Green Iguana Colors Meaning
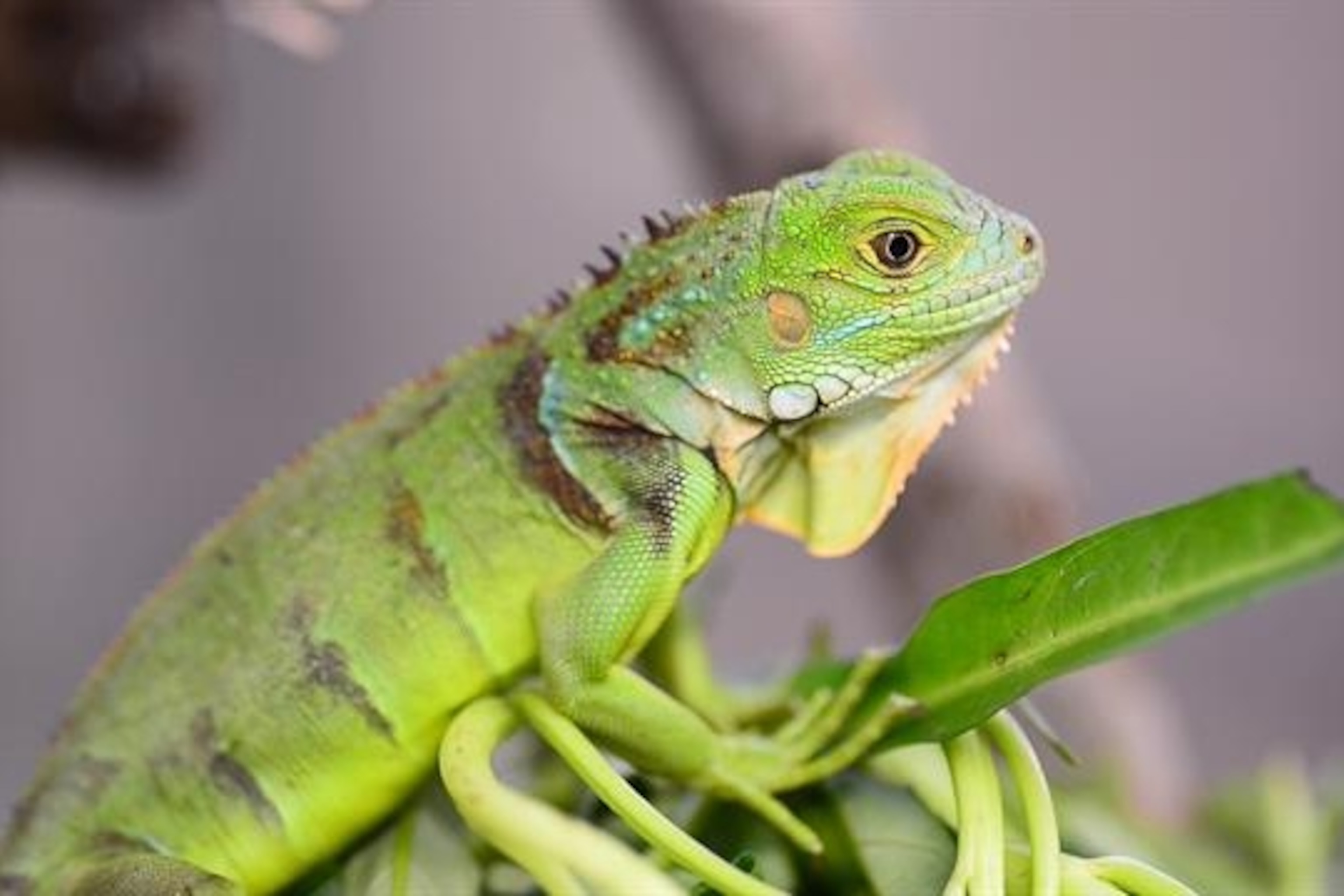
What Causes Iguanas to Change Color? Iguanas can change their skin color due to a process called physiological thermoregulation; this is a fancy term used to describe an animal's physical response to temperature changes in the environment. Iguanas may change color in order to take in more or less heat when they are cold or hot. The Green Iguana (Iguana iguana) is perhaps the most familiar species, typically showcasing a bright emerald green coloration as juveniles.

