Basic Dyes Examples
The basic dyestuff will combine with direct dyes or sulphur dyes or some acid dyestuffs. So they cannot be used together in the same bath. But basic dyestuffs are used in after treating cotton or other materials dyed with direct colors.

Here the direct dyestuff acts as mordant. What are the applications of basic dyes? Basic dyes have a complete spectrum and extremely colorful colors. With high color yield, it was widely used in the coloring of cotton, wool, silk, paper, bamboo, leather, feathers and grass products at first.

What is a basic dye | uses, working process| pulp paper mill
Later it was used in the dyeing of acetate fiber and acrylic fiber. Basic dyes are widely utilized in the dyeing process of various types of fibers, including wool, silk, and acrylic. The dye bath is usually mixed with acetic acid to make it easier for the fiber to absorb the color.

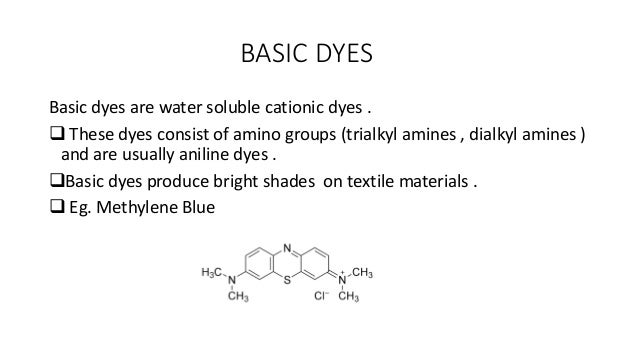
The cation in a basic dye is the colored component of the dye molecule that binds to anionic groups of nucleic acids or acidic mucopolysaccharides. Basic dyes stain basophilic structures such as nuclei, ribosomes and GAGs. Examples of basic dyes are methylene blue, toluidine blue, thionine, and crystal violet.

Characteristics and Manufacturing of Basic Dye - Textile Blog
Synonym (s). Discover the basics of dyes, their types, uses, and applications in various industries. A deep dive into the world of basic dyes.

Basic dyes are highly preferred when coloring synthetic, cationic materials, such as acrylics, for example. Since other types of dyes such as disperse dyes typically yield pale colors when used with these types of synthetic materials, this is when basic dyes perform the best. Basic dyes, also known as cationic dyes, are a class of synthetic dyes that are soluble in water and exhibit a strong affinity for materials with anionic (negatively charged) sites.
2 (1)
Known for their brilliant shades and high tinctorial strength, basic dyes are widely used in the dyeing of acrylic fibers, modified polyester, leather, paper, and plastics. Basic dyes bind to negatively charged cell structures like DNA and RNA. Common examples of basic dyes include crystal violet, safranin, and methylene blue.
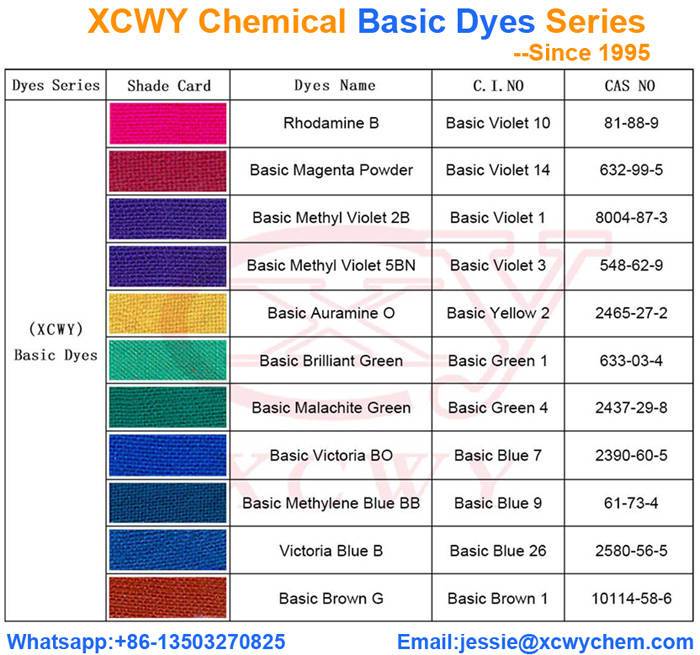
Basic dyes are often used in simple staining techniques to make cells more visible under a microscope. The positive charge of basic dyes allows them to easily penetrate bacterial cell walls. Few examples of basic dyes are the following, methylene blue, crystal violet, basic fuchsin safranin, etc.

An example of a basic dye that has amino groups as their auxochrome is pararosanilin or basic red 9 (according to the strict color index system of classification) example of alkylamino groups is methylene blue or basic blue 9. Basic dyes, also known as cationic dyes, are a type of synthetic dye that is widely used in various industries. They are called "basic" because they have a positive charge.

This positive charge allows them to easily bind to negatively charged materials. Let's dive into the characteristics, examples, and importance of basic dyes.





