Colour Of Flowers Is Due To
Plant sports are another reason for flower change. Plant sports are morphological changes due to faulty chromosomes. often self-seeding plants produce a variety that isn't true to the parent plant.

This is another scenario where the flowers will be a different color than expected. The pH chemistry of flower change is the most likely culprit, and it can be put right. Plants like hydrangea like.

8 Flower Color Meanings and the Perfect Occasions to Gift Them | LoveToKnow
Environmental conditions play a significant role in modulating pigment production and stability. For instance, soil pH affects the color of anthocyanin-rich flowers, such as hydrangeas. Acidic soil typically leads to blue flowers, while alkaline soil results in pink blooms, due to changes in the anthocyanin molecule's structure.

Flowers come in all shapes and sizes, but what makes them truly stand apart from each other is their vibrant colors. These colors are made up of pigments and, generally speaking, the fewer the pigments, the lighter the color. The most common pigments in flowers come in the form of anthocyanins.

International Conference on Light and Color in Nature - ppt download
Flowers are the most commonly seen colourful elements of the natural world, and in this primer we explain the evolution of their spectacular range of colours. To understand flower colour, we first explain what colour is and how a flower can have different colours in the eyes of different observers. We briefly introduce the molecular and biochemical basis of flower colour, which is primarily.

Discover where flowers get their colour from and understand the science behind it. Explore the factors that create nature's stunning floral displays. Flowers come in a stunning array of colors that brighten our world and inspire joy.

Frontiers | Editorial: The Role of Flower Color in Angiosperm Evolution
But what makes flowers blue, red, yellow, or other vibrant hues? The secrets behind flower coloration have fascinated people for centuries. Modern science has revealed the biological and chemical factors that produce the rainbow of floral colors. Uncover the fascinating science behind flower colors! From pigments to UV vision and cultural symbolism, explore how nature designs its floral palette.
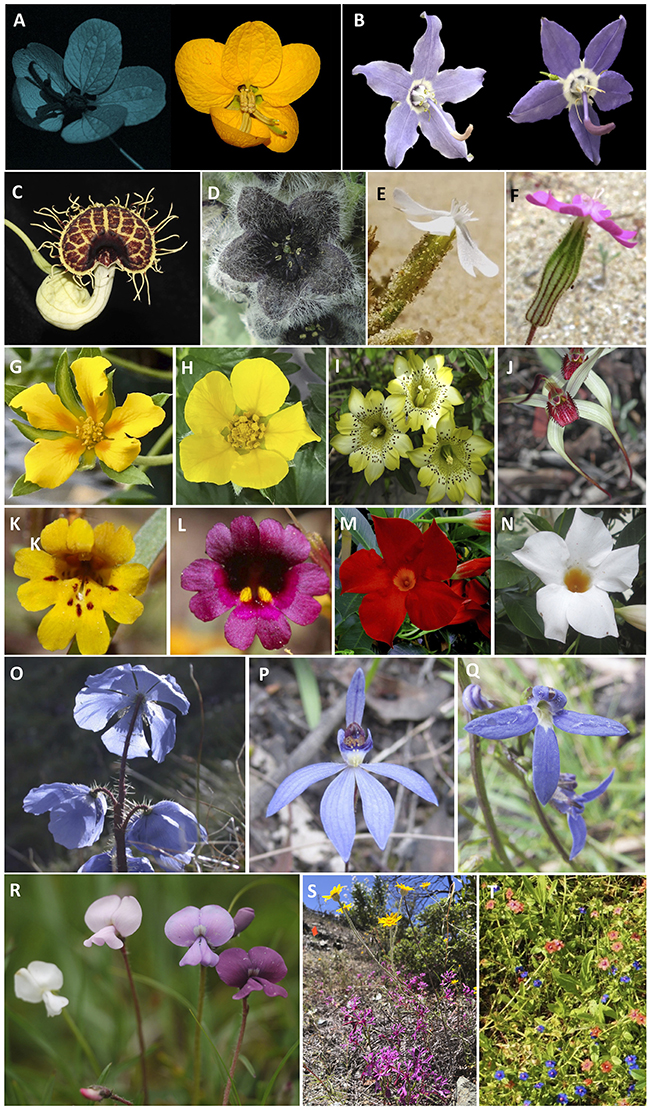