As they mature, their green can shift to various shades, including duller greens, grayish-green, brown, or even almost black. While we generally associate color-changing skin with chameleons, many reptiles change color over time. The iguanas usually kept as pets are green iguanas (Iguana iguana).

Pet Store | Vet | Grooming | Supplies | Adoption | Cats, Dogs, Hamsters
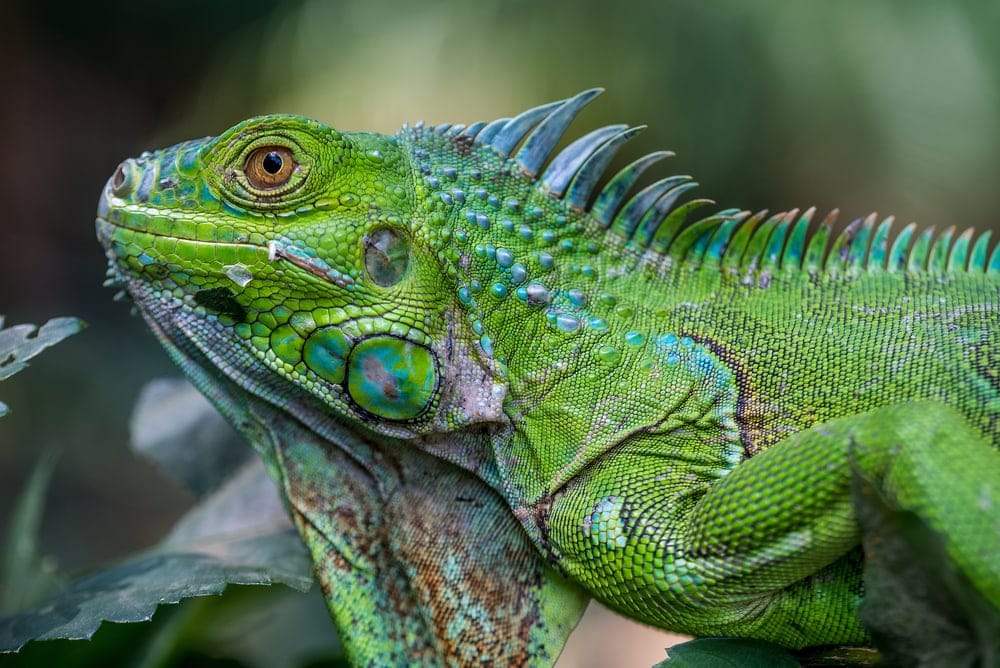
Despite their name, though, their coloring can vary from bright reddish-orange to gray-blue. This reptile's skin may also become a different color. The predominant color of green iguanas is green, but can actually range from brilliant green to a pale blue-gray.

