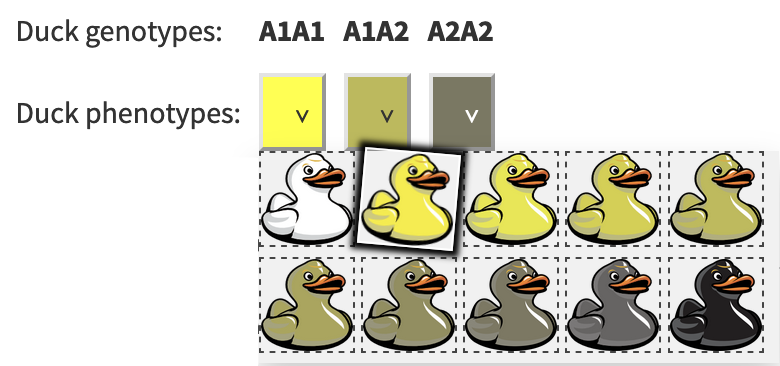
Duck Color Genetics
Mallard Derived Duck Color Genetics Basics Ducks have come a long way since they were first domesticated from mallards and now come in many beautiful colors. This article will explore how the genetics behind these colors work, and how a duck. Why do ducklings sometimes hatch in unexpected colors? Learn how duck color genetics work and what makes duckling appearances so surprising! A list of the basic duck color genetics and commonly used genotype letters as well as a brief description of how each allele effects feather color.

Duck Colour Genetics An introduction to duck colour genetics was published in 'The Domestic Duck' (2001, reprinted in paperback 2008). This analysis was based on the work of F M Lancaster and R G Jaap, and also took into account colours developed subsequent to 1963. Chocolate is known as a sex-linked color gene and is recessive in males.
Genes | Free Full-Text | Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals the ...
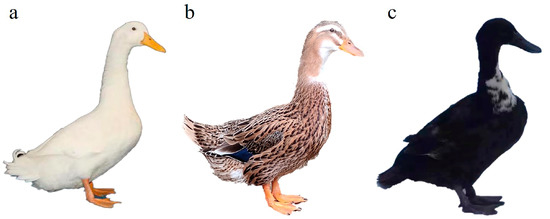
This means that when a drake is chocolate or carrying the chocolate gene and is bred to a non-chocolate female, all chocolate ducklings will be females. In wild duck populations, white coloration can occur due to genetic conditions such as leucism or, more rarely, albinism. Leucism results from a partial or total reduction in various pigments, leading to white feathers, but the duck retains normal eye color.
Genetics and Heritability Environmental Influences Conclusion: Understanding the Color of Ducks Recap of Key Points Future Directions for Research Frequently Asked Questions What are some real-world examples of how duck coloration helps with camouflage and adaptation? How do environmental influences affect a duck's coloration over time? If you're looking for a unique color project that will turn heads - I would recommend trying your hand at developing lavender and lilac ducks. CRAIG BORDELEAU raises rare, threatened, and unique waterfowl in southern New England. He preserves heritage breeds, and researches domestic duck plumage genetics, as his main breeding focus points.

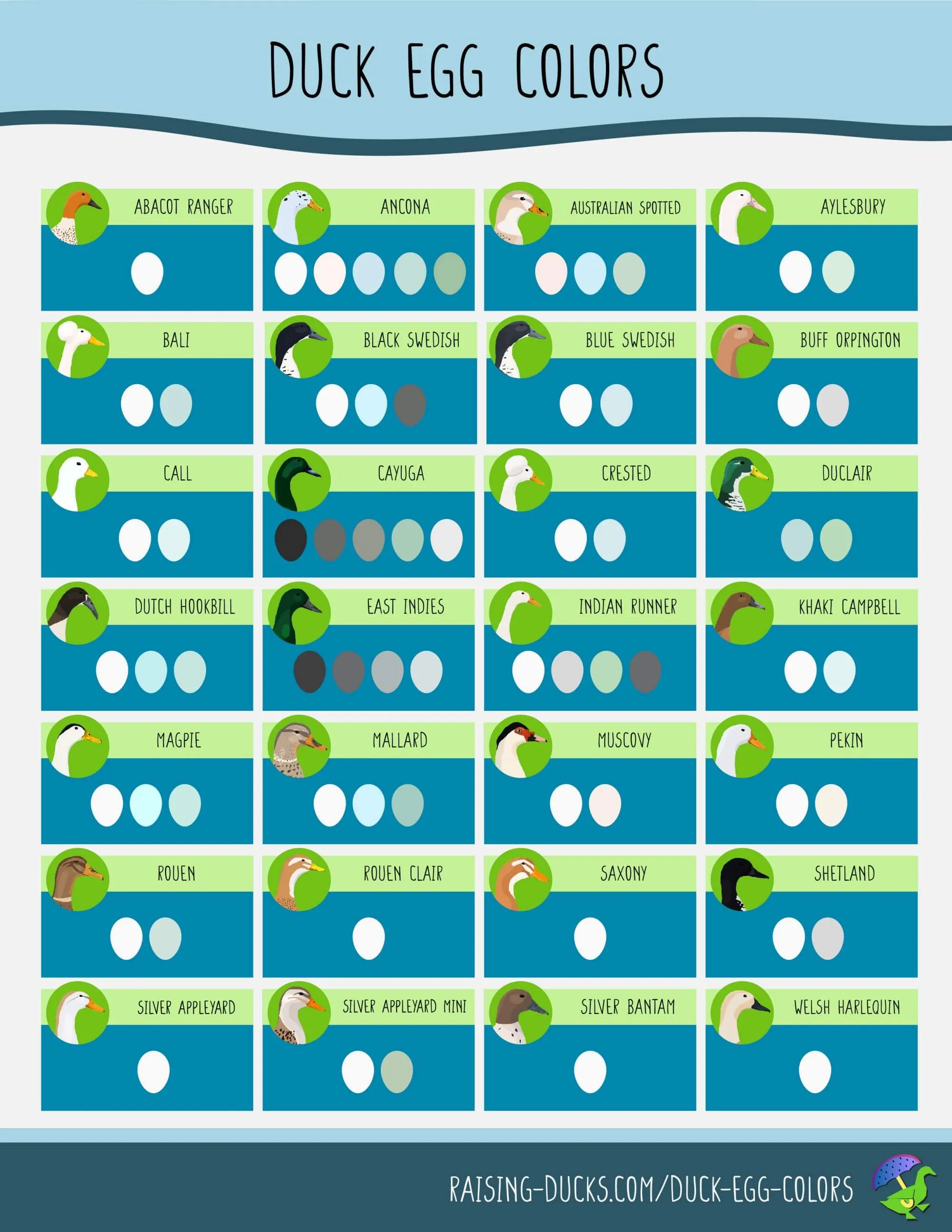
Green, Blue, Black, and White: Duck Egg Colors By Breed — Raising Ducks
White body, black head: A duck with albinism exhibits a lack of melanin pigmentation, resulting in a pure white body with no black feathers or markings. Melanism, on the other hand, causes an excess of melanin, leading to a very dark or black body. The presence of a black head and a white body can indicate a mix of albino and melanistic traits, while the absence of these traits may suggest a.
Chromosomes are composed (in part) of many genes, ie, units of heredity that code for all of the genetic traits in the living organism, for example, shape, size, & colour. In Ducks, Somatic cells have 80 chromosomes or 40 pair, while the Gametes only have 40 chromosomes in total ie only one chromosome from each pair. See diagram below:-.