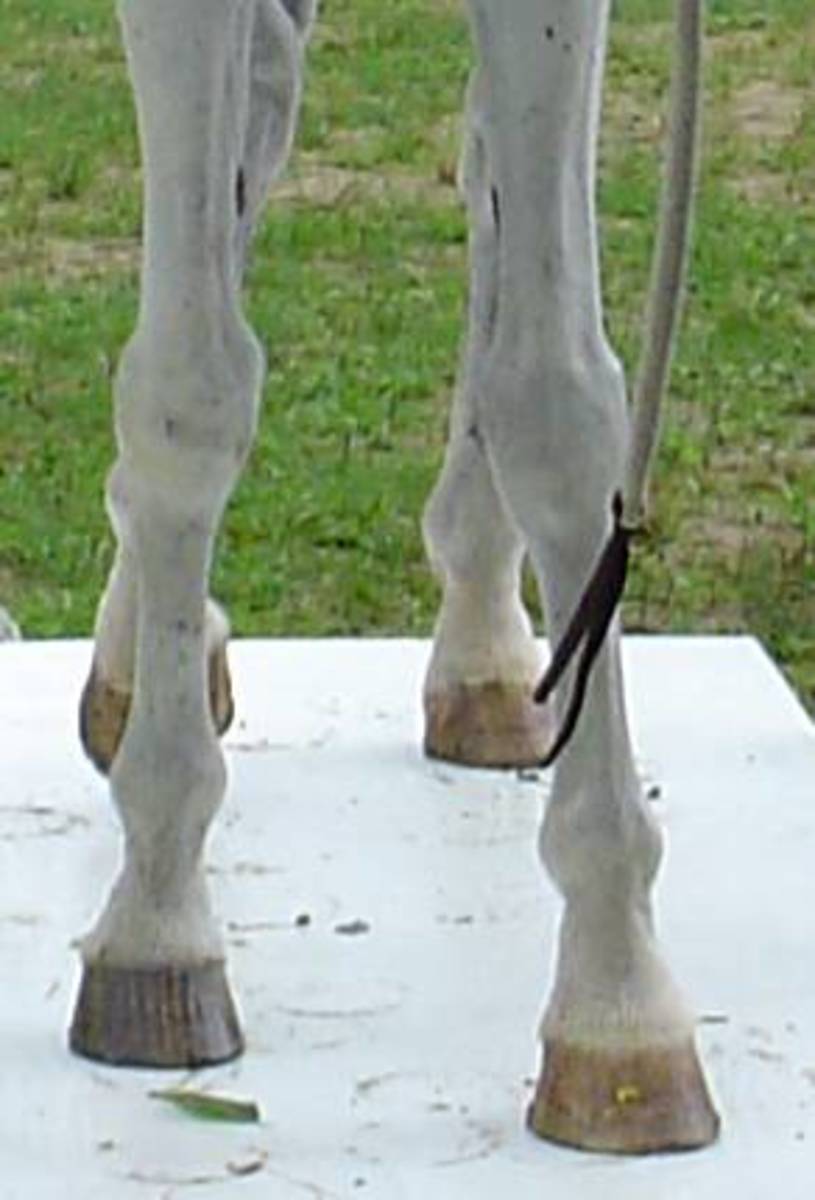
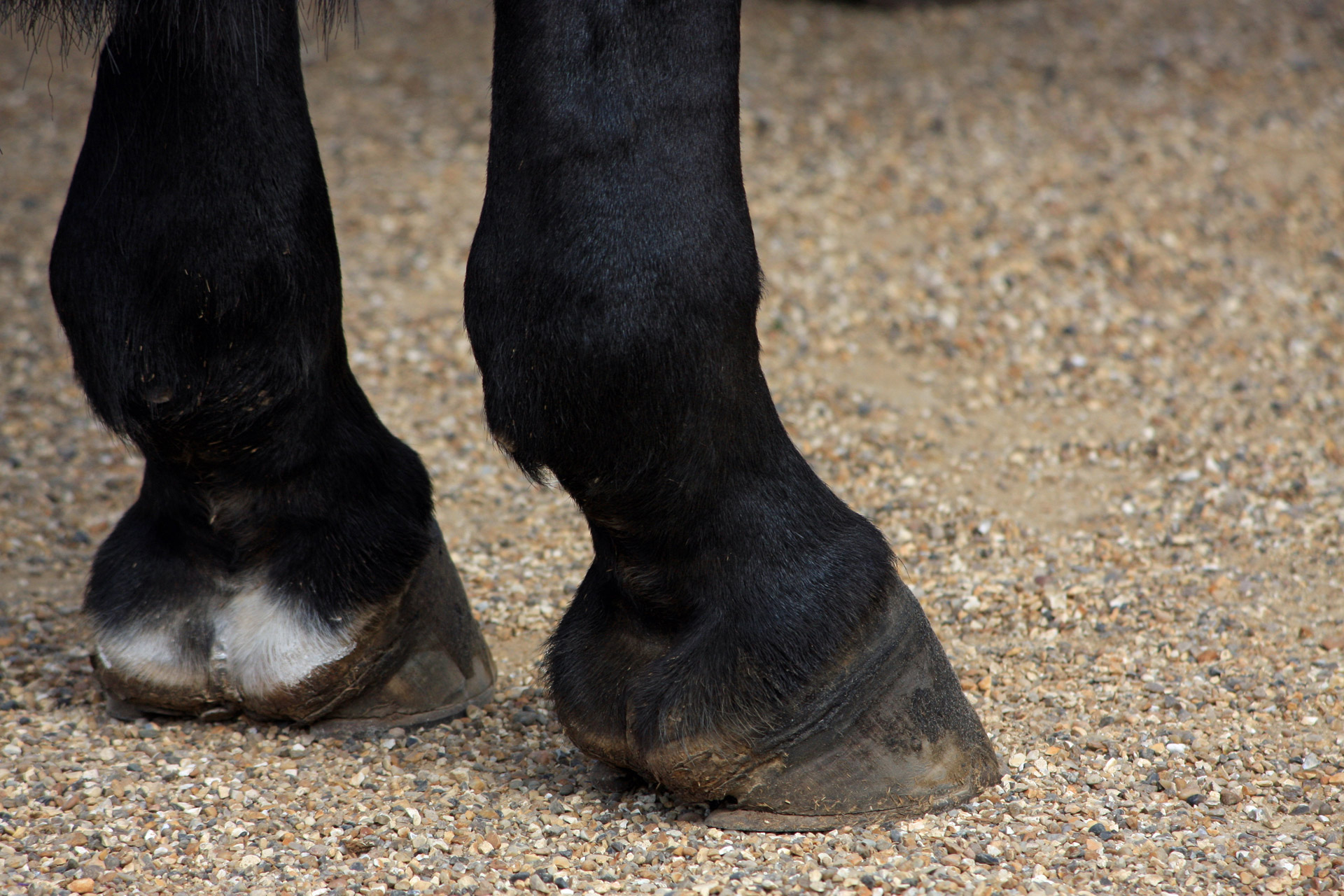
Horses do not have much variety in foot color, unless they happen to be owned by little girls who like to embellish them with polishes, then they may even glitter. But, the natural colors of the horse's hooves are basic white, black or brown, and combinations of the two called striped or parti-colored hooves. Not saddled with fashion mores of humans, they can wear mix.