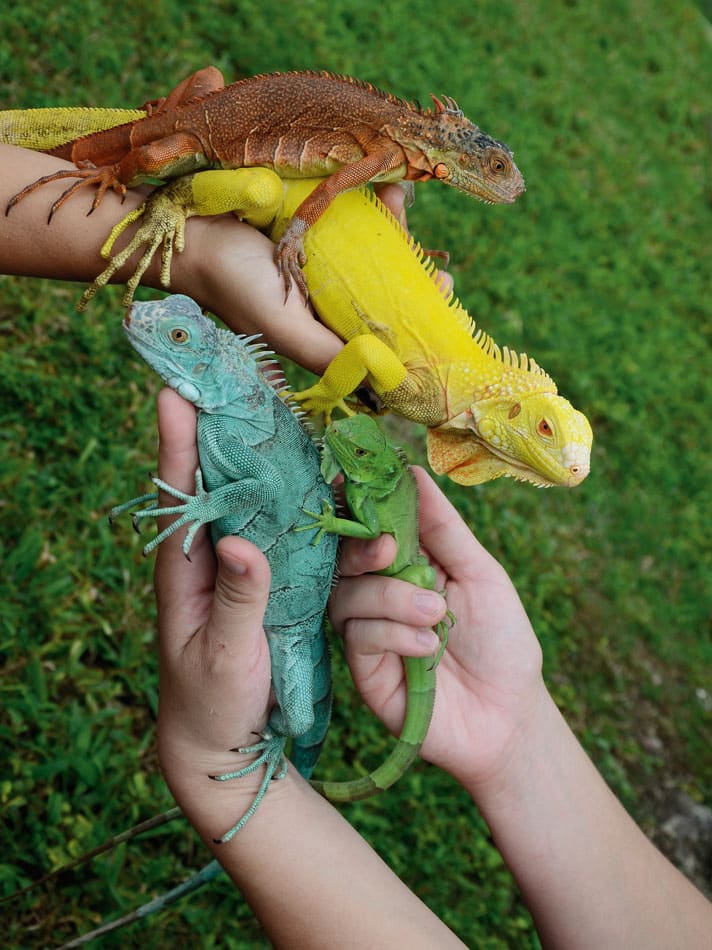
There are genetic variations in the color of iguanas. Some can appear more brown in color, while others are almost a turquoise blue. Blue, red and albino iguanas have also been bred and are available, however we will be focusing this article on color changes in green iguanas.

The Green Iguana Can Grow up to 7 Feet Long | HowStuffWorks
One. These changes in skin color camouflage them from predators. Iguanas are mostly green, with some exceptions, color changes can be a sign of stress or ill health.
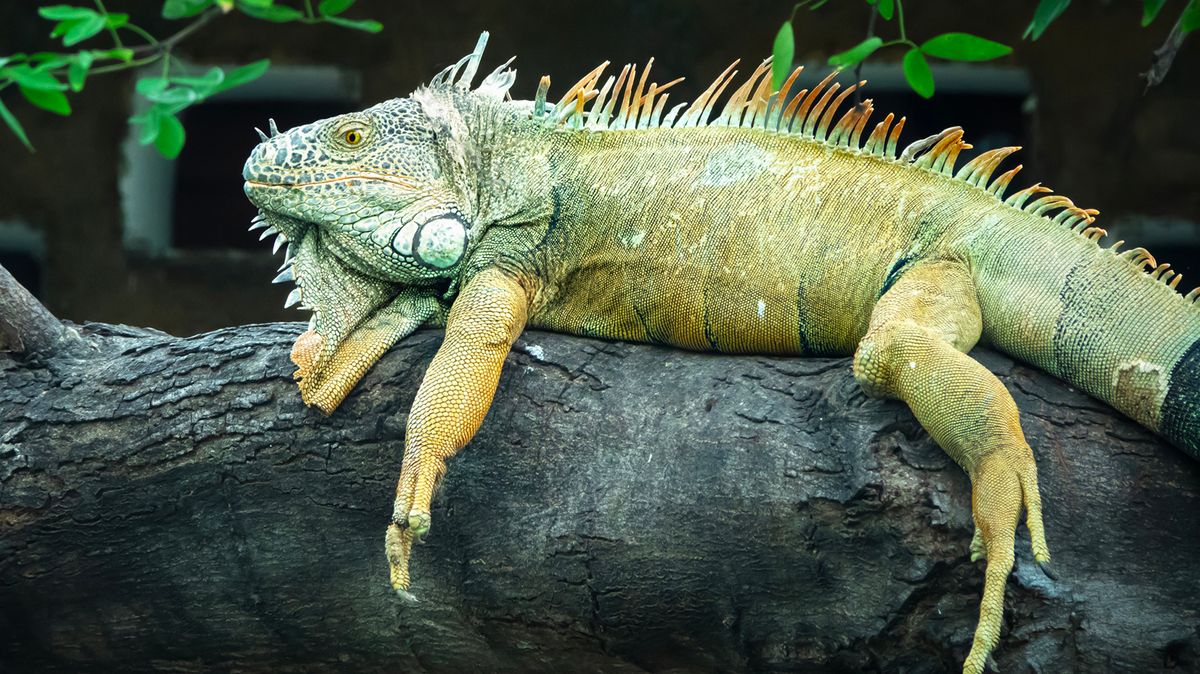