Have you ever wondered what makes flowers so colourful? And why in the first place do flowers need to be coloured? How and why did flower colour appear? Kellenberger and Glover point out that the colour of the petals must have originated in leaf-like structures meant to protect plant reproductive organs. For instance, in gymnosperms, such as the European larch (Larix decidua) and the seagrape (Ephedra distachya), the seed cones display a striking hue due to the accumulation of red pigments in the scales. However, inducible flowers will eventually change color due to senescence even without pollinator activity.
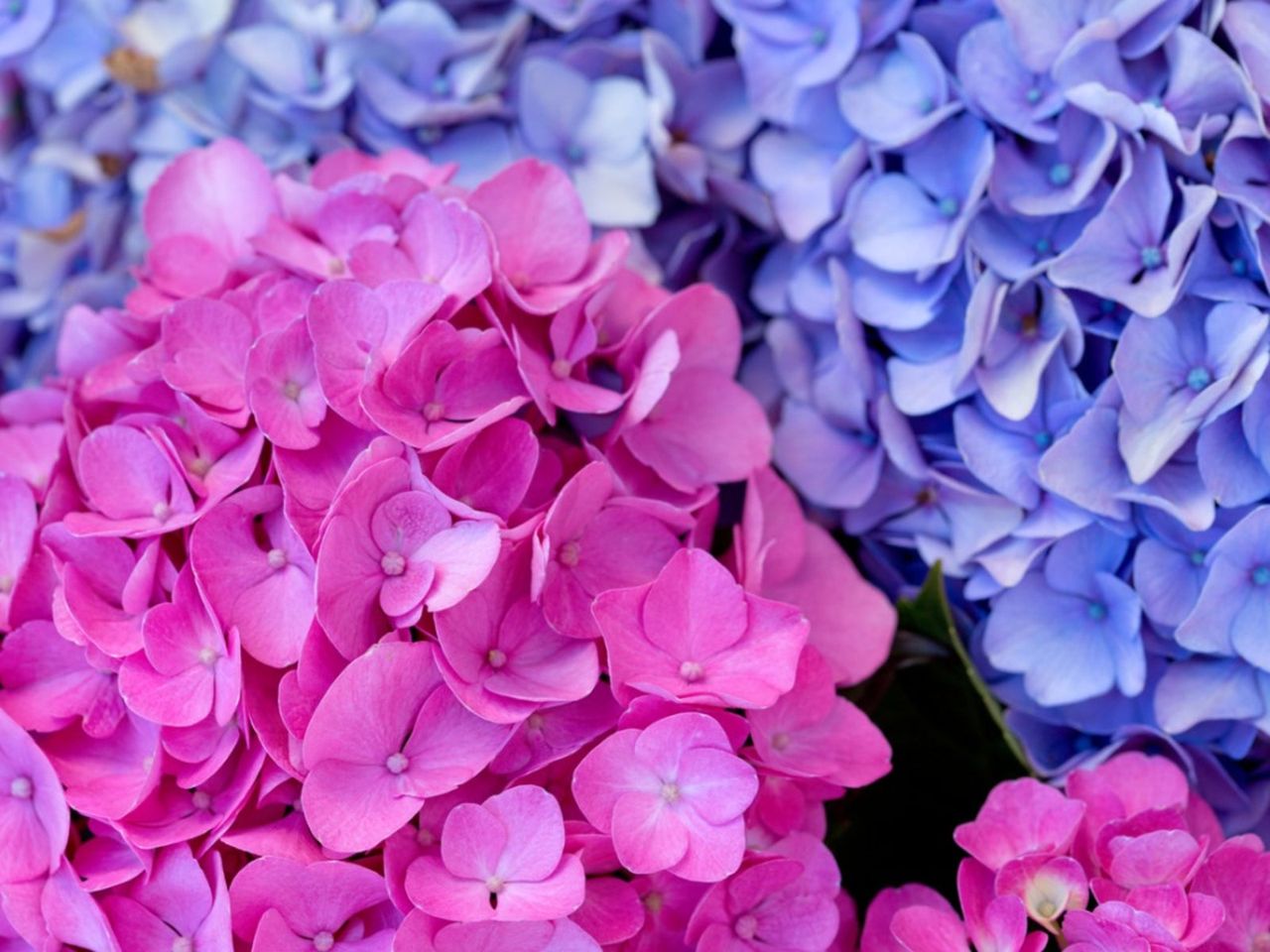

Depending on the species, floral color change can affect an entire flower or it can occur in localized parts.