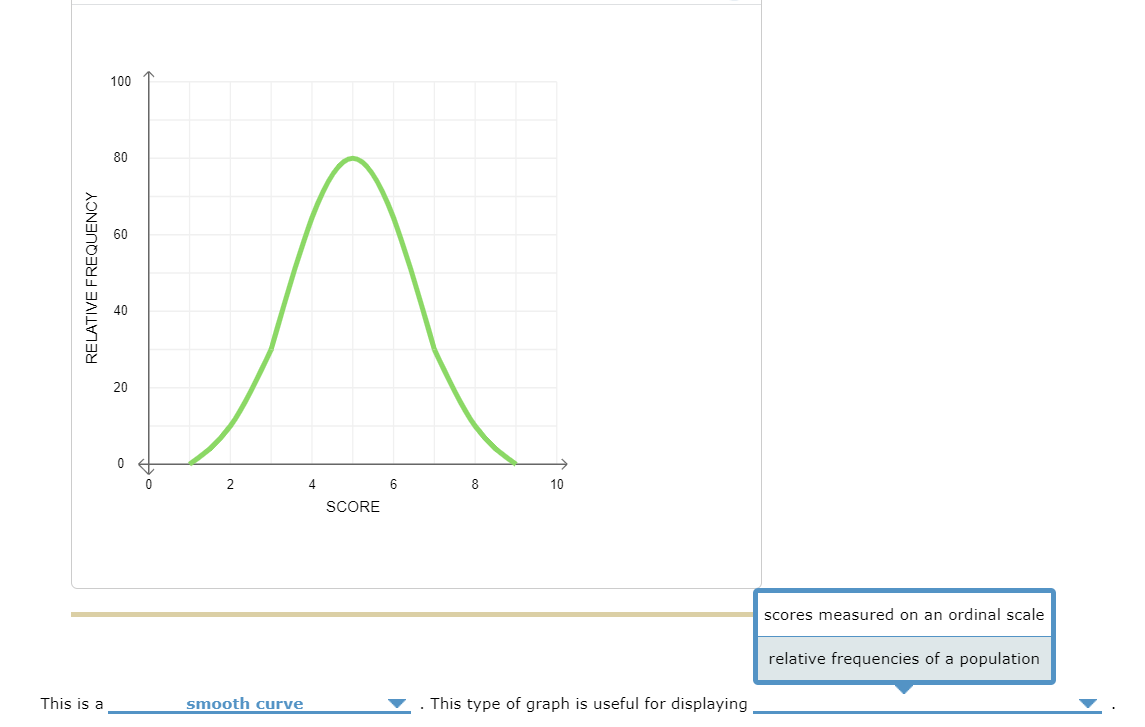
Smooth Frequency Graph
If you are plotting time series graph and if you have used mtplotlib for drawing graphs then use median method to smooth-en the graph smotDeriv = timeseries.rolling(window=20, min_periods=5, center=True).median(). The main difference between a frequency polygon and a frequency curve is that the frequency polygon is a discrete graph, whereas the frequency curve is a continuous graph. While a frequency curve is a smooth curve drawn through a histogram's midpoints, a frequency polygon is a line graph created by connecting midpoints of intervals in a.

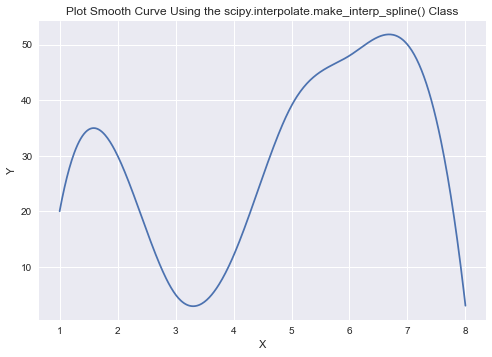
This video contains how to draw a smoothed polygon curve from the frequency distribution table. #Statistics #Polygon #FrequencyDistributionTable #LineGraph. Output: Example 1: Smooth Spline Curve with PyPlot: We draw a smooth spline curve using scipy.interpolate.make_interp_spline (), which fits a smooth curve through the given data points.

Statistics 8, Smoothed frequency Curve - YouTube
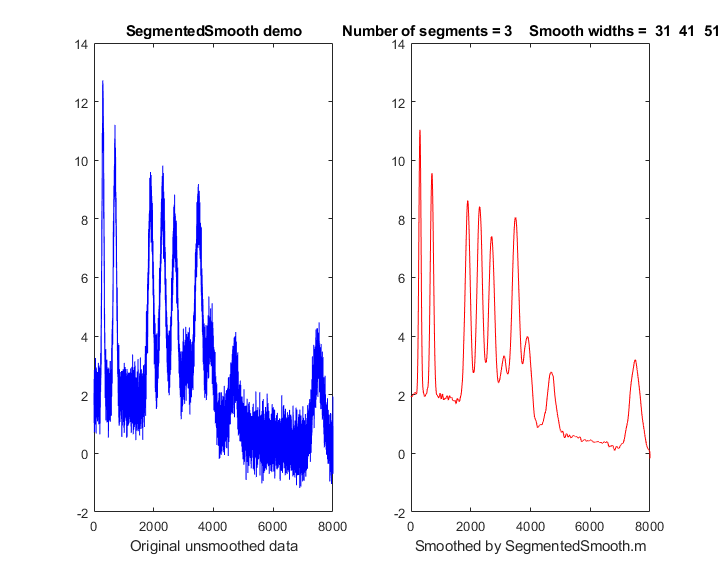
To make the curve appear smooth, we generate many closely spaced x-values using np.linspace (), which creates evenly spaced numbers in a range. The bottom three graphs above show the same data after smoothing (averaging 10 values on each side, and using a second order smoothing polynomial). When you look at these graphs, you see trends.
The first one tends to trend down. The second one seems to oscillate in a regular way. The third graph tends to increase.
Create An Equation And Sketch A Graph That Is Smooth Curve - Tessshebaylo
Need to learn how to smooth data in Excel? Then, you've come to the right place. Here, we'll show 6 easy ways of it with proper illustration. A frequency curve is a smooth curve for which the total area is taken to be unity.
It is a limiting form of a histogram or frequency polygon. The frequency curve for a distribution can be obtained by drawing a smooth and free hand curve through the midpoints of the upper sides of the rectangles forming the histogram. Types of Frequency Curves There exist four types of frequency curves namely.
Intro. to Signal Processing:Smoothing
Frequency Polygons Frequency polygons are analogous to line graphs, and just as line graphs make continuous data visually easy to interpret, so too do frequency polygons. To construct a frequency polygon, first examine the data and decide on the number of intervals, or class intervals, to use on the x. A smooth curve which corresponds to the limiting case of a histogram computed for a frequency distribution of a continuous distribution as the number of data points becomes very large.

Let us therefore consider some other ways by which you might smooth a sample distribution. Smoothing by running averages If you are familiar with running means you might assume they would be an attractively simple way to smooth frequency distributions. Moving averages are seldom used to smooth frequency distributions.