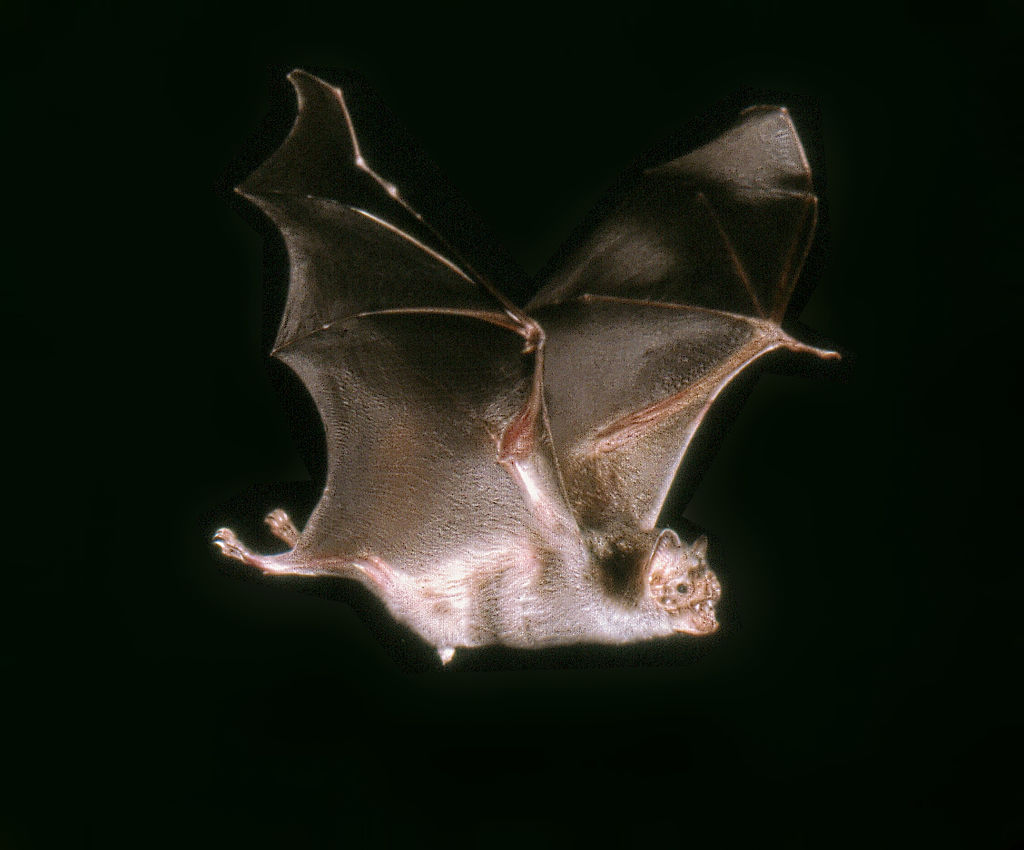
What Color Are Vampire Bats
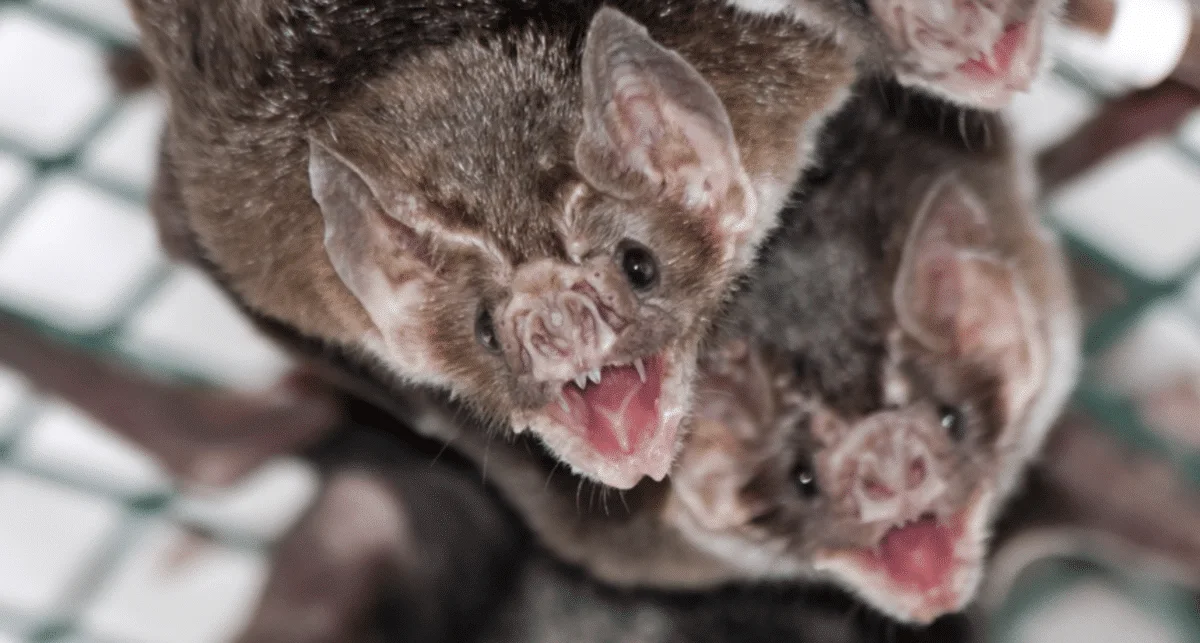
Vampire bats, members of the subfamily Desmodontinae, are leaf-nosed bats currently found in Central and South America. Their food source is the blood of other animals, a dietary trait called hematophagy. Three extant bat species feed solely on blood: the common vampire bat (Desmodus rotundus), the hairy-legged vampire bat (Diphylla ecaudata), and the white-winged vampire bat (Diaemus youngi.

