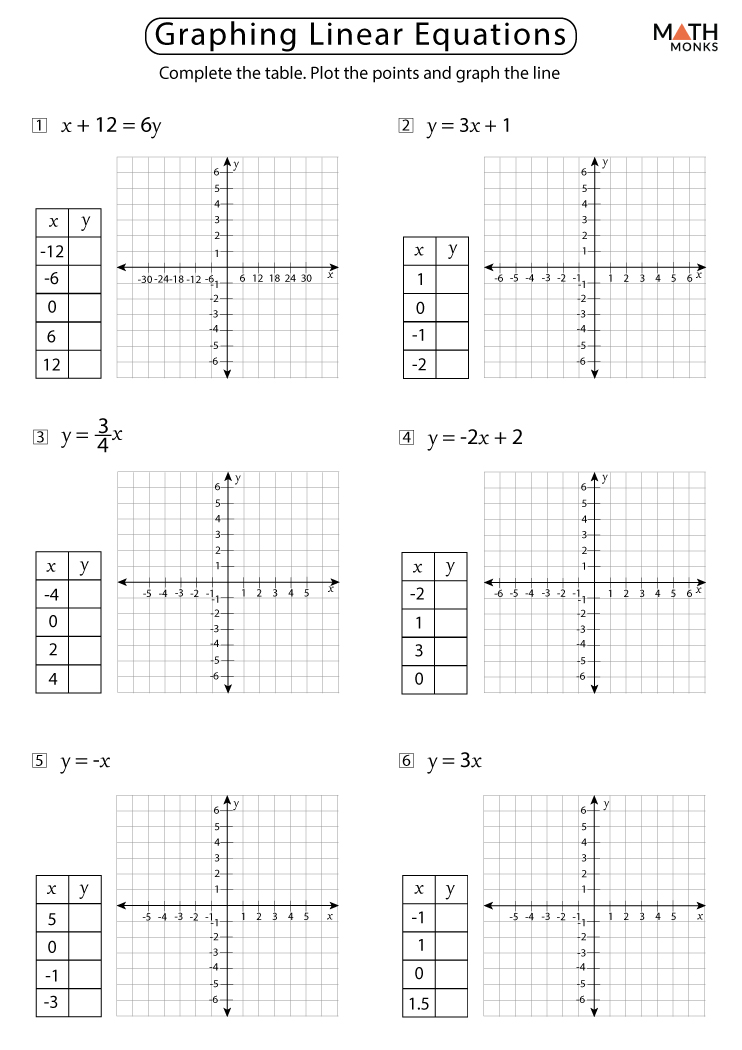
Linear Graphs Examples
A linear graph is the graphical representation of a straight line. A graph when plotted gives a single straight line then it is known as a linear graph. Linear graph is a straight line graph to represent the relationship between two quantities.

about it along with other graphical representations. Free linear graph school math topic guide, including step-by-step examples, free practice questions, and more! Linear Graph - Explanation and Examples A linear graph is a representation of a linear relationship in the Cartesian coordinate system. Essentially, a linear graph is a straight line plotted on the x y coordinate plane.

Linear Function Graphs Explained (Sample Questions)
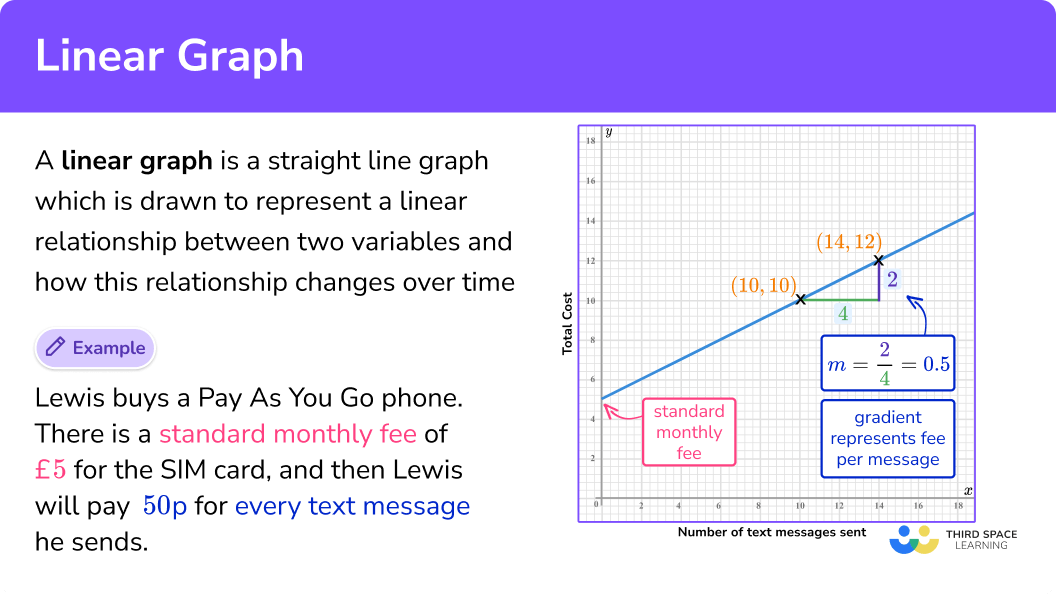
Linear graphs are a key concept in math related to calculus and statistics. Learn about linear graphs with Brighterly. A linear graph represents relationships between quantities using straight lines, defined by the equation y = mx + c, where m is the slope and c is the y-intercept.