Equine coat color Three horses with different coat colors Horses exhibit a diverse array of coat colors and distinctive markings. A specialized vocabulary has evolved to describe them. While most horses remain the same coat color throughout life, some undergo gradual color changes as they age.

Basic horse hoof tutorial by pookyhorse on DeviantArt
Body color white; skin is pink; eyes are usually dark; small black spots may be found in the skin, but usually are not accompanied by colored hair. Some white horses may be variegated, meaning they have patches of colored hair, usually intermixed with white. Learn all the names and types of horse coat colours, shades, patterns & markings in our simple guide with pictures.

Chestnut versus sorrel? Paint or pinto? And how do you breed for color? Use our guidelines to about coat color and equine color genetics. Eye, hoof and skin colours in horses are determined by genetics. Each colour and marking guide states any specific affects they have on eye or skin colour.

Hoof | Description, Anatomy, Function, Examples, & Facts | Britannica
Eye colours should be natural, according to their base coat, meaning no purple, bright red or neon/rainbow colours. Blind eyes should have pale, clouded silvery or blue look. Pupils should be distinctly lighter than the iris.

Tobiano. Paint or pinto? Chestnut or sorrel? How can you breed for a specific color? Use our essential guide as a refresher course on the rainbow of equine coat colors and to about the fascinating genetics behind color. Key Takeaways: Healthy horse hooves should be strong, intact, smooth, shiny, and have a uniform color and texture.
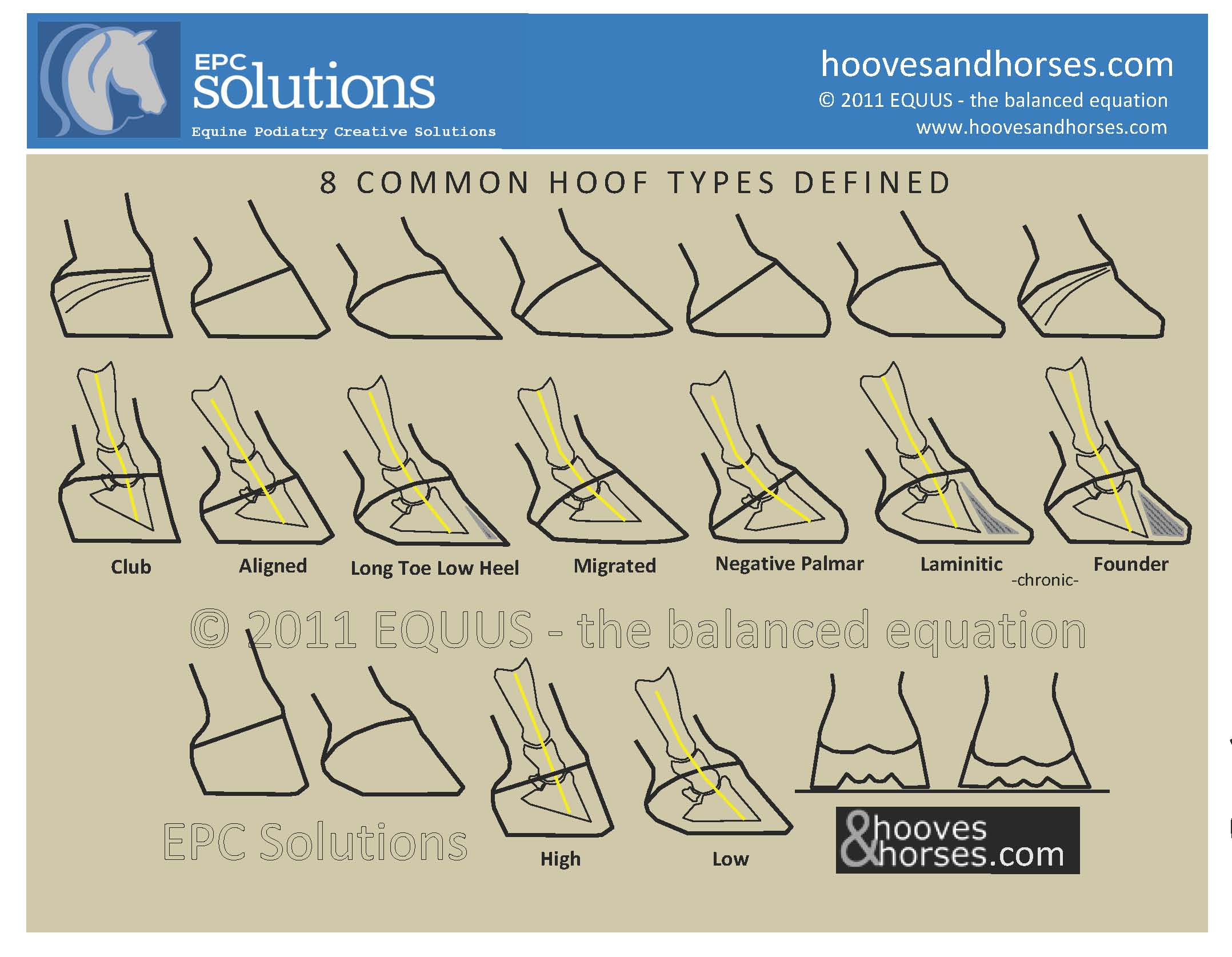
The main types of horse hoof shapes. Equine Care, Hoof Care, Types Of Horses, Horses And Dogs ...
Factors such as nutrition, exercise, environment, genetics, and proper hoof care play a crucial role in maintaining hoof health. Signs of unhealthy horse hooves include cracks, chips, discoloration, uneven growth, thrush, and laminitis. These two colours commonly interact to produce another base color, a dark brown known as bay.

The variation we see in horse colors is caused by additional genes, which modify and enhance the coat color. If you've ever wondered how to identify horse colors, here's our helpful guide to the many different variations in the equine world. The color of the hoof wall doesn't affect its quality.
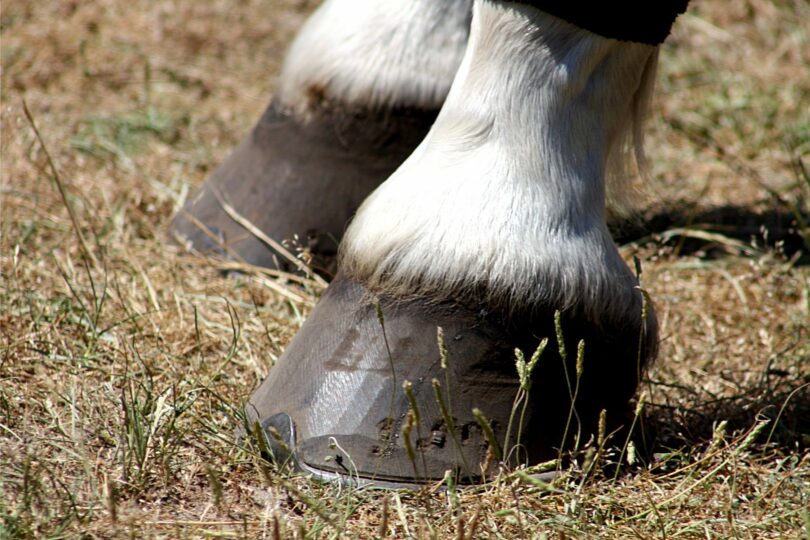

Genetics plays a role, as does nutrition. Dr. Robert Agne of Rood & Riddle Equine Hospital in Lexington, Kentucky, says, "Nutritional deficiencies will be reflected in the hoof wall quality and growth rates.".