Vampire bats (Desmodus rotundus) are bats that feed on blood. This particular habit in certain animals is known as 'hematophagy'. There are only three bat species that actually feed on blood: The Common Vampire Bat (Desmodus rotundus), the Hairy-legged Vampire Bat (Diphylla ecaudata) and the White-winged Vampire Bat (Diaemus youngi).

Common Vampire Bat - Facts, Diet, Habitat & Pictures on Animalia.bio
All three species are native to the Rainforests of. The Common vampire bat (Desmodus rotundus) is a small, leaf-nosed bat native to Latin America. It is one of three extant species of vampire bat.

The common vampire bat mainly feeds on the blood of livestock and usually approaches its prey at night while they are sleeping. Because it feeds on livestock and is a carrier of rabies, the Common vampire bat is considered a pest. Vampire bat, (family Desmodontidae), any of three species of blood-eating bats, native to the New World tropics and subtropics.
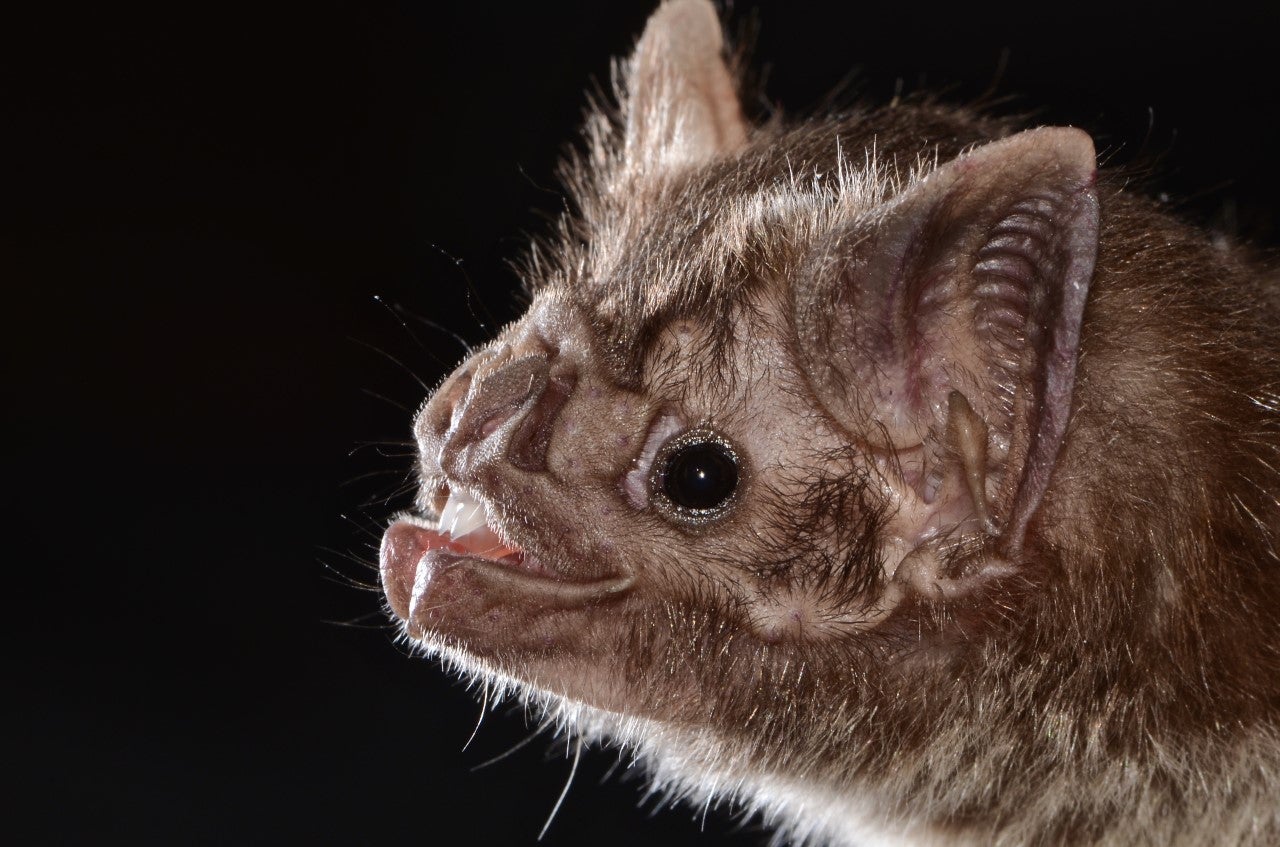

