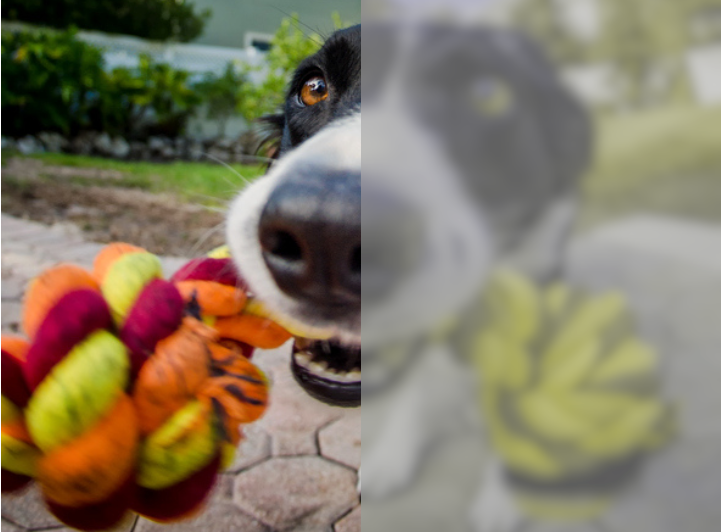
What Color Do Humans Look Like To Dogs
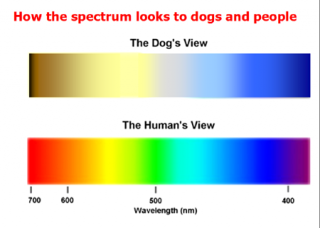
Colors like red and green often appear as variations of brown or gray to them, similar to red-green color blindness in humans. Canine visual acuity, or sharpness of vision, is less detailed than human vision. How do they perceive humans, and what do we look like to them? As pet owners, it's natural to be curious about how our pets view us, so let's dive into the fascinating world of what humans look like to dogs.
Dogs have evolved to see clearly at night, but they can still see in color in daylight, though not as effectively as humans. Humans can see better in color than dogs because we have more cone photoreceptors. Cones allow us to see in color and are used for day vision.