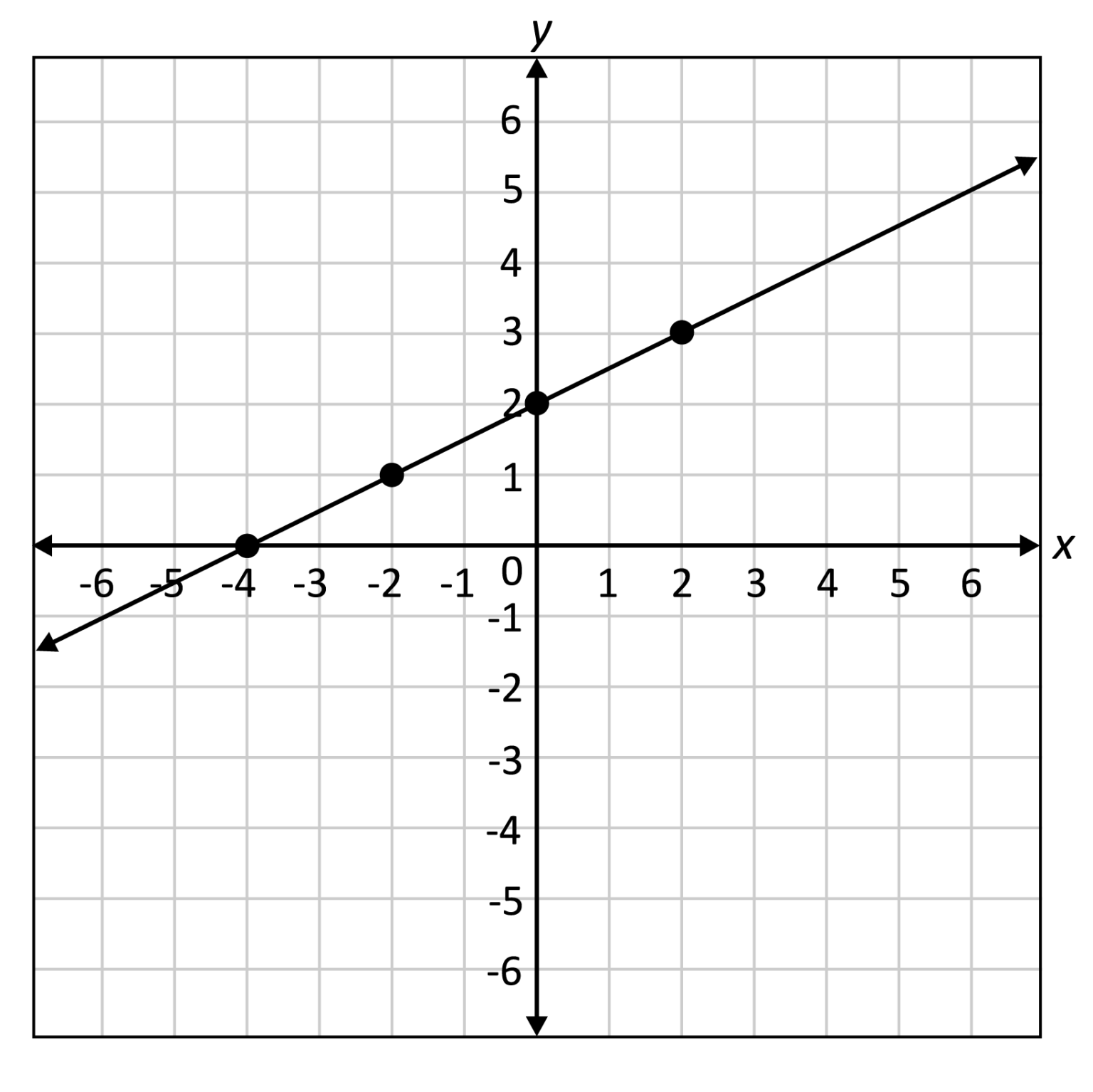
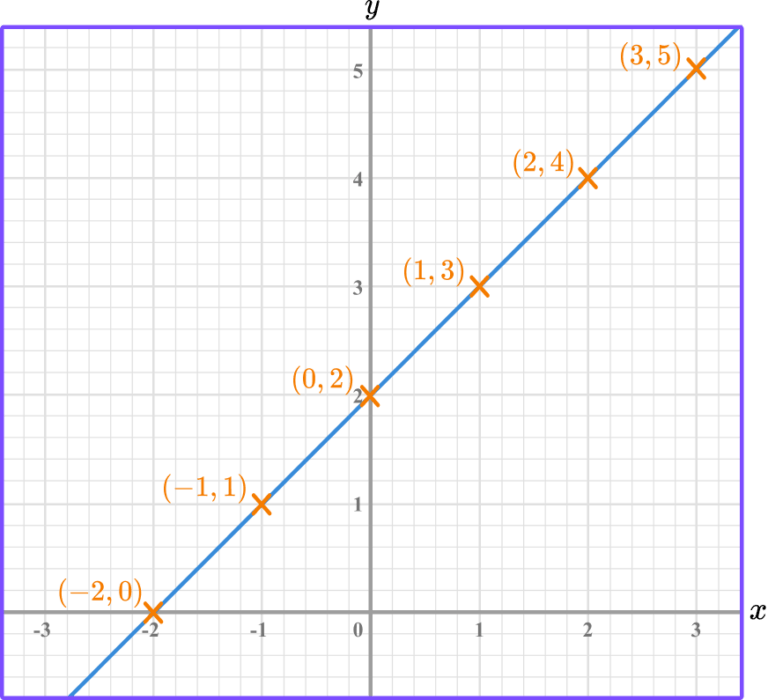
All points on linear graphs are collinear, forming continuous straight lines with infinite solutions. Definition of Linear Graphs A linear graph depicts a linear relationship between two variables. You can express this relationship with the equation (y = mx + b), where (m) is the slope and (b) is the y-intercept.

