State Space Tree For Graph Coloring
Time Complexity: O (V * mV). There is a total of O (mV) combinations of colors. For each attempted coloring of a vertex you call issafe(), can have up to V-1 neighbors, so issafe() is O(V) Auxiliary Space: O (V + E).

The recursive Stack of the graph coloring function will require O (V) space, Adjacency list and color array will required O (V+E). This video contains State Space Tree for Graph Coloring Problem and Algorithm for Graph Coloring Problem using Backtracking.Graph Coloring ProblemGraph Colo. The number of anode increases exponentially at every level in state space tree.
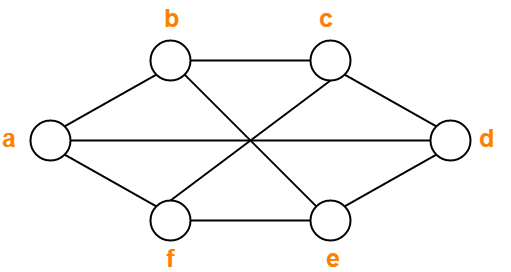
Graph Coloring Problem - Scaler Blog
With M colors and n vertices, total number of nodes in state space tree would be. The state-space tree can be constructed as a binary tree like that in Figure shown below for the instance A = {3, 5, 6, 7} and d = 15. The number inside a node is the sum of the elements already included in the subsets represented by the node.
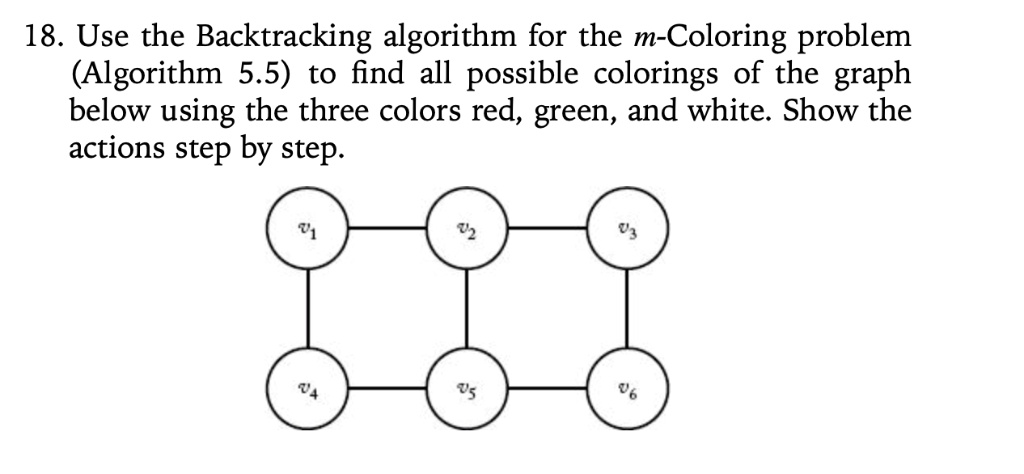
The inequality below a leaf indicates the reason for its termination. Lakshmi Priya P, CSE, ACSCE Page. Each level of the tree would represent the coloring of one node.

Graph Coloring Problem using Backtracking || Graph Coloring Problem ...
Branches would represent different color choices for a node, and leaf nodes would represent complete valid colorings of the graph. Step 8: Find all valid colorings By exploring the state space tree, we can find all possible valid colorings of the graph. Of the many ways that graph coloring can be adapted for parallel programming there are two main approaches in literature: the iterative and state-space search methods.

The iterative approach begins by dividing the vertices of the graph to be colored into di erent groups, each of which is assigned to a node in the cluster. We use the fact that cubic graphs have perfect match. A state in the state space tree is a partially colored input graph, and child states are produced from parent states by coloring one of the uncolored vertices.
Graph Colouring Problem using C | Find Chromatic number of a graph and ...
A solution is found if one of the leaves if a legitimately colored input graph. Each processor is responsible for exploration of a part of the state space tree. In the backtracking approach to the graph coloring problem, the time complexity is O (mV), and space complexity is O (V).

The greedy approach to solving the graph coloring problem can be used at most x+1 colors if the maximum degree of a vertex is x. Are you struggling to understand Graph Coloring in ADA? In this video, we explain the State Space Tree for M Coloring when N = 3, M = 3 in the simplest way possible.