How Can Kids Die
This report details the 10 leading causes for the 20,360 deaths of children and adolescents in the United States in 2016. The analysis also includes trends over time and comparisons among countries. The share of children and teens who die each year declined for nearly three decades and leveled off in the 2010s.
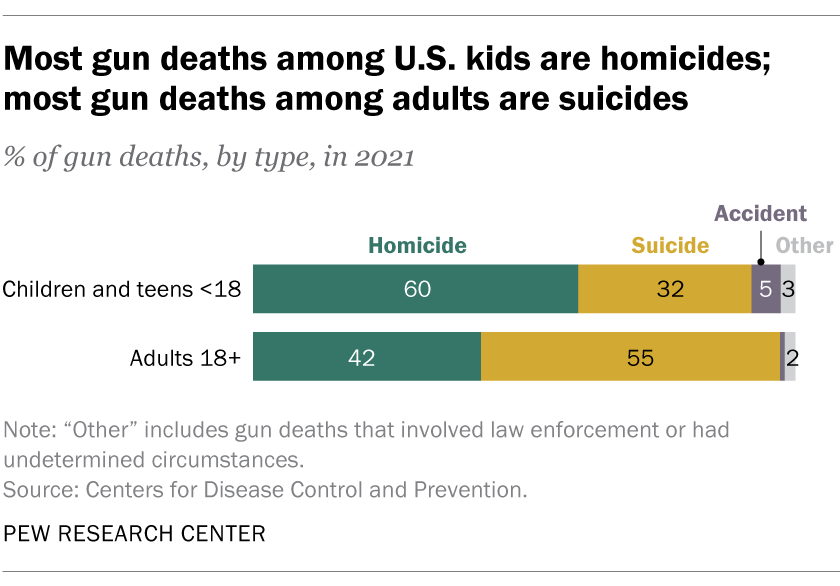
Then, in 2020, the rate began to increase. By 2021, it reached its highest rate since 2008. Although this coincided with the pandemic, the virus itself accounted for a small share of the increase.
PPT - Disease Outbreak Investigation and Response PowerPoint ...
According to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the. Enroll children in swimming classes as soon as they are old enough, and supervise bath time. Fire: 116 children died from fires.
Install smoke and carbon monoxide alarms in the sleeping areas of everyone in the family, including babies and children, and change the batteries at least once each year. Choking: 85 children died from choking. Children and adolescents are defined as persons 1 to 19 years of age.
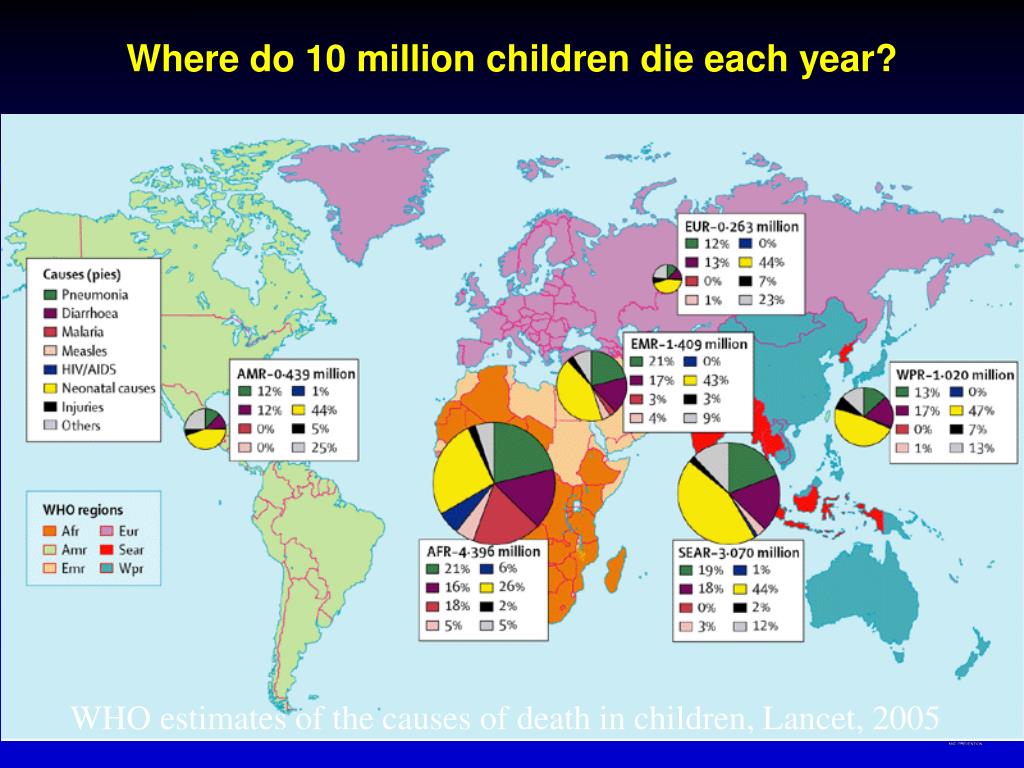
Levels and trends in child mortality 2024 - UNICEF DATA
In addition, drug overdose and poisoning increased by 83.6% from 2019 to 2020 among children and adolescents, becoming the third leading cause of death in that age group. Children aren't supposed to die. When children die unexpectedly, Public Health-Seattle & King County pays extra attention.

The department looks for lessons to help families and communities prevent future tragedies, using a process that brings together an extraordinary range of expertise. The program is called Child Death Review, and their most recent report. Here are the top 10 causes of death for kids around the world and the number of lives they claim, according to a 23.

90,000 children are expected to die in Nigeria over the next 12 months ...
Share of children born alive that die before the age of 5 (2017) [1] Breakdown of child mortality by cause, OWID Child mortality is the death of children under the age of five. [2] The child mortality rate (also under-five mortality rate) refers to the probability of dying between birth and exactly five years of age expressed per 1,000 live births. [3] It encompasses neonatal mortality and.

Globally, infectious diseases, including acute respiratory infections, diarrhoea, and malaria, along with pre-term birth complications, birth asphyxia and trauma and congenital anomalies remain the leading causes of death for children under 5. Child mortality remains one of the world's largest problems and is a painful reminder of work yet to be done. With global data on where, when, and how child deaths occur, we can accelerate efforts to prevent them.

Most often, the death of a child happens in the hospital or emergency department (1, 2). Death can occur after a prolonged illness, such as cancer, or suddenly and unexpectedly, such as after an injury, sudden infant death, or severe infection. Families often find it difficult to cope with the emotional and practical realities of caring for a severely ill or dying child.
Pediatric palliative.