Fascinating Facts About the Vampire Bat (Desmodus rotundus)
The common vampire bat (Desmodus rotundus), together with the white-winged vampire bat (Diaemus, or Desmodus, youngi) and the hairy-legged vampire bat (Diphylla ecaudata). Common vampire bats are highly social and have sophisticated social organization and behaviors. Female bats form close associations with other females, observed through activities such as social grooming and sharing food.

How often these bats share their food depends on a variety of factors including kinship, association, and reciprocal help. Classification and Evolution Vampire bats are a small subgroup of bat native to Central and South America. There are three recognized species of Vampire Bat, all of which also belong to a genus all their own.
Vampire Bat - Animal Facts for Kids - Characteristics & Pictures
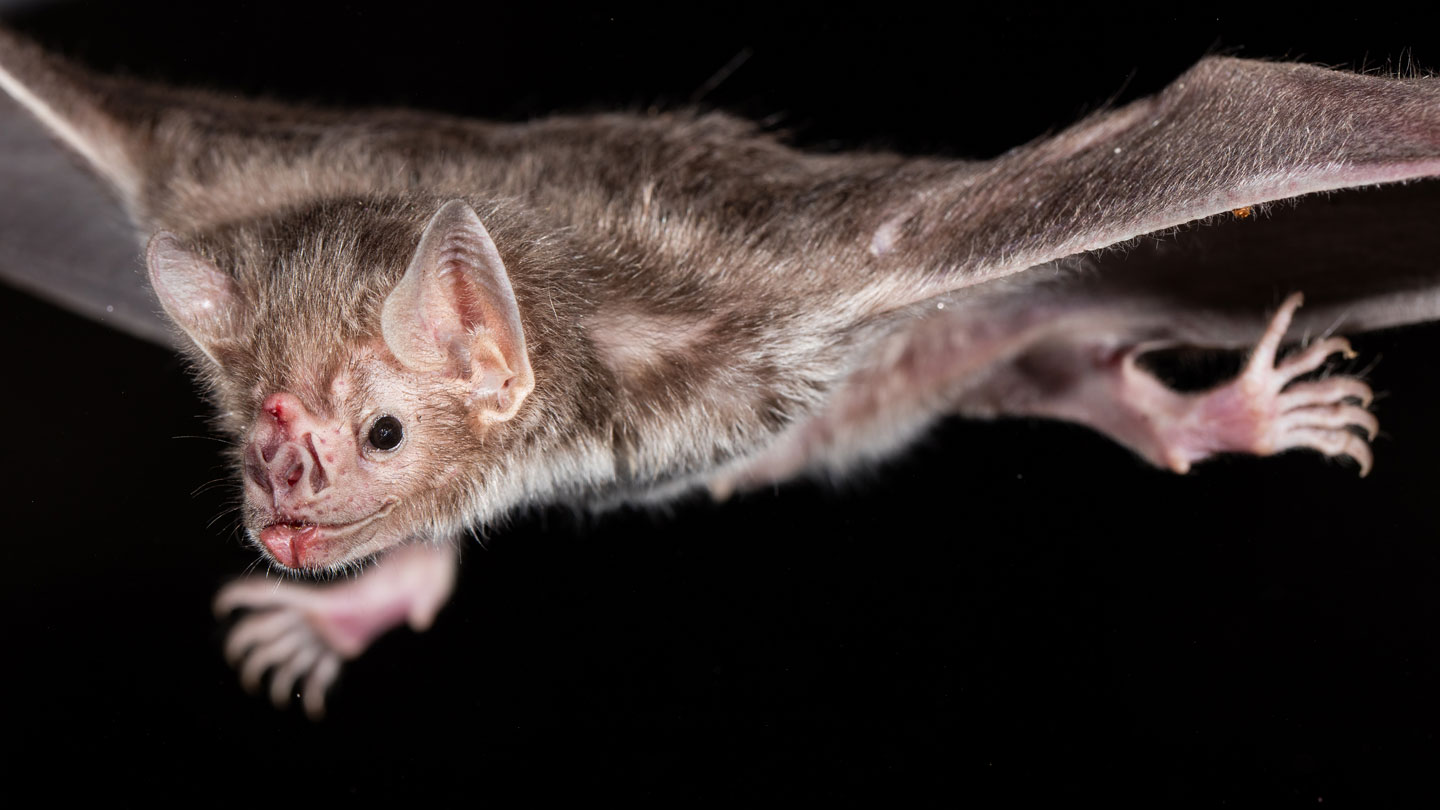
The Common Vampire Bat, the Hairy-Legged Vampire Bat, and the White-Winged Vampire Bat are all closely related and share []. These bats are dark gray or brownish in color on the head and back with paler undersides. Common vampire bats have pointed ears, no tail and larger thumbs than other species of vampire bat.