Iguanas can develop a muddy brown color when they are stressed in the beginning before turning a very dark brown to black; this is a sign that an iguana is suffering. The most common type, the green iguana, typically exhibits a bright green color. However, iguanas can display a range of colors, including orange, blue, and even pink.
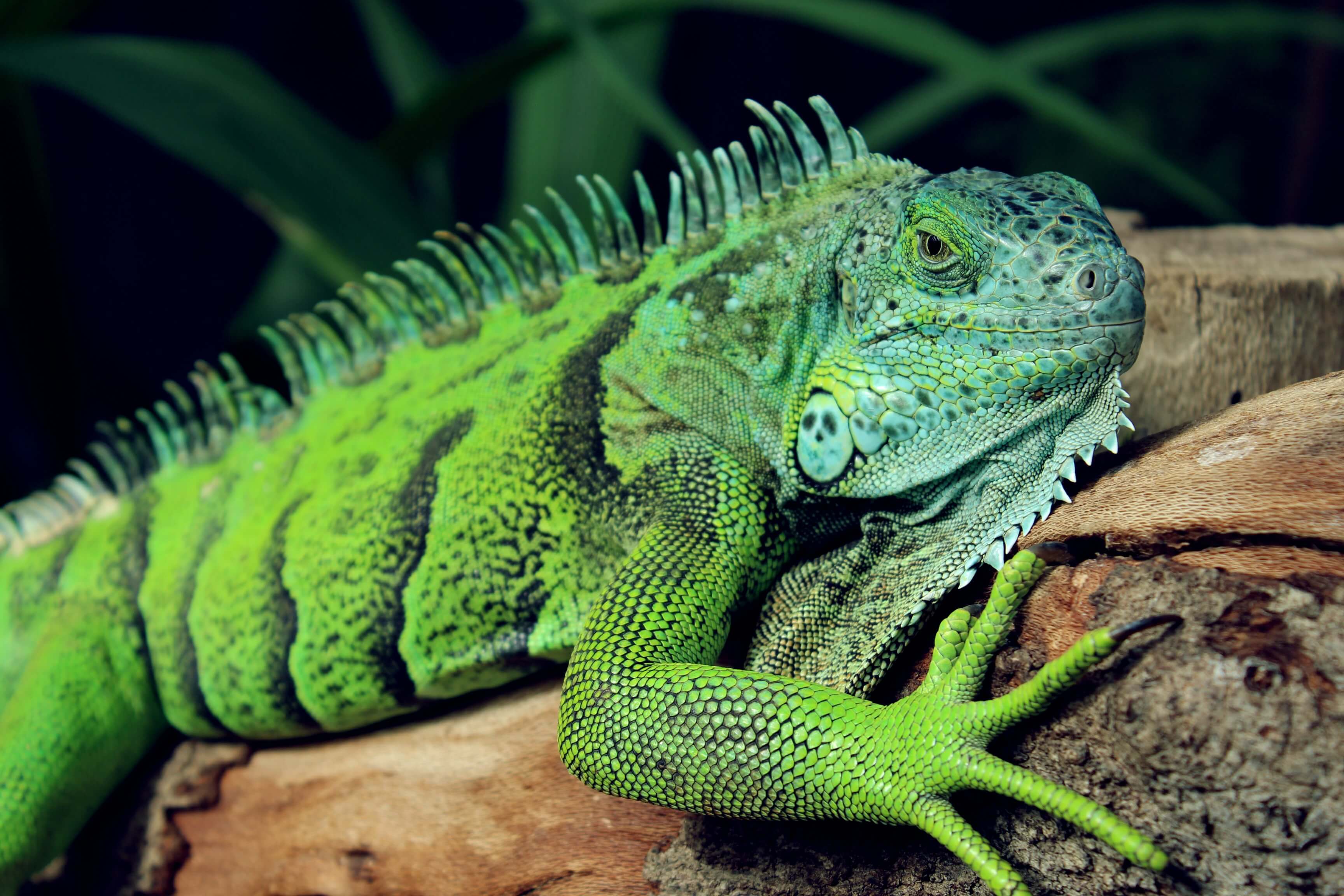