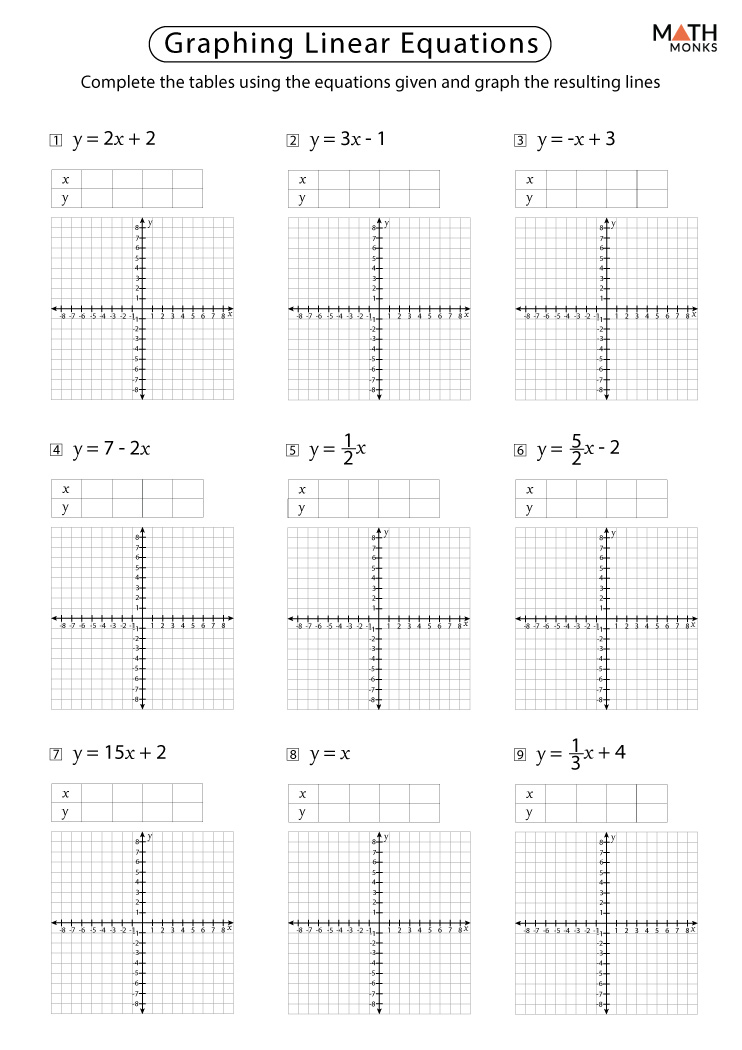
Graphing Linear Equations - Examples, Graphing Linear Equations in Two ...
This format shows how changes in one variable affect another directly. For instance, if you plot time against distance traveled at a constant speed, you'll see a straight line. Learn Linear Graph at Bytelearn.