Can Dogs See Color? Exploration of How They View the World | LoveToKnow ...
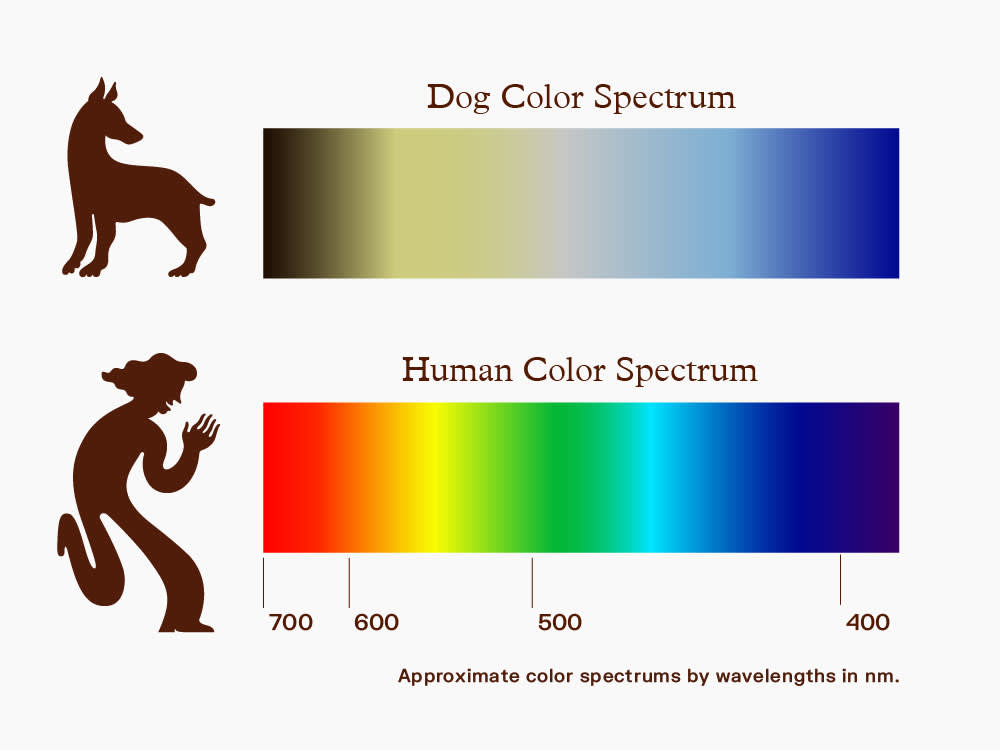
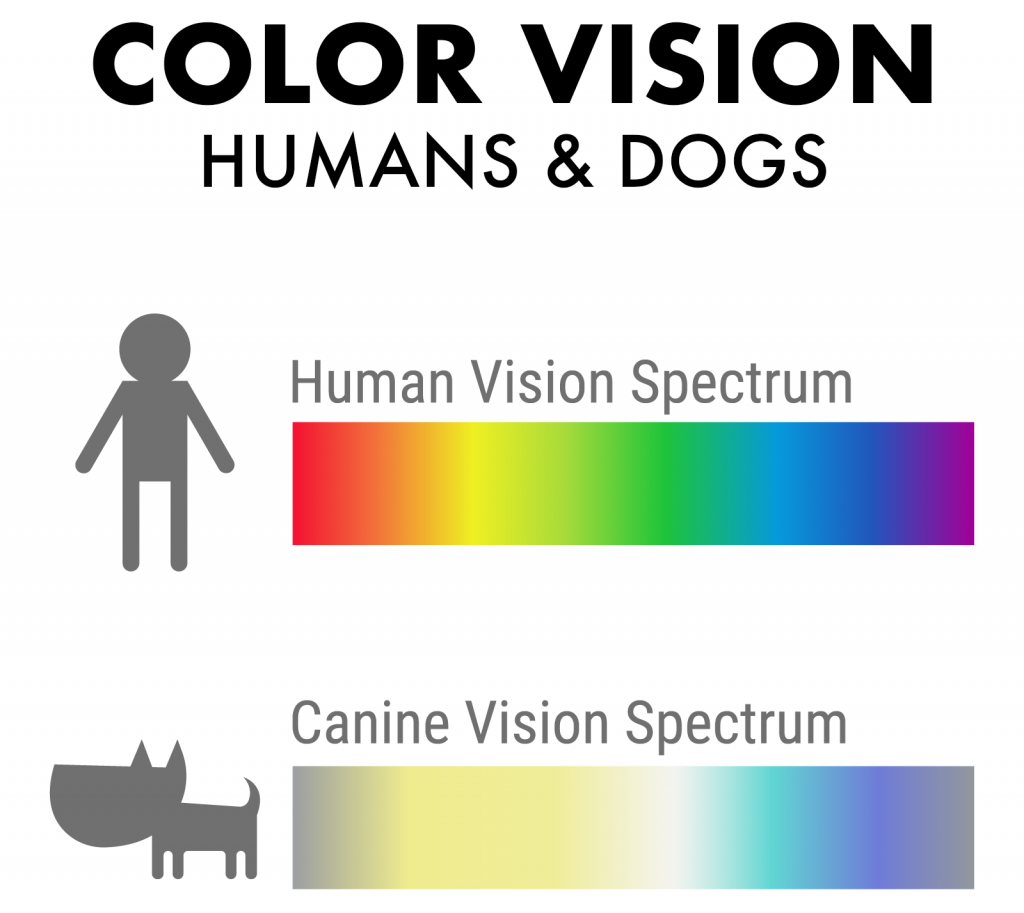
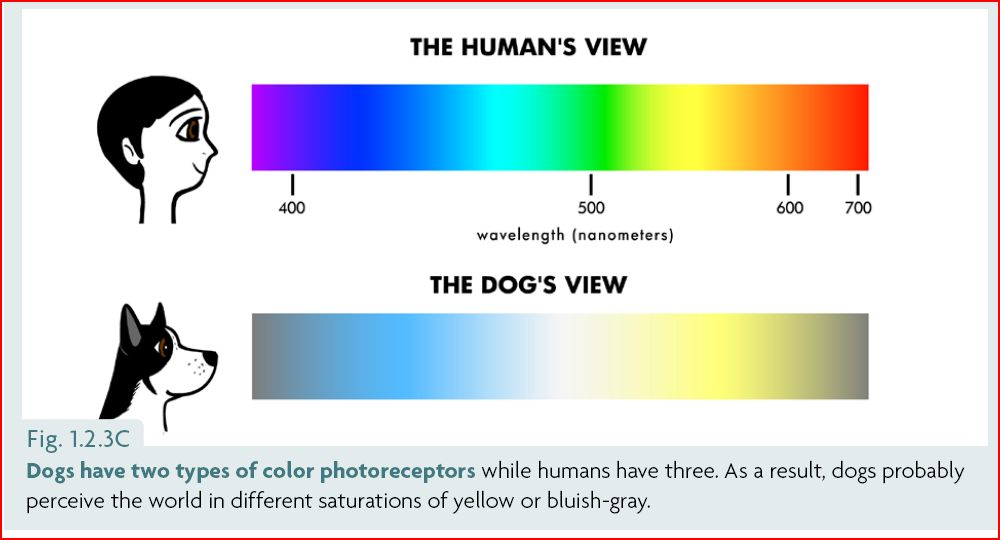
In dogs only 3% of the cells in the retina are cones. What colors do dogs see? Dogs have two types of color-detecting cone cells in their retinas, while we humans have three. This means dogs have what's called dichromatic vision, compared to our trichromatic vision.

So what does the world look like to your dog? Imagine a spectrum divided into two main color groups. Take a look at what we know about which colors dogs see best, which colors dogs like, and what owners can do to maximize that knowledge. The First Order of Business: Debunking the Biggest Myth About How Dogs See Color For years, people have been repeating the myth that dogs are completely color blind.