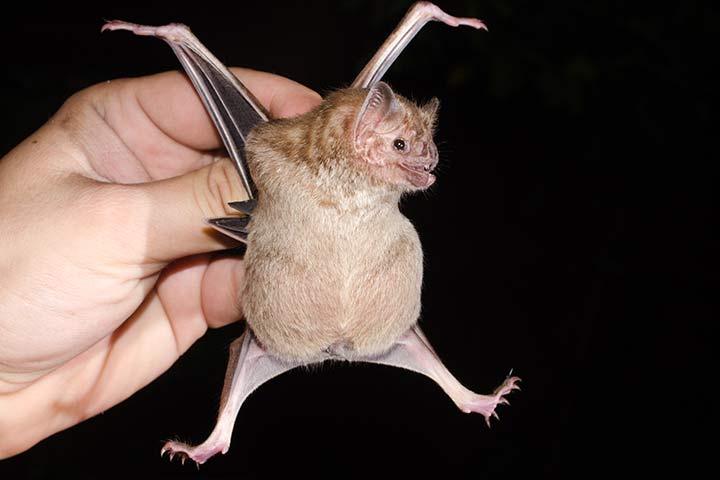

They have deep grooves in their lower lip that aids them in lapping up blood. Vampire bats have a heat sensing organ on the tip of their nose that helps them to locate the blood vessels close to the skin on. Vampire Bat While much of the world sleeps, vampire bats emerge from dark caves, mines, tree hollows, and abandoned buildings in Mexico and Central and South America.

Vampire BatDesmodus rotundus Taxonomy: Kingdom - Animalia Phylum - Chordata Class - Mammalia Order - Chiroptera Family - Phyllostomidae Genera - Desmodus Species - Rotundus Description: The Chiroptera is the second largest mammalian order with approximately 202 genera and over 1,120 of living species. The vampire bats are dark gray or brownish in color on the head and back with. Vampire bats are in the subfamily Desmondontinae, as there are three different species alive today; they are the Common Vampire bat (Desmodus rotundus), the Hairy-legged Vampire Bat (Diphylla ecaudata), and finally the White-winged Vampire Bat (Diaemus youngi).

Each species has their own unique differences but are closely related, as they all are able to metabolize and break down blood (the.