Horse Color Ee Aa
Genetics Genetic Symbols Explained Note: We recommend the UC Davis for genetic testing. Feel free to use the table below to interpret your horse's results. For example, our buckskin stallion was "Ee A" - this is short hand for "Ee AA" which means heterozygous for black and homozygous for the agouti.

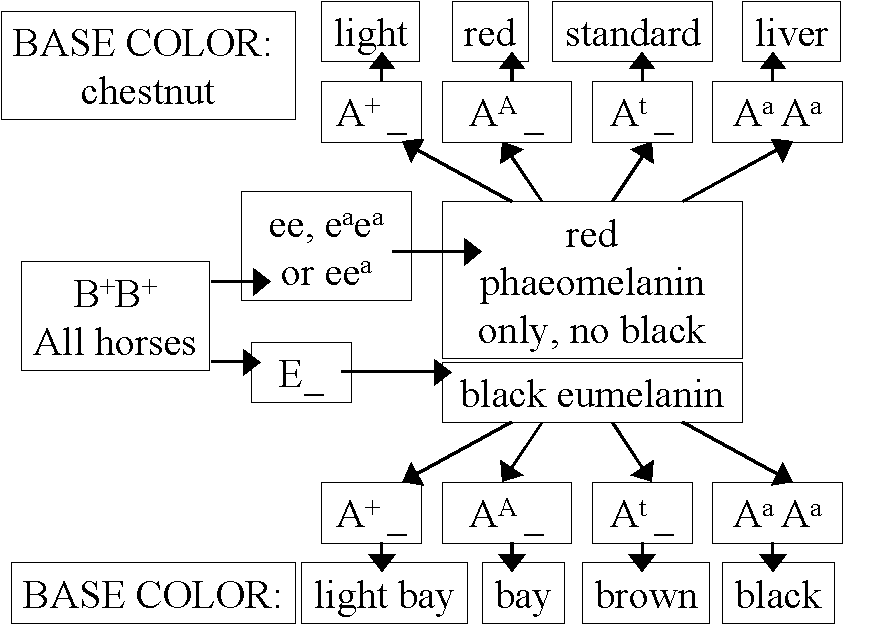
Equine Coat Color Genetics Base Coat Color The basic coat colors of horses include chestnut, bay, and black. These are controlled by the interaction between two genes: Melanocortin 1 Receptor (MC1R) and Agouti Signaling Protein (ASIP). What color horse is EE AA? EE, Ee, or Ee a: Horse forms black pigment in skin and hair, and may be black, seal brown, or bay.

Horse Colors ID STATIONS Base Colors The extension
ee, ee a, or e a e a: Horse is chestnut; it has black pigment in skin, but red pigment in hair. Equine coat color genetics Before domestication, horses are thought to have had these coat colors. [1] Equine coat color genetics determine a horse 's coat color.

Many colors are possible, but all variations are produced by changes in only a few genes. Bay is the most common color of horse, [2] followed by black and chestnut. EE or Ee (black based) with aa (unrestricted black) = Black horse.

What is EE in horse genetics? - DIY Seattle
The reason for few truly black horses is that there are many black-based horses, but most of those turn out bay. What Color Horse is EE AA? The EE AA gene is responsible for the production of the bay or chocolate coloring in horses. Horses that have two copies of the EE AA gene will typically have a coat color that ranges from light brown to dark chocolate.

The mane, tail, legs, and muzzle of these horses are usually a few shades lighter than the rest of the body. Equine Coat Color Testing Base Color Every horse has a base color, which can be black, bay, or red. This is controlled by the Extension (Red/Black Factor) and Agouti genes.

Different Horse Colors with Pictures
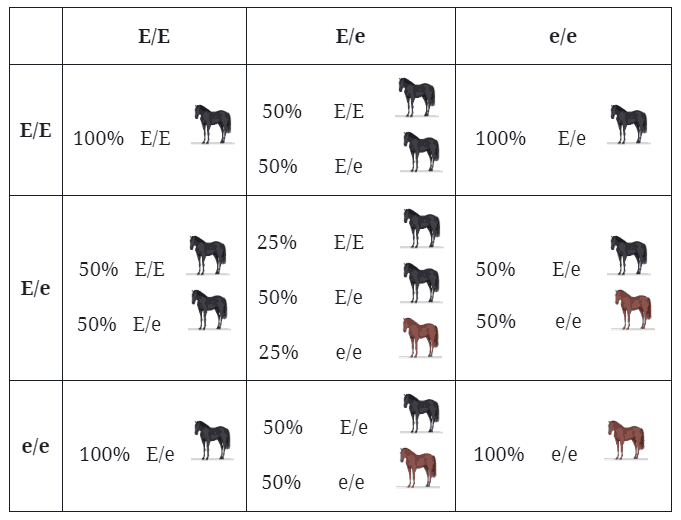
The Extension gene controls the production of black or red pigment throughout the coat. The allele for black color (E) is dominant over the red allele (e), so a horse only needs one copy of the black allele to appear black. A Punnett square illustrating the possible coat color outcomes (black or bay) for the offspring of a bay mare (Ee) and a black stallion (EE) Horse color genetics involves many interacting genes.

Understanding inheritance, dominant and recessive genes, and Punnett squares helps us appreciate the diversity of equine coat colors. Ee Aa Chch (heterozygous for all genes) This horse has one each of these dominant genes, so it is the same as the one above, because a dominant gene always shows! If a horse does not carry Agouti at all, it is aa (so a black horse would be EE aa or Ee aa). So that gives us our four common colours: chestnut, black, brown and bay and a brief explanation of the colour genetics 'alphabet soup' that can seem so confusing.