Know the definitions, see the examples, and practice problems of Linear Graph. Your one. This section focuses on the key features and methods for working with linear graphs.
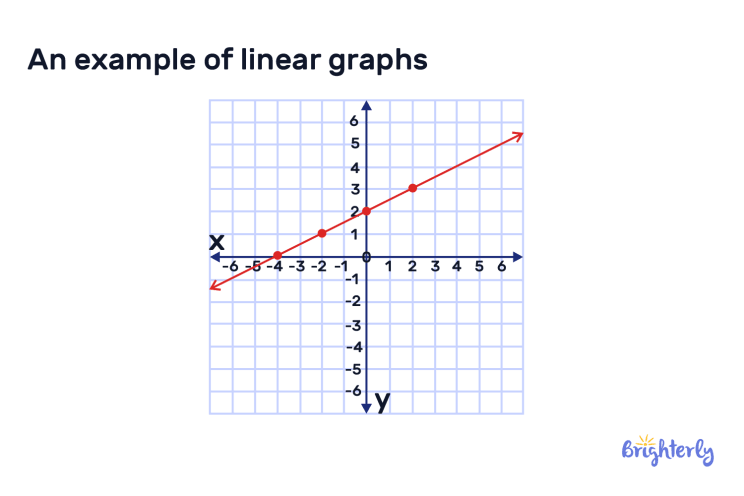
Linear Graph - Definition, Examples | What is Linear Graph?
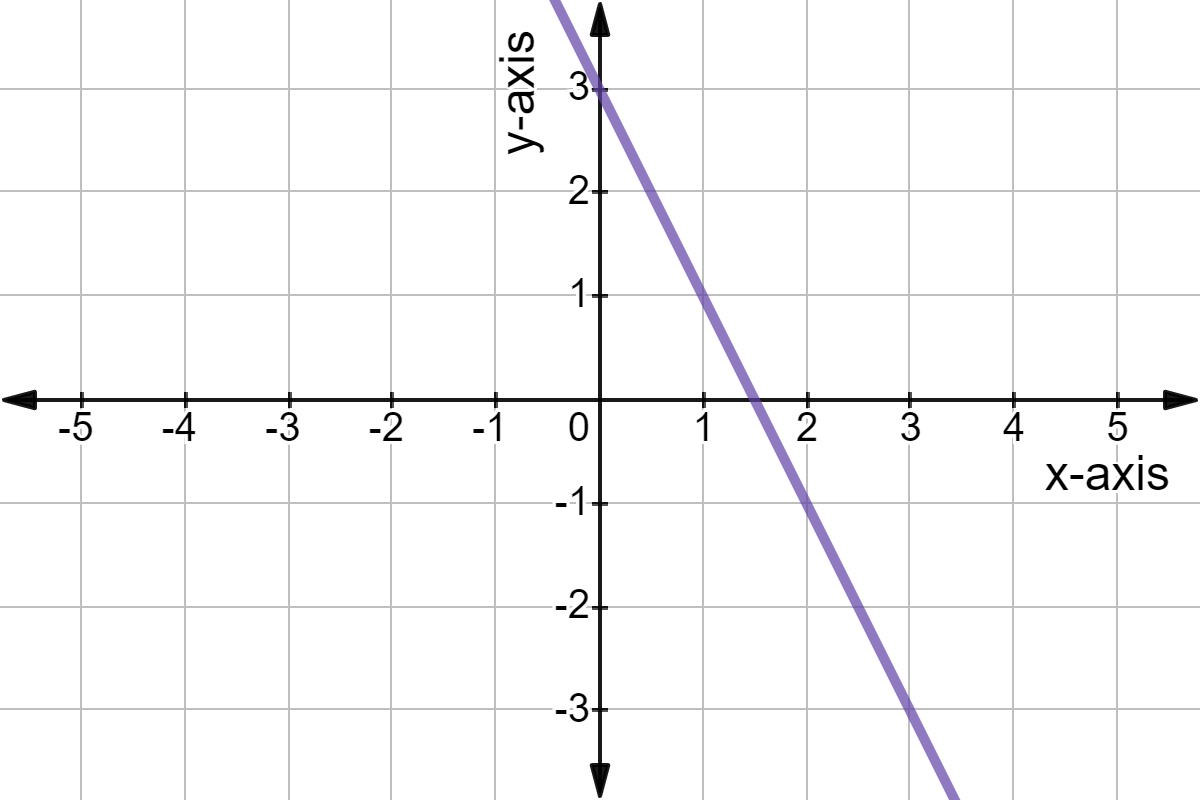
It demonstrates how to sketch graphs from rules, derive rules from graphs, and calculate key features such as the gradient and \(x\)- and \(y\). A linear equation is an equation for a straight line. Let us look more closely at one example: The graph of y = 2x+1 is a straight line.

And so.