What Colors Do Dogs Like Best? Canine Vision Explained – Dogster
If that were true, it would mean that dogs could only see the world represented in black. But have you ever wondered what we look like to them? Do they see us as the majestic beings we believe ourselves to be, or are we simply oversized, smelly, and sometimes confusing creatures? This article delves into the fascinating world of canine perception, exploring how dogs see, smell, and interpret their human counterparts. Humans see red, green, and blue because we have receptors in our eyes that are sensitive to these three colors individually.
But in dogs, the cells that read green and red are the same, making. What do humans look like to a dog? Along with superior night vision, dogs have better motion visibility than humans have. However, because their retinas' contain only about one-tenth the concentration of cones (that humans have), dogs do not see colors as humans do.

The Dog’s Color Vision and What It Means for Our Training – Ethology ...
Dogs see like a color-blind human. These colors are blue-violet and yellow. Is it true people look like their dogs? That's.
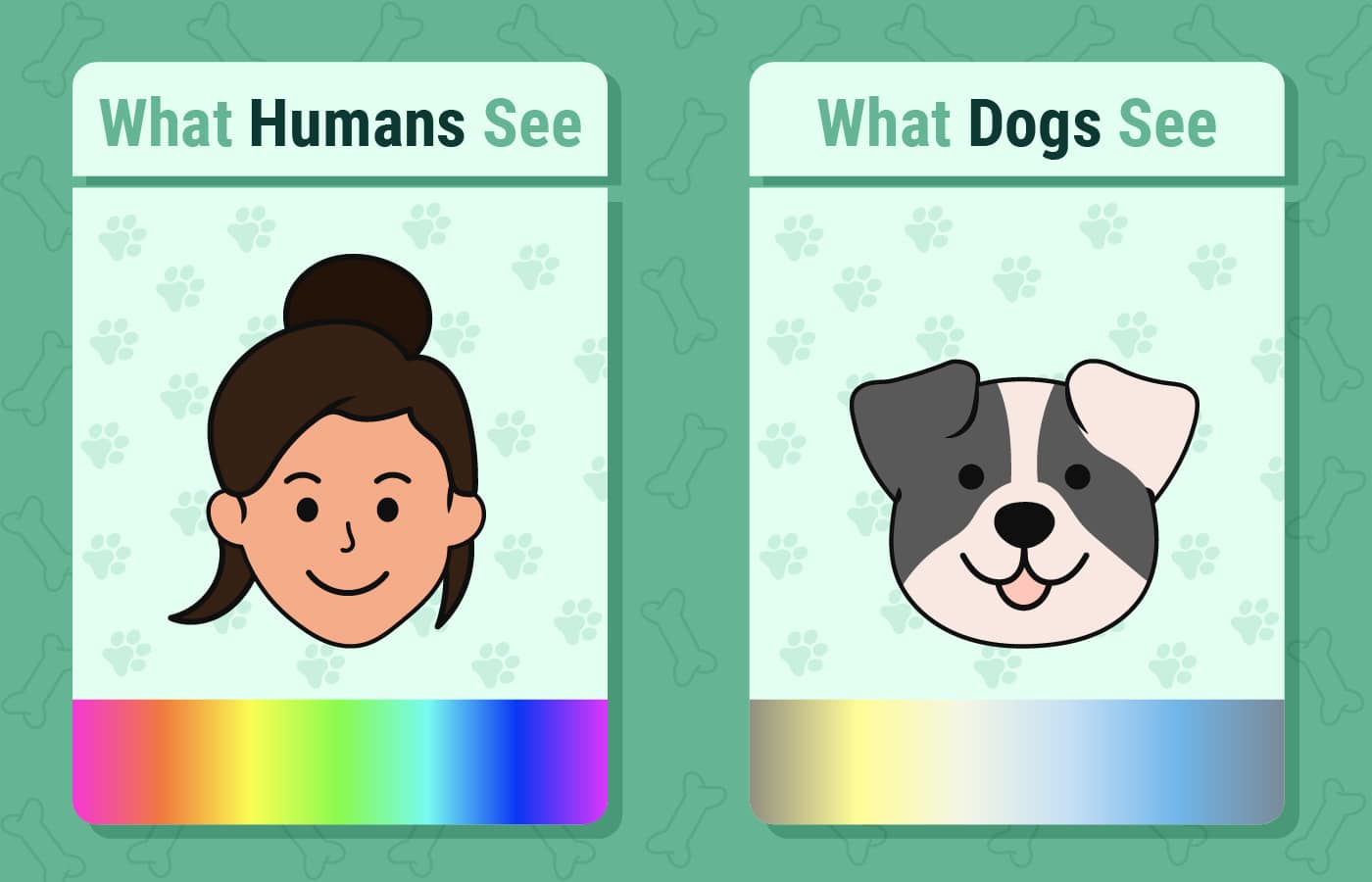
Explore how dogs perceive humans, combining visual, olfactory, and social cognition, to recognize us uniquely. Have you ever wondered what you look like through your dog's eyes? Comparing the visual systems of humans and dogs reveals distinct visual experiences. While both species rely on sight, their eyes have specific adaptations.

Understanding these differences helps explain how dogs interpret their surroundings, from the colors they perceive to their ability to see in low light and detect movement. This comparison offers insights into how each species interacts.