Premium Photo | Portrait of a green iguana in bright colors
Why Do iguanas change colors? This depends on various factors, including their environment, health, and emotional state, which we will talk about more below. Camouflage Color patterns in iguanas serve a critical role in camouflage, helping them blend seamlessly into their natural habitats. For species like the green iguana (Iguana iguana), their predominantly green coloration with darker mottling or stripes mimics the dappled sunlight and foliage of tropical forests.

This camouflage is essential for evading predators such as birds of prey and large. However, baby green iguanas start out a grayish or brownish color with bold dark stripes and can take up to 2 years before turning their green hue. One of the most fascinating abilities of green iguanas is their capacity to change colors.

Underneath their green skin are cells called chromatophores that contain pigments of yellow, orange, black, blue and red. By contracting and expanding these. Green Iguana Facts: aka the ORANGE IGUANA Animal Fact Files What is the color of a healthy iguana? Healthy young iguanas are bright green in color.

Their color gradually fades to a brown, dull orange or grayish green as they reach adulthood. Iguanas are usually fairly docile and harmless, but can cause severe scratches with their long claws. Iguanas may also change colors when stressed or afraid, which can be an essential signal to their owners or handlers.
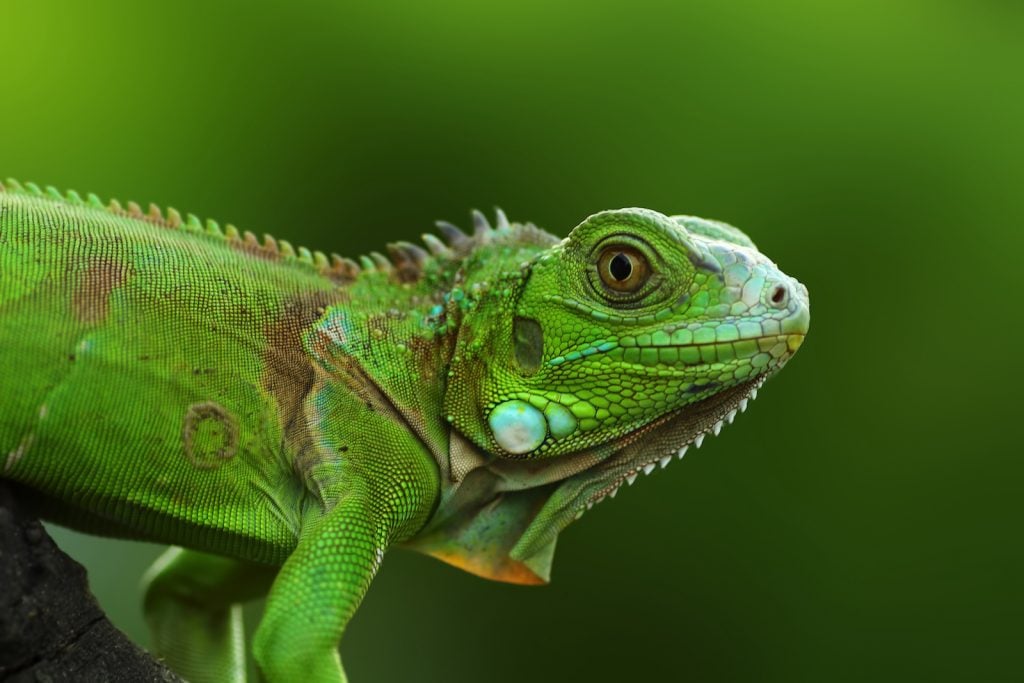

In conclusion, the many colors of iguanas reflect their unique adaptations and behaviors. By understanding these colors and their meaning, we can better appreciate these beautiful reptiles and care for them properly.